JEDDAH: Saudi-grown pink roses are loved throughout the Arabian Peninsula for their expert cultivation, vivid color, alluring fragrance and the many luxurious products derived from their petals, which constitute a multimillion-dollar industry.
Two kinds of pink rose are cultivated in the Kingdom — the Madinah rose, which has a light pink blush and grows year round, thriving in warm and cool climates, and the Taif rose, also known as the Jory or Damascus rose, which grows only in the spring.
Taif produces more than 550 million flowers each harvest season, which lasts for between 45 and 60 days. The rose-picking season typically begins late in March or early April.

Spanning 270 hectares, 910 rose farms nurture about 1.14 million bushes across areas such as Al-Hada, Al-Shifa, Wadi Muharram, Al-Wahat and Al-Wahit, according to the Saudi Press Agency.
The products derived from these flowers enjoy widespread popularity, with a domestic market value of SR64 million ($17 million).
Considered a hallmark of the region’s natural beauty, Taif roses are known for their exquisite, sweet fragrance, vibrant pink hues, and delicate petals. Cultivated at high altitudes, these roses thrive in the region’s cool temperatures and fertile soil.
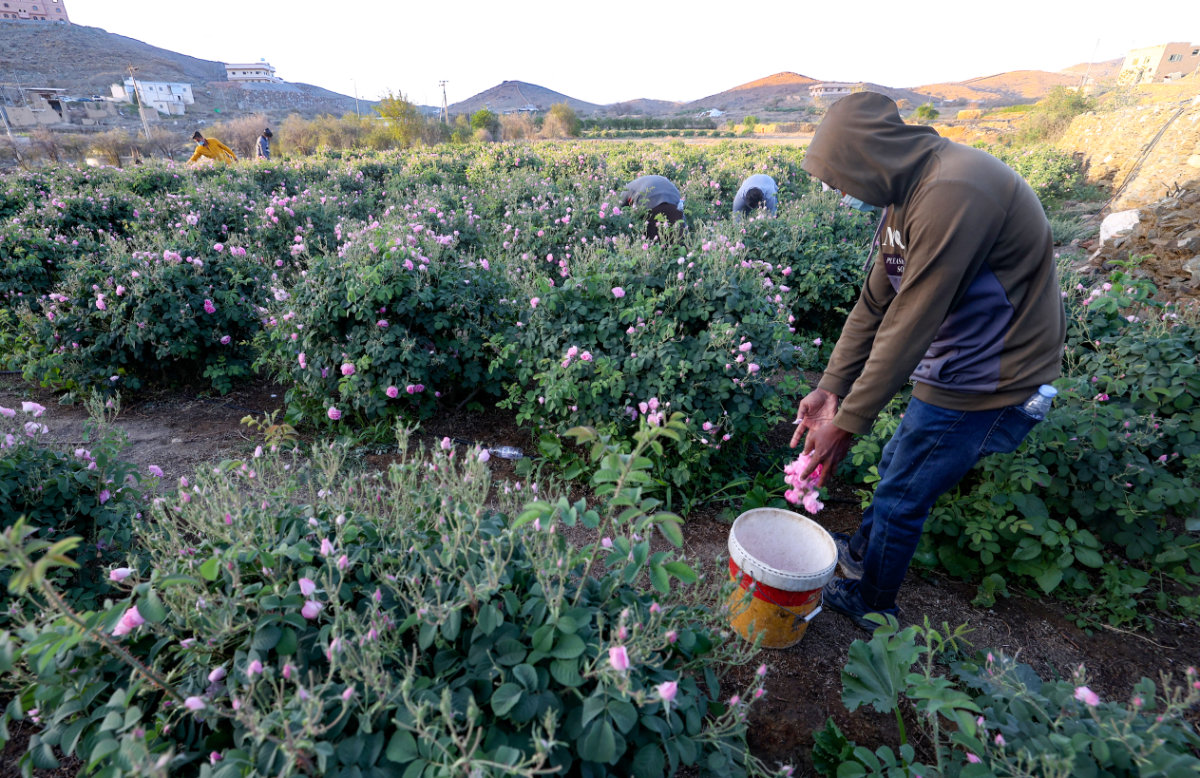

Every spring, roses bloom in Taif, transforming pockets of the Kingdom's vast desert landscape into fragrant pink patches. (AFP photo)
More than 60 farms and the families who run them participate in the region’s annual Rose Festival, which typically falls in April and May, where they display their products over five days of festivities.
