LONDON: Sudan’s prolonged conflict has brought devastation, but this year a new enemy has emerged: torrential rains and floods, killing over 100 people and reigniting a deadly cholera outbreak.
The situation has sparked a public health emergency in the violence-wracked African nation, where waterborne diseases like cholera, exacerbated by floods and poor sanitation, continue to surge.
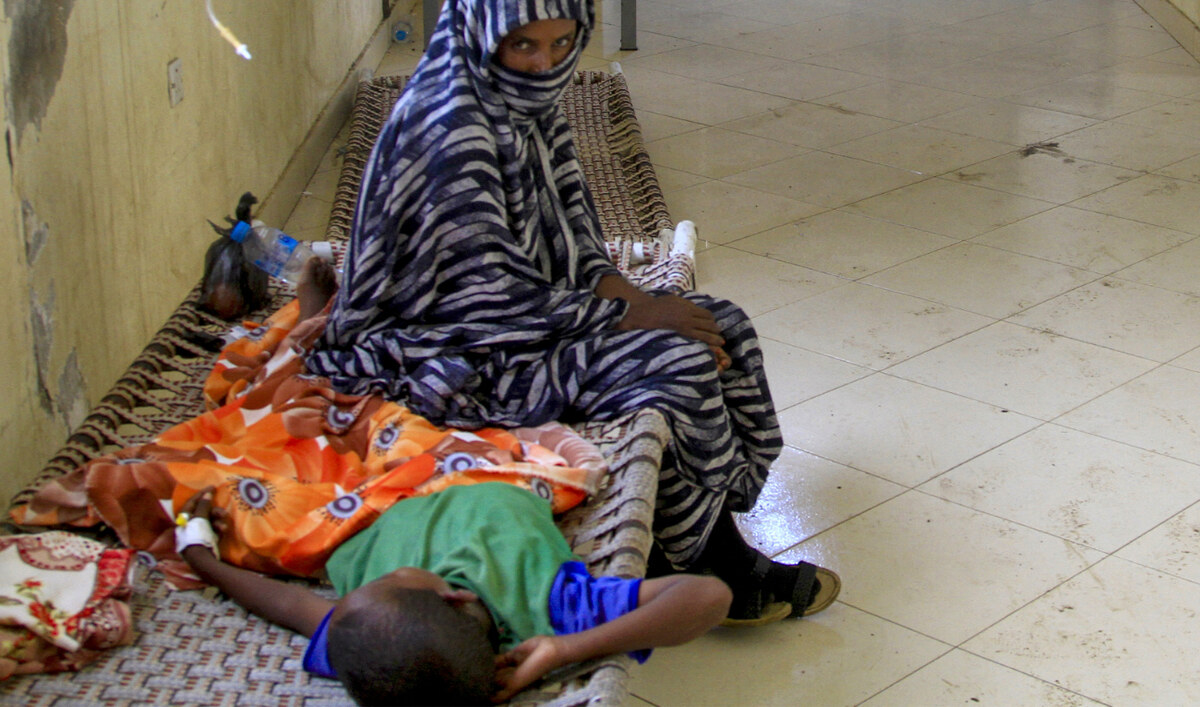

A child suffering from cholera receives treatment at a rural isolation centre in Wad Al-Hilu in Kassala state in eastern Sudan, on August 17, 2024. (AFP)
The World Health Organization reported over 11,327 cholera cases and 316 deaths since June 2023, but the real numbers are likely higher. Haitham Mohamed Ibrahim, Sudan’s health minister, officially declared a cholera outbreak on Aug. 17, just a day after the WHO report.
“Cholera is caused by bacteria that are transmitted through contaminated water and the fecal-oral route,” said Dr. Zaher Sahloul, president of the medical NGO MedGlobal. “There are hundreds of new cholera cases in southeastern states, worsened by the recent torrential rains and floods.”
