WASHINGTON: A six-day-old US pier project in Gaza is starting to get more aid to Palestinians in need but conditions are challenging, US officials said Thursday. That reflects the larger problems bringing food and other supplies to starving people in the besieged territory.
The floating pier had a troubled launch, with crowds overrunning some of the first trucks coming from the new US-led sea route and taking its contents over the weekend. One man in the crowd was shot dead in still-unexplained circumstances. It led to a two-day suspension of aid distribution.
The US military worked with the UN and Israeli officials to select safer alternate routes for trucks coming from the pier, US Vice Admiral Brad Cooper told reporters Thursday.
As a result, the US pier on Wednesday accounted for 27 of the 70 total trucks of aid that the UN was able to round up from all land and sea crossings into Gaza for distribution to civilians, the United States said.
That’s a fraction of the 150 truckloads of food, emergency nutrition treatment and other supplies that US officials aim to bring in when the sea route is working at maximum capacity.
Plus, Gaza needs 600 trucks entering each day, according to the US Agency for International Development, to curb a famine that the heads of USAID and the UN World Food Program have said has begun in the north and to keep it from spreading south.
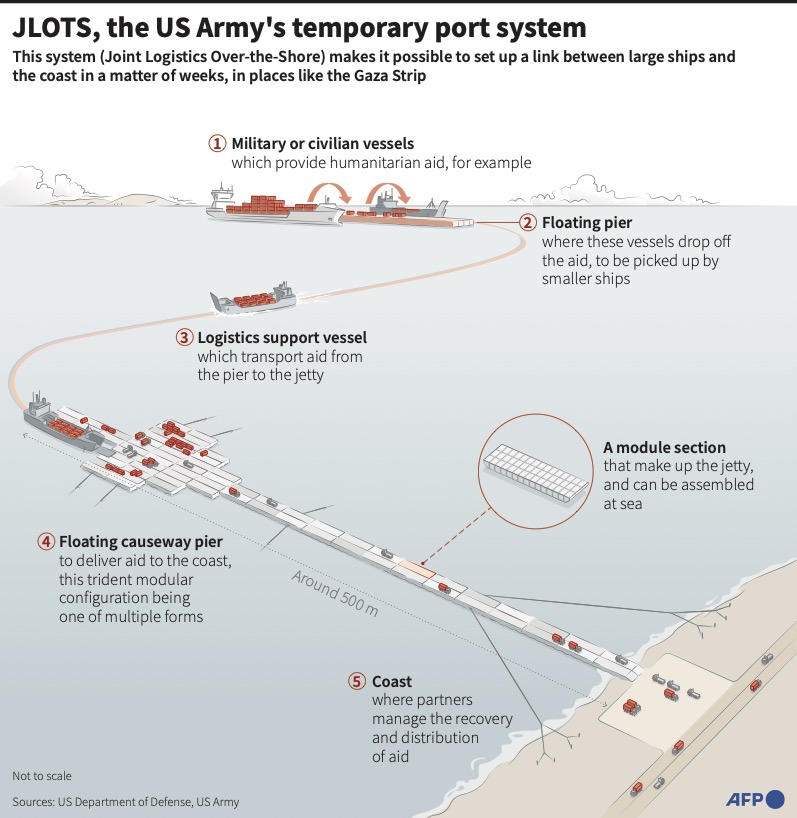
Only one of the 54 trucks that came from the pier Tuesday and Wednesday encountered any security issues on their way to aid warehouses and distribution points, US officials said. They called the issues “minor” but gave no details.
A deepening Israeli offensive in the southern city of Rafah has made it impossible for aid shipments to get through the crossing there, which is a key source for fuel and food coming into Gaza. Israel says it is bringing aid in through another border crossing, Kerem Shalom, but humanitarian organizations say Israeli military operations make it difficult for them to retrieve the aid there for distribution.
The Biden administration last week launched the $320 million floating pier for a new maritime aid route into Gaza as the seven-month-old Israel-Hamas war and Israeli restrictions on land crossings have severely limited food deliveries to 2.3 million Palestinians.
For all humanitarian efforts, “the risks are manifold,” Daniel Dieckhaus, USAID’s response director for Gaza, said at a briefing with Cooper. “This is an active conflict with deteriorating conditions.”
Dieckhaus rejected charges from some aid groups that the pier is diverting attention from what the US, UN and relief workers say is the essential need for Israel to allow full access to land crossings for humanitarian shipments.
For instance, Jeremy Konyndyk, a former USAID official now leading Refugees International, tweeted that “the pier is humanitarian theater.”
“I would not call, within a couple of days, getting enough food and other supplies for tens of thousands of people for a month theater,” Dieckhaus said Thursday when asked about the criticism.
At maximum capacity, the pier would bring in enough food for 500,000 of Gaza’s people. US officials stressed the need for flow through open land crossings for the remaining 1.8 million.






