These fragrant crops have elevated the mountainous governorate into a global rose capital, which earned a place in the Guinness World Records in 2022 for the largest basket of roses, containing 84,450 flowers.
To grow the industry, the Ministry of Environment, Water and Agriculture has launched several projects, including the rehabilitation of agricultural terraces, the application of rainwater harvesting technologies, and the Sustainable Rural Agricultural Development Program.
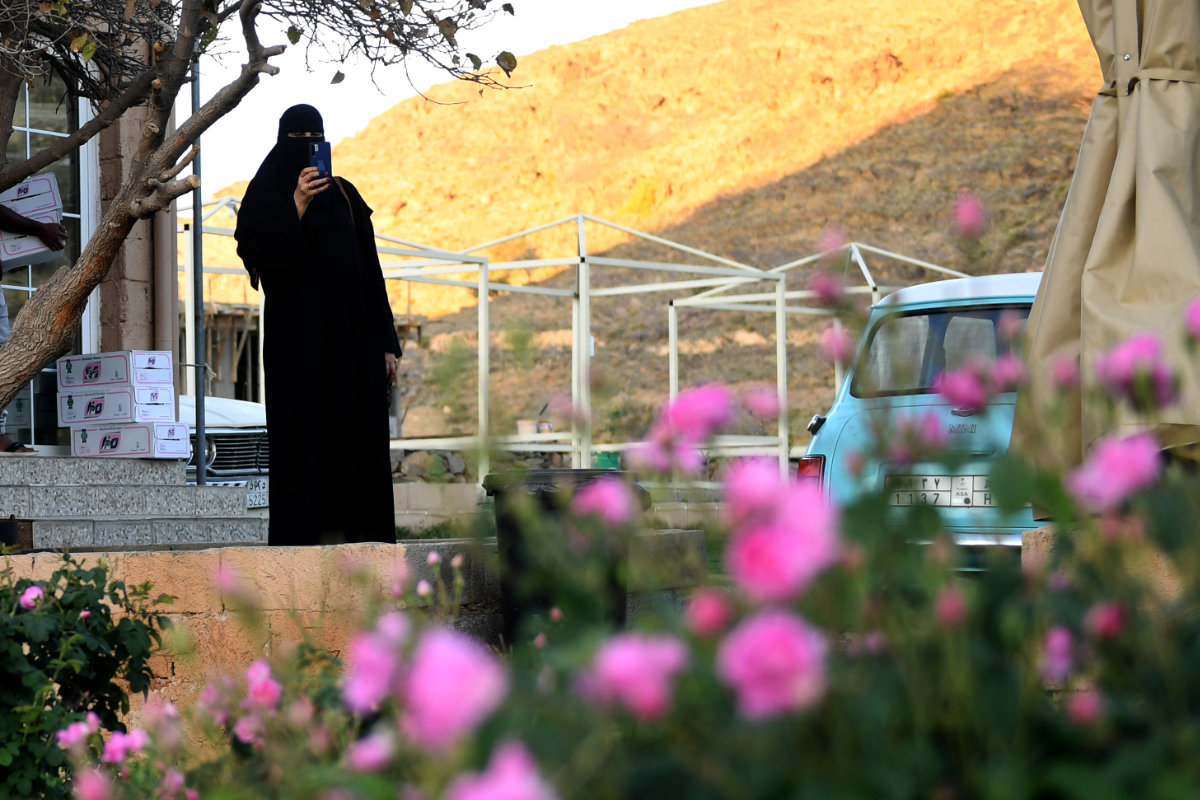

A Saudi woman takes a picture of a rose orchard at the Bin Salman Farm in Taif on March 13, 2021. (AFP photo)
The ministry also supports specialized agricultural cooperatives, including the recently established Rose and Aromatic Plants Association. This support allows them to invest in ministry lands, produce aromatic oils, and benefit from the Agricultural Development Fund.