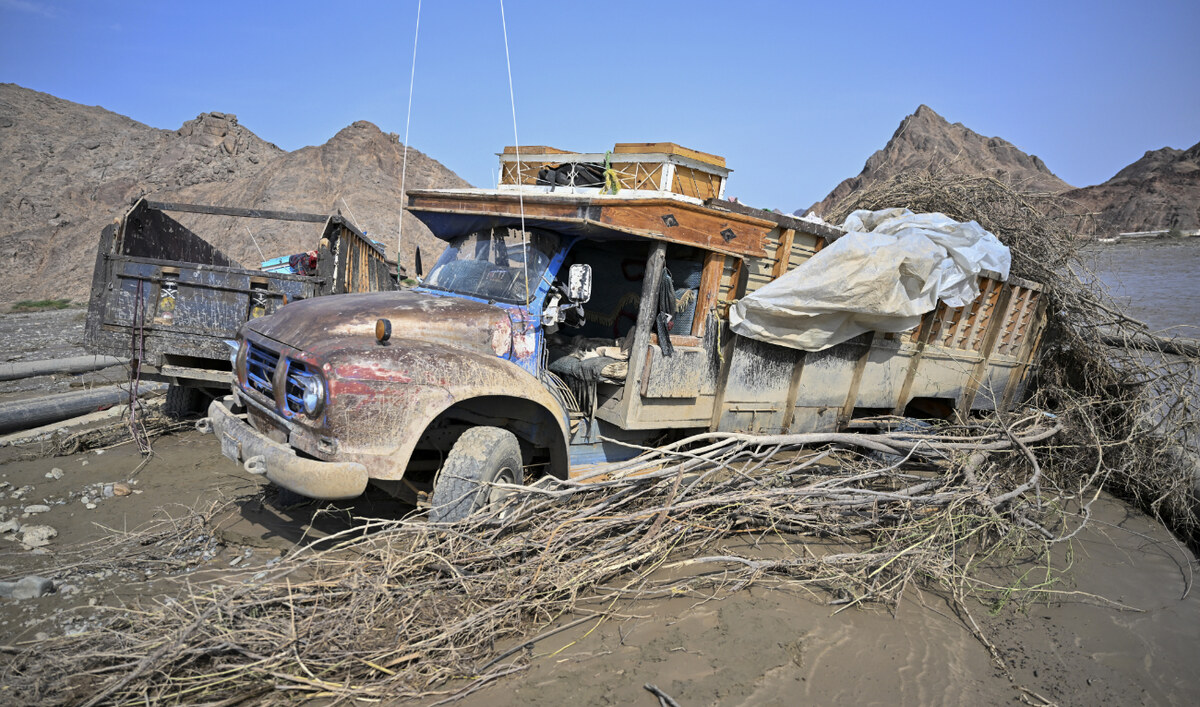

Damaged trucks burried in the mud after the collapse of the Arbaat Dam, 40km north of Port Sudan following heavy rains and torrential floods on August 25, 2024. (AFP)
Sudan’s history with cholera runs deep. A 2017 outbreak infected over 22,000 people within two months, killing at least 700. Today, a worsening humanitarian crisis driven by conflict has led to a resurgence of diseases, including dengue fever and meningitis.
Heavy rains have flooded conflict zones including Al-Jazirah, Khartoum and Darfur, contaminating water sources and amplifying the spread of disease.
IN NUMBERS
- 11,327+ Cholera cases from June 2023 to August 2024.
- 316+ Deaths from cholera during the same period.
(Source: WHO)
The rain, forecast to continue into September, has killed 114 people and displaced thousands already weakened by war and acute food shortages, according to Sudan’s Health Ministry.
Floods have displaced 20,000 people in 11 of Sudan’s 18 states since June, according to the International Organization for Migration. The Nile and Kassala states, near Eritrea, have been particularly hard-hit.
Sahloul cautioned that cholera would continue to spread due to the collapse of Sudan’s healthcare system, lack of clean water, and a shortage of medicine.

The fighting between the Sudanese Armed Forces and the paramilitary Rapid Support Forces, which broke out on April 15 last year, has claimed at least 15,000 lives and displaced 12 million people. Out of them, nearly 2 million are now refugees in three neighboring countries — Chad, Egypt and South Sudan.
The violence has decimated the healthcare system, with about 70 percent of hospitals in conflict zones no longer operational.
