ALULA: Although Saudi Arabia is home to a wealth of ecosystems, from its coastal mangroves and coral reefs to its high-altitude forests and lush oases, the Kingdom is perhaps best known for its deserts.
However, these landscapes, which are fast becoming popular with outdoor adventurers, are home to a remarkable array of animals, which inhabited the region long before the arrival of humans.
Despite the hardiness of these animals, given the harshness of their environment, the encroachment of humans into these pristine habitats is raising concerns among conservationists.

“The rapid growth in tourist flows in recent decades has been accompanied by diversification, both geographically, and in terms of tourism segments or products,” Basmah Al-Mayman, Middle East regional director of the UN Tourism (formerly UN World Tourism Organization), told Arab News.
“Desert destinations have shared in the benefits of this double-diversification process, making it an even more pressing priority to define a sustainable approach to tourism development in desert areas.”
As a Saudi national herself, Al-Mayman recognizes the value of the Kingdom’s precious ecosystems as a source of revenue and national pride. However, she believes the tourism industry, developers, and travelers themselves have a responsibility to act sustainably.
Opinion
This section contains relevant reference points, placed in (Opinion field)
“In the desert, more than anywhere, with destinations still relatively untouched by the adverse effects tourism can bring, sustainability represents a particularly critical challenge,” she said.
“The messages conveyed by UN Tourism are not only preventive in character, but also offer stakeholders at international as well as local levels the advice and tools they need to combat poverty and desertification while enabling tourism to properly play its role as a vehicle for development.”
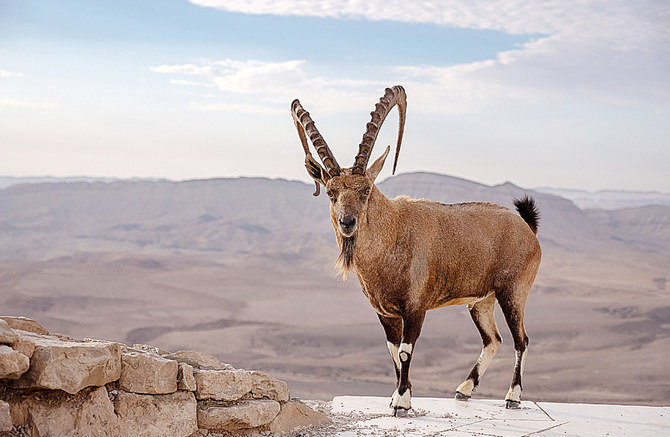

The Nubian ibex isnow among the wildlife of Saudi Arabia. (Shutterstock)
According to UN Tourism, sustainability principles refer to the environmental, economic, and socio-cultural aspects of tourism development. A balance must be established between these dimensions to guarantee its long-term sustainability.
Sustainable tourism should therefore make optimal use of environmental resources that constitute a key element in tourism development, while maintaining essential ecological processes and helping to conserve natural heritage and biodiversity.
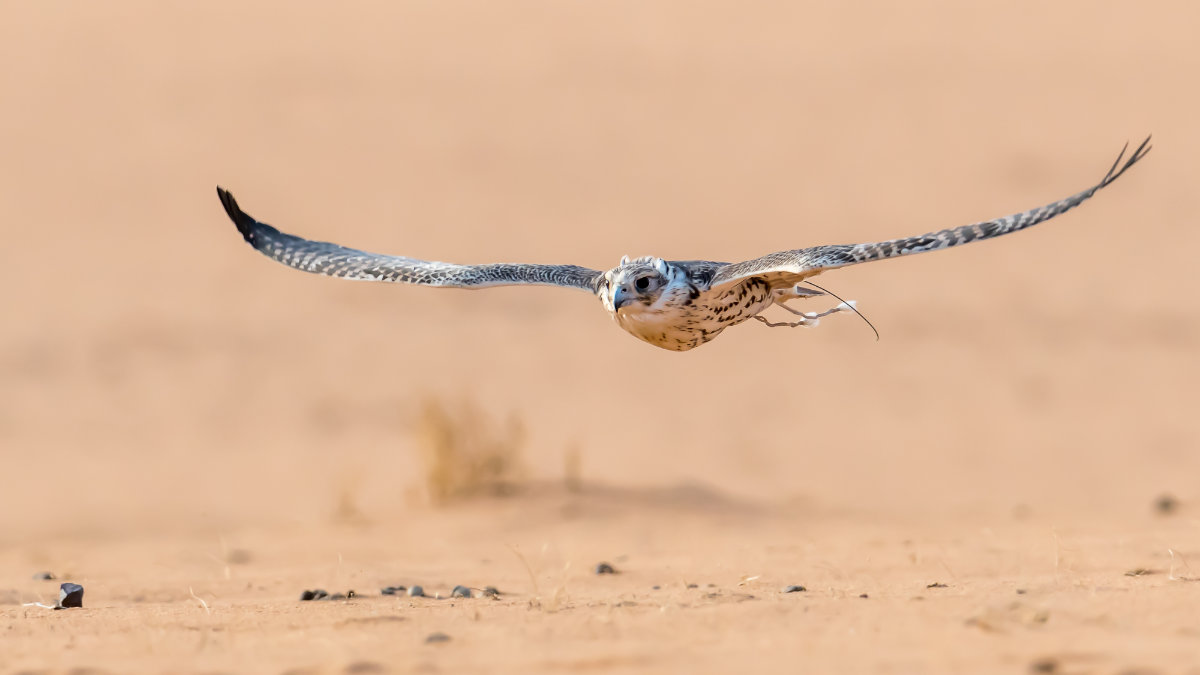