“The ministry is working on several initiatives and plans to achieve global leadership in Taif rose industries and increase its production to 2 billion roses by 2026,” Saleh Bindakhil, spokesperson for the Ministry of Environment, Water and Agriculture, told Arab News.
DID YOUKNOW?
• Taif produces more than 550 million flowers each harvest season, which lasts for 45-60 days.
• Spanning 270 hectares, 910 farms in the west of the Kingdom nurture 1.14 million bushes.
• Products derived from rose oil have a domestic market value of SR64 million ($17 million).
A group of horticulturalists from the Agricultural Guidance Department were recently sent to Bulgaria, the Philippines and Thailand to learn about the latest technologies in rose-oil production and environmentally friendly farming practices.
Farmers receive expert guidance on best agricultural practices, with dedicated pest control teams responding promptly to requests for pesticide spraying to safeguard crops from potential threats.
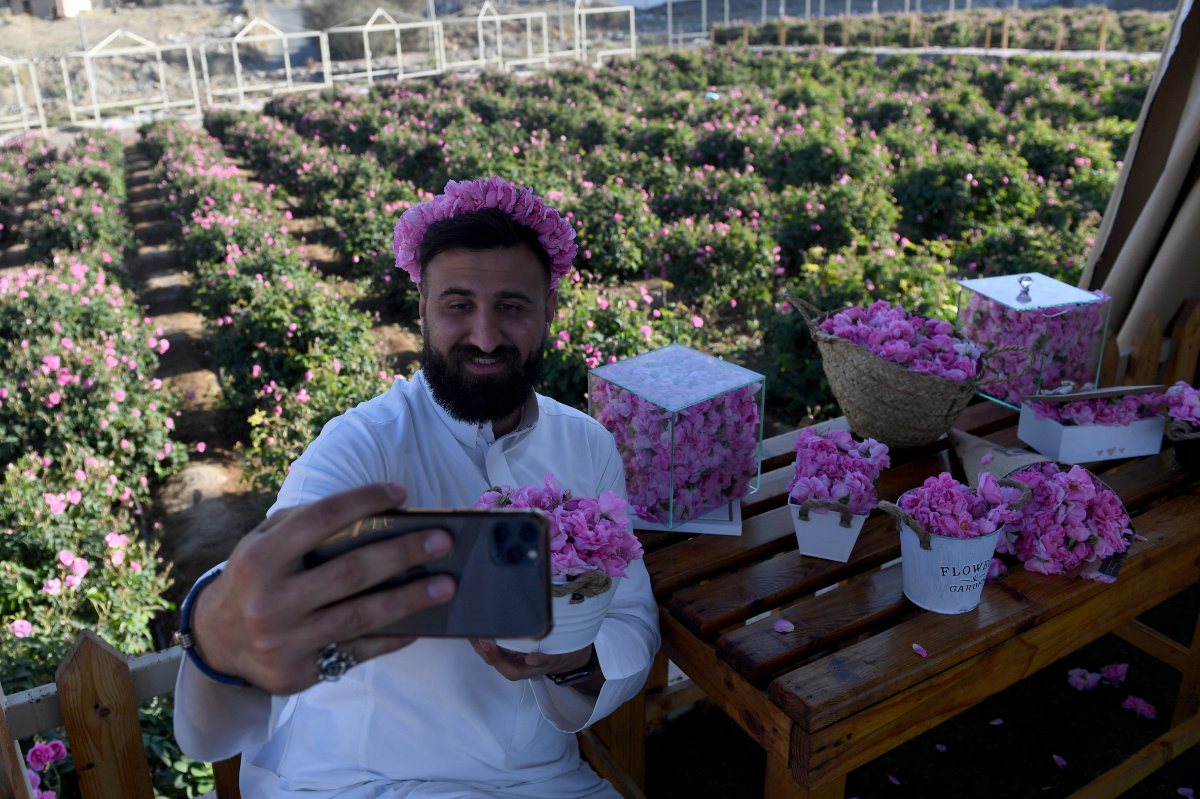

A tourist takes a photo with Taif roses at the Bin Salman Farm in the city of Taif on March 13, 2021. (AFP)
The ministry also leads the construction of essential water infrastructure, including tanks and barriers, while also facilitating the establishment of irrigation networks to boost agricultural activities.