The humanitarian crisis in Sudan has been the largest in the world for many months now. More than half of the country’s 45 million people need urgent relief aid. Some food security specialists fear that as many as 2.5 million people could die from hunger by the end of this year.

The violence has decimated the healthcare system, with about 70 percent of hospitals in conflict zones no longer operational. (MSF)
In addition to cholera, Sudan faces another health crisis: the spread of mpox, formerly known as monkeypox. The WHO has declared a public-health emergency following the rapid spread of a new clade of mpox in eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo and neighboring countries.
“The emergence of a new strain of mpox, clade 1, its rapid spread, and the reporting of cases in several neighboring countries are very worrying,” Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, the WHO director-general, said in mid-August.
Sahloul of MedGlobal, which has been providing essential aid in Sudan, cited the “regional increase in mpox cases and the spread to nearby Central and East African countries, including Uganda,” which borders Sudan, as the main reason for the declaration.
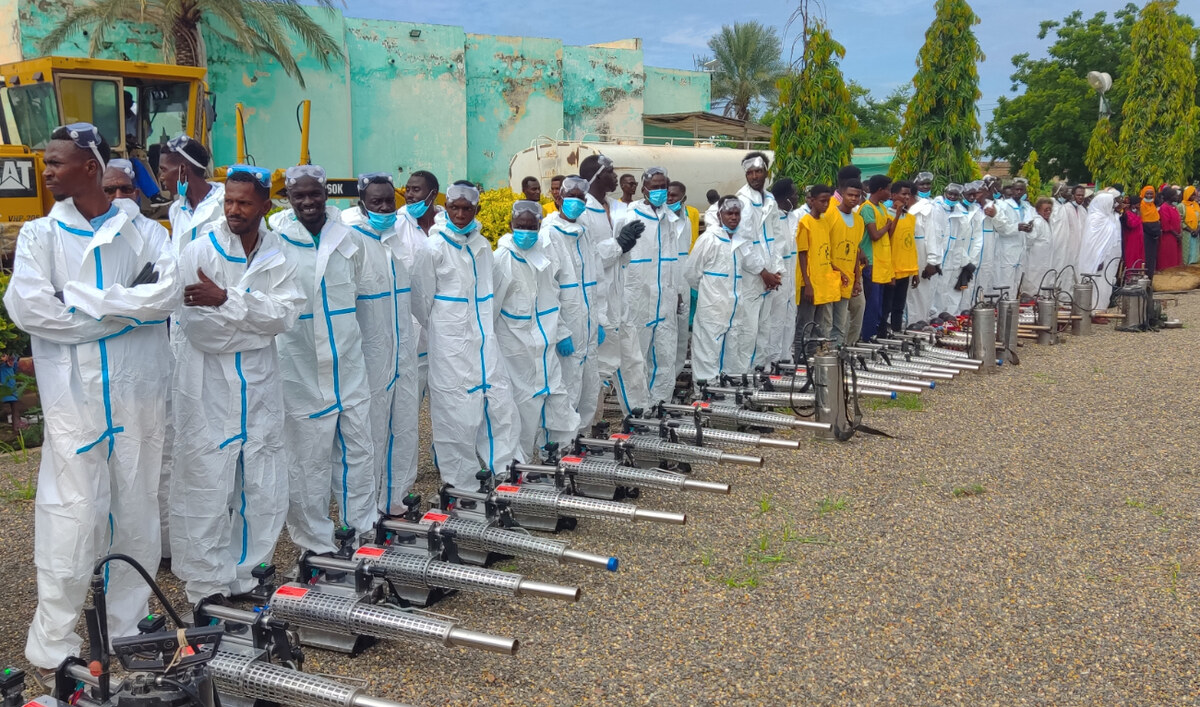

Workers gather to kickstart a hygiene and sanitation campaign initiated by health authorities in Sudan’s eastern city of Gedaref on August 24, 2024, to combat the spread of disease in the country. (AFP)
The virus, which causes flu-like symptoms and blistering rashes, can be deadly if left untreated. Sudan’s limited health infrastructure is already struggling to cope with multiple disease outbreaks, placing the country and its neighbors at risk.