Falcons are among the most loved wildlife in the Kingdom. (SPA photo)
As the largest country in the Middle East, occupying more than 80 percent of the Arabian Peninsula, Saudi Arabia is home to five distinct climatic regions.
These biomes include coastal fog desert, the southwestern savanna foothills, the southwestern montane woodlands, the Arabian Desert, the Nubo-Sindian tropical desert, and areas of semi-desert.
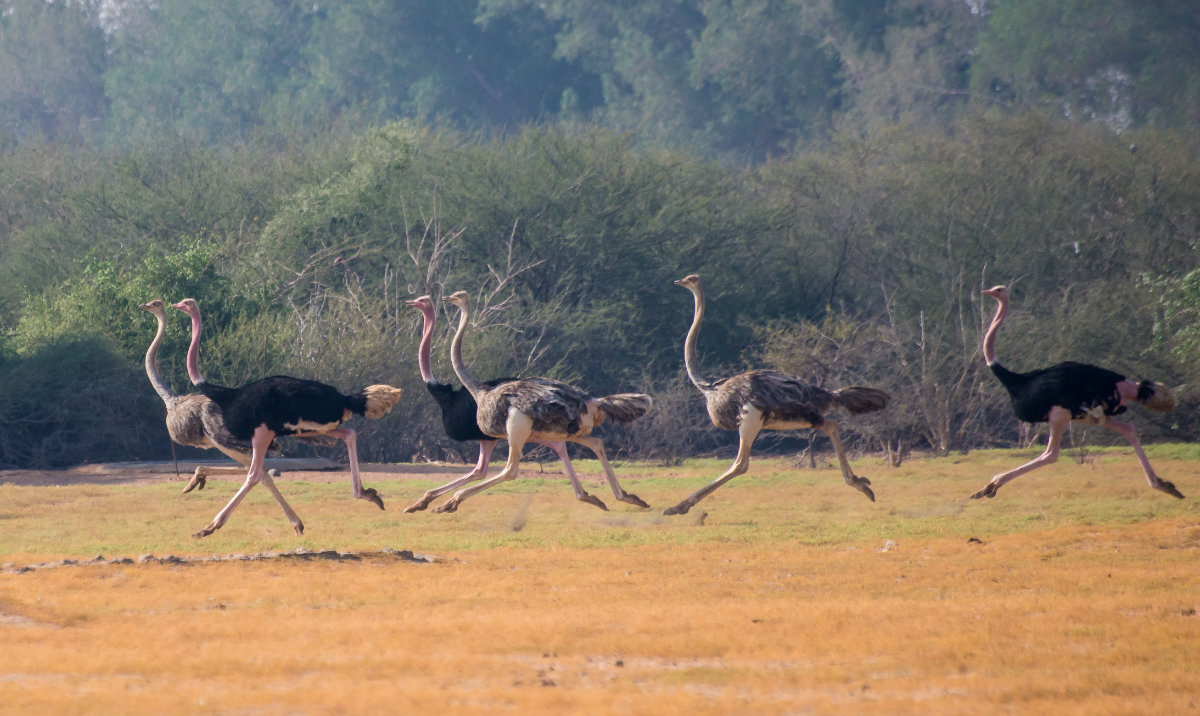