Emphasizing the importance of sustainable practices, the ministry encourages small-scale rose farmers to embrace and implement best agricultural methods, providing them with valuable insights into the use of advanced technologies and optimal rose production techniques, including essential oil extraction as part of a value chain development approach.
“Taif governorate has long been recognized as the ideal and original environment for Taif rose bushes,” Bindakhil said.
“Generations have cared for these roses, passing down the tradition of harvesting, distilling and extracting rose oil and water. They have enjoyed the fragrant history of these roses in the mild, cool climate and mountainous nature at the summit of the renowned Jabal Ghazwan.”
One use for the rose water extracted from Taif roses is for washing the Kaaba in Makkah each year — a traditional practice upheld by the Saudi government.
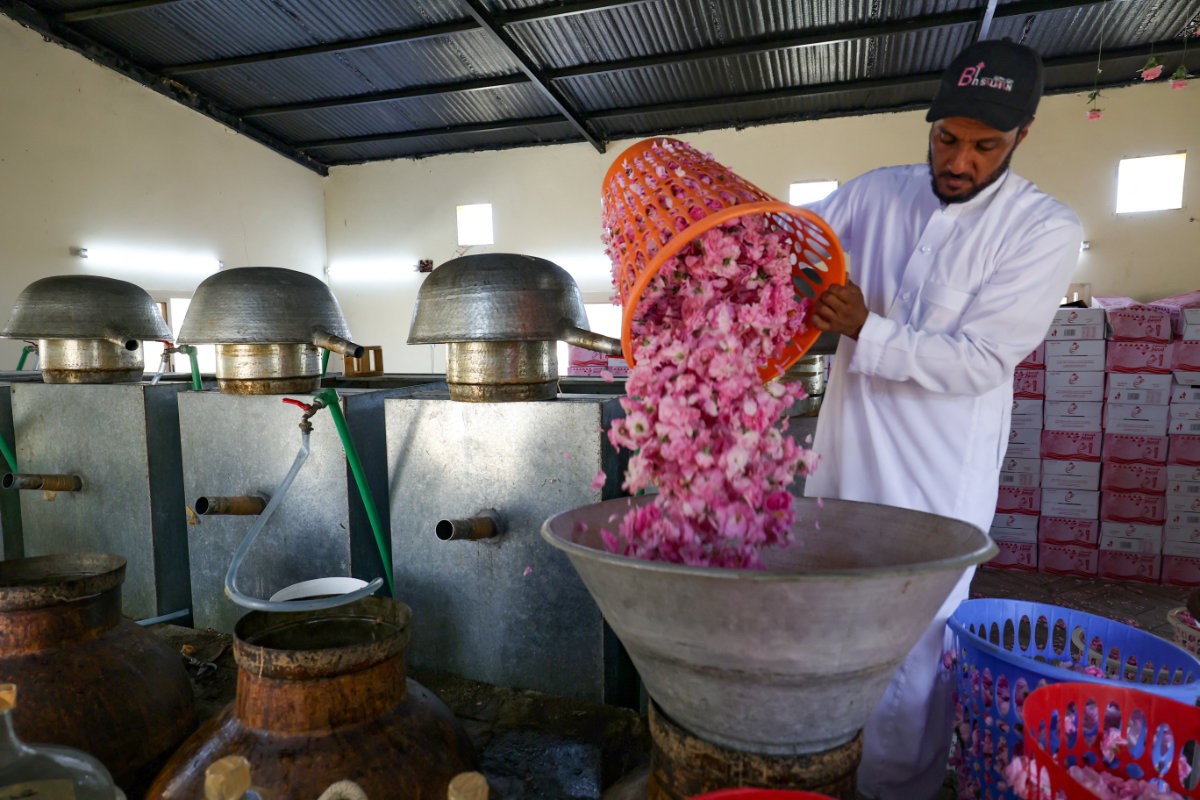

The distillation process, which last nine to 12 hours, is done using tightly sealed copper pots. (AFP photo)
The Kingdom has many factories and workshops dedicated to extracting and manufacturing more than 80 products from rose derivatives, producing various aromatic products and body care items.