With a fatality rate of 3.6 percent, clade 1 “is a dangerous disease caused by a virus that is from the same family of now-extinct smallpox,” Sahloul said.
“Like cholera, mpox is an infectious disease that spreads in an environment of displacement, crowding, and lack of access to personal hygiene and clean water.”
He added: “The spread of mpox in overcrowded camps and regions with poor sanitation could have catastrophic consequences.”
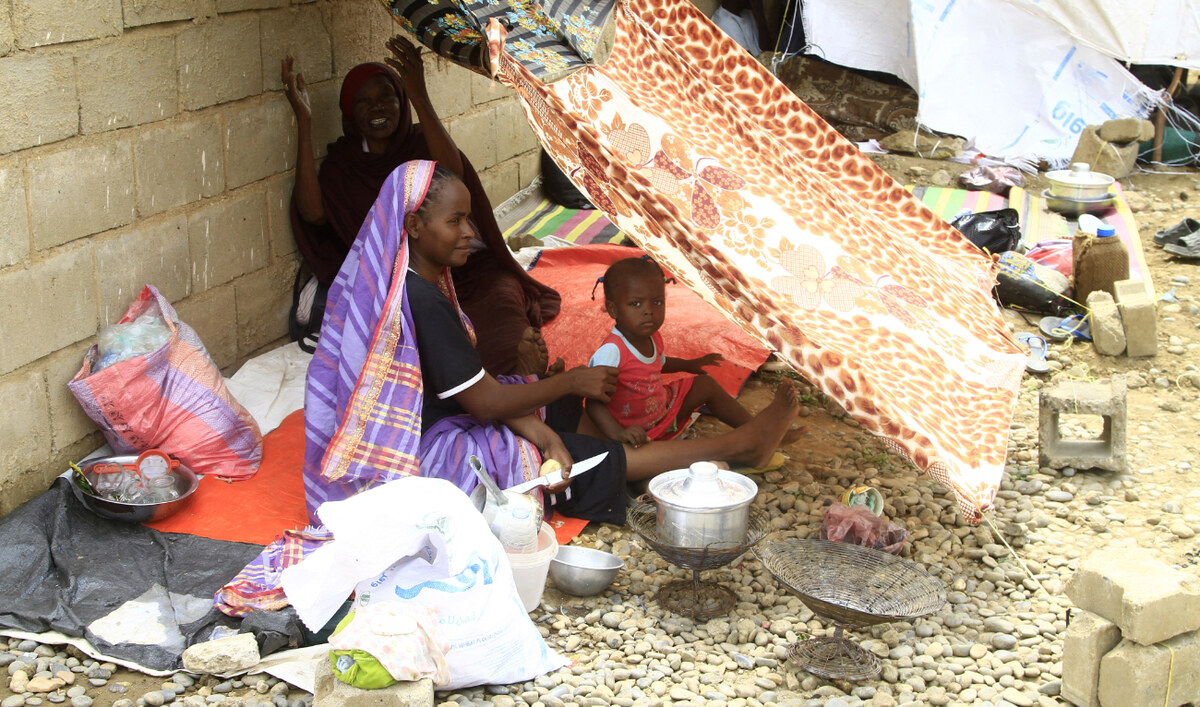

Sudanese already displaced by conflict, rest under a blanket at a makeshift campsite they were evacuated to following deadly floods in the eastern city of Kassala on August 12, 2024. (AFP)
Sahloul said both cholera and mpox “can undermine health security regionally and internationally, and may spread quickly to neighboring countries like Egypt, Libya, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Somalia and South Sudan.”
The situation is especially concerning as “many of these countries have their own separate crises.”
Against this alarming backdrop, the international community has been calling for a ceasefire to allow humanitarian aid to reach the affected areas in Sudan.

The US opened talks in Switzerland on Aug. 14 aimed at easing the human suffering and achieving a lasting ceasefire. The talks were co-hosted by Saudi Arabia and Switzerland, with the African Union, Egypt, the UAE and the UN completing the so-called Aligned for Advancing Lifesaving and Peace in Sudan Group (ALPS).