Ostriches racing at a conservation center in Jeddah. (Supplied)
Extensive hunting in the 19th century resulted in the population decline of many of Saudi Arabia’s indigenous animals, including oryx, leopards, and cheetahs. The Kingdom has since imposed bans on poaching and launched breeding programs to help bolster populations.
Other wildlife found in these habitats included striped hyenas, mongoose, baboons, sand cats, and hopping desert rodents known as jerboa. Visitors willing to brave the region’s harsh temperatures may be rewarded with a glimpse of a Nubian ibex, sand gazelles, or a whole array of reptiles.

Gazelles restin one of the wildelife conservation centers of Saudi Arabia, safe from predators and hunters. (Shutterstock)
Occupying some 25 percent of Saudi Arabia’s territory, the Rub’ Al-Khali, also known as the Empty Quarter, is anything but what its name might suggest. The world’s biggest sand desert is in fact home to a dizzying array of wildlife.
Likewise, the Kingdom’s scrublands, steppes, mangroves, volcanic fields, palm oases, and mountain ranges are teeming with creatures — nesting, hunting, feeding, and burrowing, many of them out of sight, coming out only in the cool hours of night.
DIDYOU KNOW
• 2024 was designated the Year of the Camel by the UN and Saudi Ministry of Culture.
• AlUla has made great strides in ensuring that desert tourism is eco-friendly.
• UN Tourism has put forth structured targets to support sustainable desert tourism.
• National Center for Wildlife estimates there are 4,481 endangered species in the Kingdom.
No desert animal is perhaps better recognized than the camel. It is because of its iconic status that the UN and Saudi Arabia’s Ministry of Culture has designated 2024 as the “Year of the Camel.”
This year, Saudi Arabia will host several camel-centric events and organize special spaces to educate the public about these much-loved “ships of the desert.”
Just this past week, the second ever AlUla Camel Cup was celebrated in the Kingdom’s ancient northwestern region. The four-day event centered on the animal, which has become synonymous with the country’s identity.
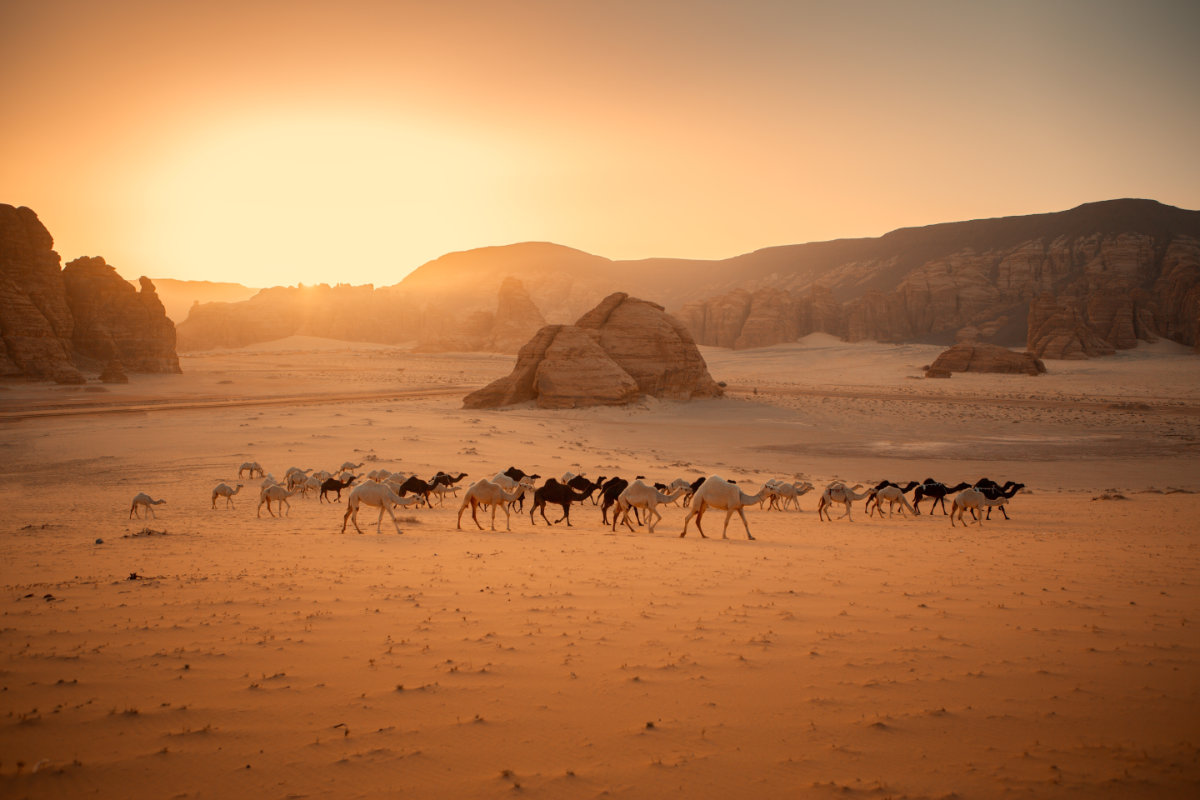