The rose industry plays a significant role in regional development and the local economy, providing numerous job and marketing opportunities, and encouraging more women to enter the workforce.
To extract the rose oil, sacks containing thousands of rose petals are poured into 90-liter copper pots, which are then sealed tightly for a distillation process that lasts nine to 12 hours.
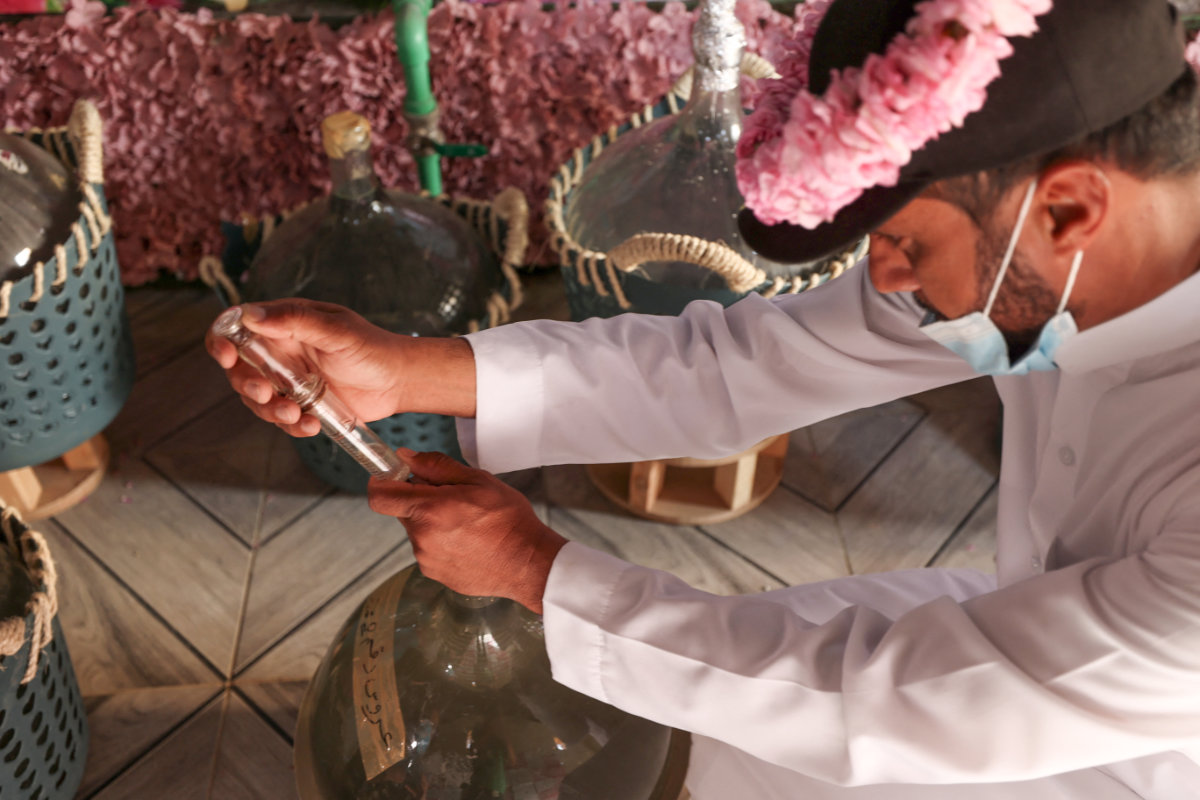

It takes 45,000 roses to produce the oil extract, which is then poured into 12 milliliter vials. (AFP photo)
It takes 45,000 roses to produce the oil extract, which is then poured into 12 milliliter vials, the price of which starts at $400, depending on the season.
Al-Kamal, established in 1831, is the oldest factory manufacturing rose-derived cosmetics and cleaning products in the Kingdom. Located in Madinah’s Al-Hada, it is managed by Khalid Al-Kamal, whose family has worked at the firm for generations.