According to an AFP report, an RSF delegation showed up but the SAF were unhappy with the format and did not attend, though they were in telephone contact with the mediators. The talks ended on Aug. 16 without a ceasefire but with progress on securing aid access on two key routes into the country.
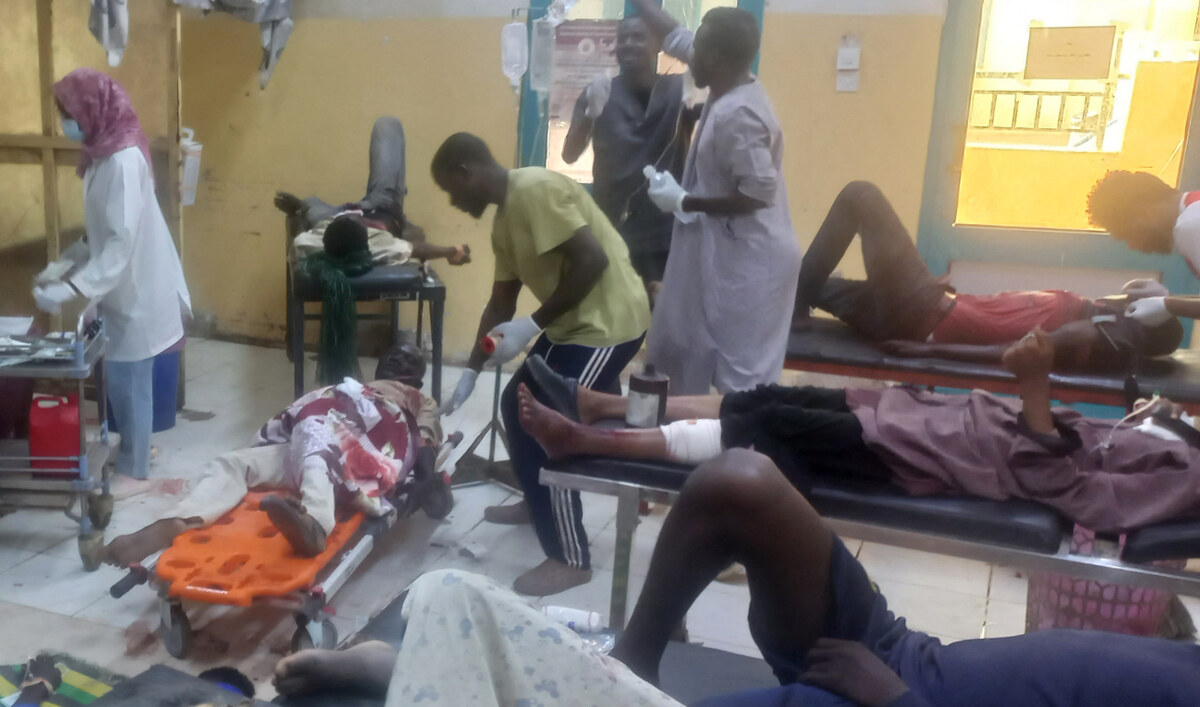
People receive treatment at the Bashair hospital in Sudan's capital on September 10, 2023. (AFP)
The reopening of the Adre crossing from Chad is a key development for aid organizations. The crossing is the most effective route for delivering relief supplies into Sudan, where millions are in dire need of food, clean water, and medical care.
“The reopening will enable the entry of aid needed to stop the famine and address food insecurity,” said a joint statement from the five countries. The statement called on Sudan’s warring parties to coordinate with humanitarian groups to ensure aid reaches the most vulnerable people.