The camel has been the Bedouin’s best friend for centuries, as well as a loyal companion and a lifeline. (Shutterstock)
The camel has been the Bedouin’s best friend for centuries, as well as a loyal companion and a lifeline. Even the Prophet Muhammad relied on camels for transportation and as a source of food and fuel.
Camels are not the only animals getting their moment in the limelight. Saudi Arabia’s National Center for Wildlife and the Saudi Green Initiative have been working hard to ensure none of the Kingdom’s fauna is overlooked.
Assigning an animal to be championed during a specific year, month, or day has been instrumental in raising awareness about the wellbeing and conservation of the region’s distinctive species.
In 2022, the Royal Commission for AlUla launched a campaign for the recognition of “International Arabian Leopard Day.” In 2023, the UN General Assembly unanimously designated Feb. 10 as the “International Day of the Arabian Leopard.”
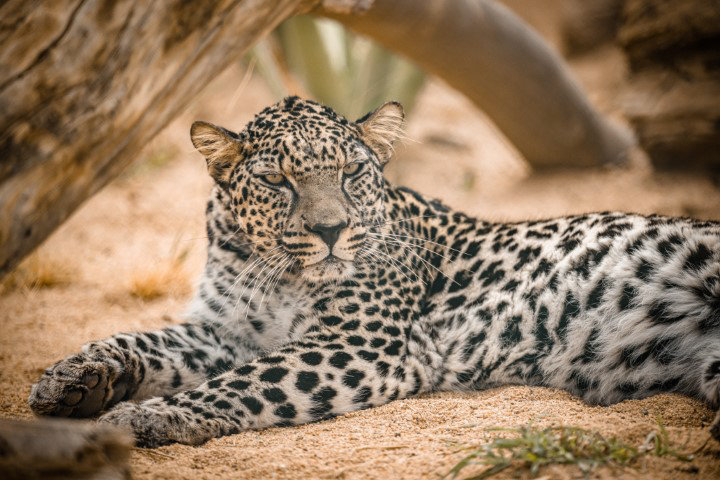

Facing extinction, the Arabian leopard is one of the wildlife species at the center of the Kingdom's animal conservation program. (Royal Commission of AlUla photo)
The Arabian leopard once enjoyed a range stretching across a large swathe of the Arabian Peninsula, from southern Jordan to Yemen.
But, after years of human encroachment on its habitat, resulting in the depletion of its natural prey, the International Union for Conservation of Nature listed the big cat as a critically endangered species.
Saudi Arabia has long been at the forefront of animal conservation, with the Imam Abdulaziz bin Mohammad Royal Reserve Development Authority reintroducing more than 220 endangered species into the wild in the Kingdom’s royal reserves over the past five seasons.
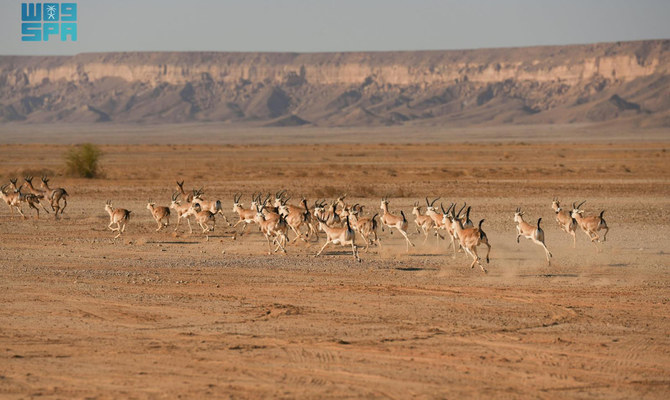