“It is an inherited career from father to son — from one generation to another — and I am very proud to tell you that I am the seventh generation to inherit this legacy,” Al-Kamal told Arab News in a 2021 interview.
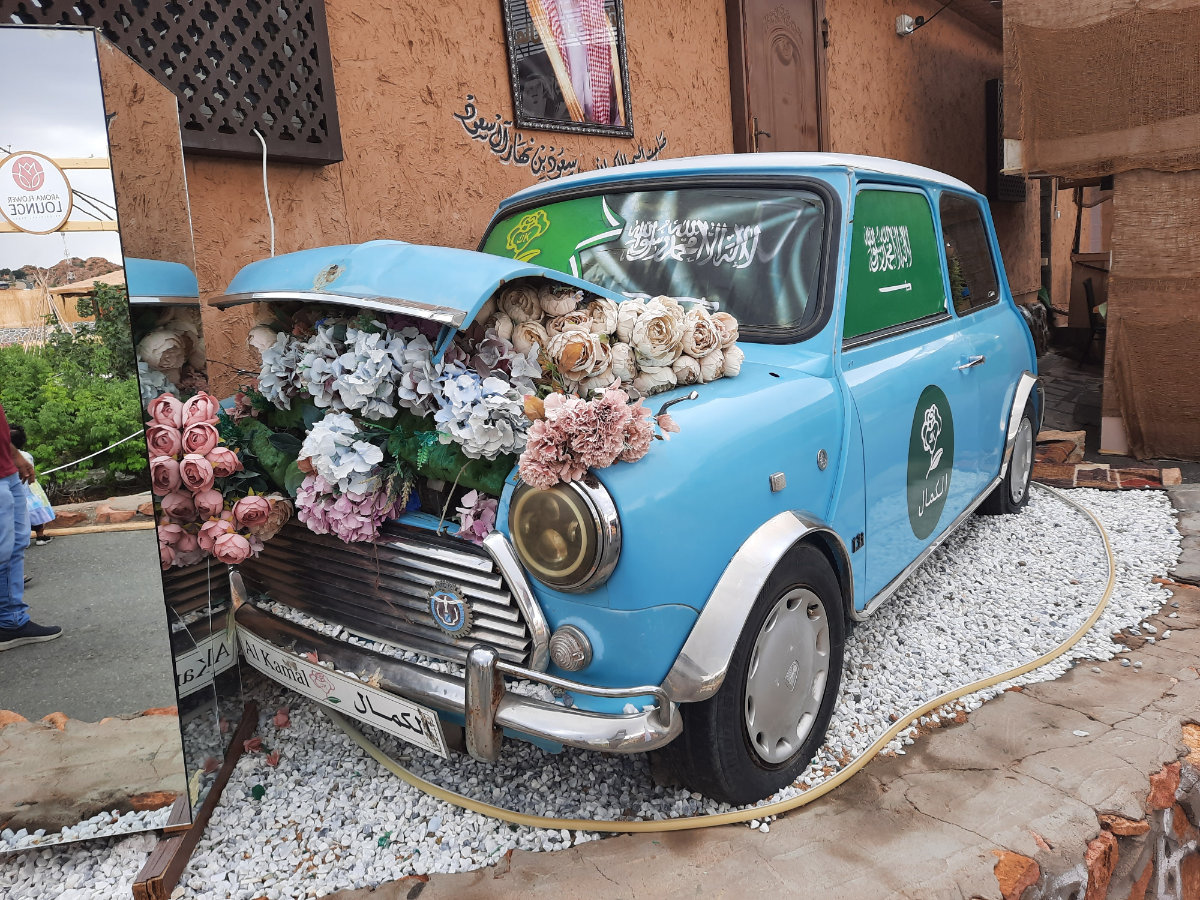

A view of the entrance to the Al-Kamal Rose Factory in Taif. (Shutterstock)
“Working in the field of farming roses requires a lot of delicacy, as the quality of the roses is affected by the soil and weather as well as the method of cultivation. I learned from my forefathers, and now my three sons manage the factory along with several workers.”
With many new government investments in the pipeline promoting the sustainable use of water resources, Saudi Arabia’s rose industry will no doubt continue to blossom in years to come.