More than 220 endangered animal species have been reintroduced to the wild in Saudi royal reserves over the past three years. (SPA)
Much of this has been done in tandem with sustainable tourism initiatives, designed to protect the Kingdom’s ecosystems, while providing jobs, services, and prosperity to local communities.
For instance, in the ancient deserts of northwest Saudi Arabia, framed by curious rock formations with their dramatic silhouettes, the lush green oasis of AlUla has been continuously occupied by humans since before the 12th century.
Throughout that time, animals have been vital to the area and to the livelihoods of its human residents.
In line with Saudi Vision 2030, the Royal Commission for AlUla has launched an initiative to rehabilitate 65,000 hectares of degraded land, activating the space and resurrecting the harmony between humans and nature — an organic partnership that has defined the region for millennia.
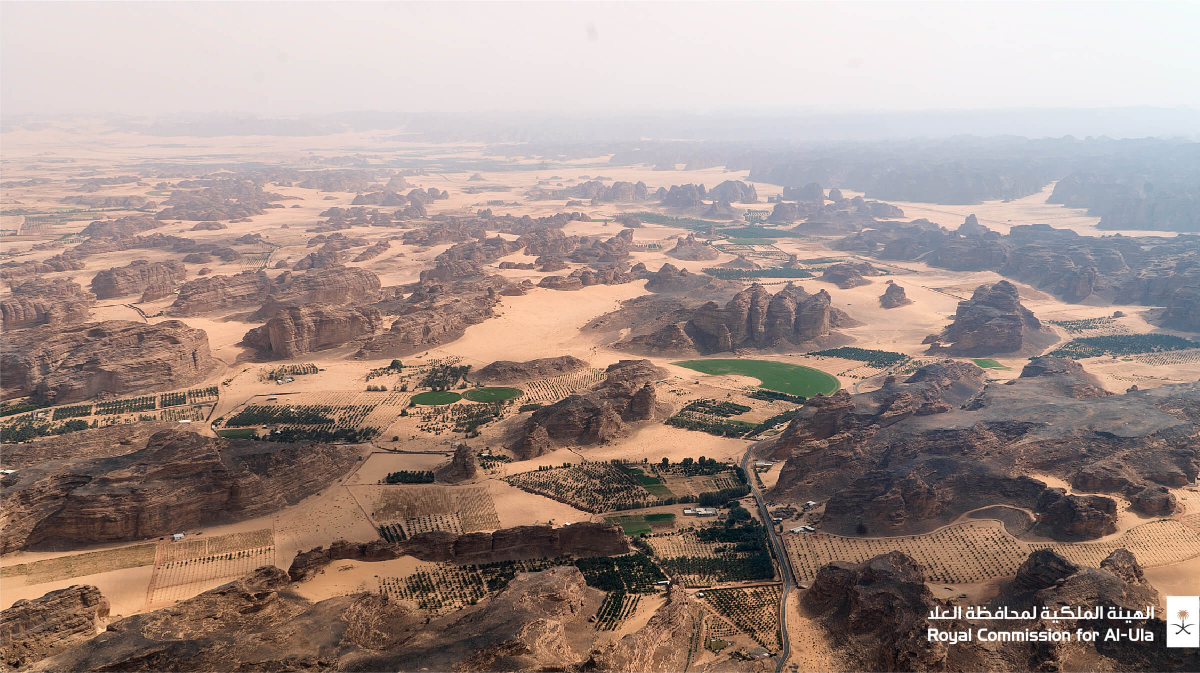

The lush green oasis of AlUla has been continuously occupied by humans since before the 12th century. (RCU photo)
Besides AlUla, nearly every other desert space in the Kingdom has introduced curated tours that mindfully lead humans into the wilderness with the intention of enjoying, honoring, and respecting the animals that live there.
The Kingdom has made significant strides in ensuring that its animals continue to flourish in a rapidly changing world and a nation that aims to become a major tourism magnet in the years to come.
But with more people, vehicles, and infrastructure coming to the desert, it is a collective responsibility to ensure visitors do so without disturbing these precious ecosystems and their animal inhabitants.