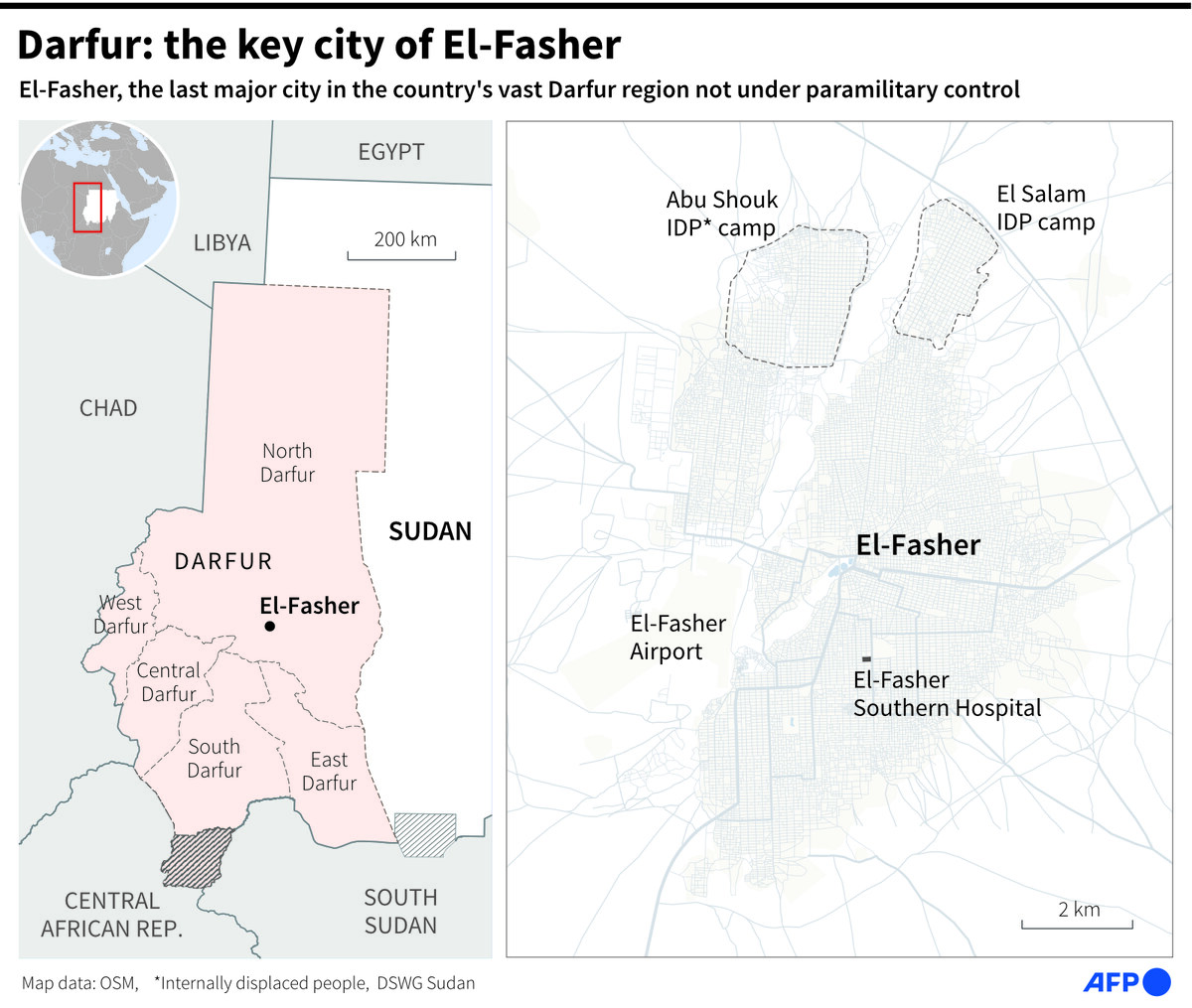
Sudan’s hunger crisis has left more than 25.6 million people vulnerable to infections, according to the UN. The breadbasket regions of Al-Jazirah and Sennar along the Blue Nile have been devastated. People there are going hungry for the first time in generations, according to a recent BBC report.
It says starvation is worst in Darfur, especially in El-Fasher, the only city in the region still controlled by the army and its local allies.
With limited access to clean water and sanitation, many Sudanese — especially in refugee camps — are at high risk of contracting cholera, mpox and other diseases. “The combination of displacement, crowding, and lack of clean water creates a perfect storm for outbreaks,” said Sahloul.

Sudan’s history with cholera runs deep. A 2017 outbreak infected over 22,000 people within two months, killing at least 700. (AFP)
UNICEF has reported that more than 17.3 million people in Sudan currently lack access to safe drinking water, while the International Federation of Medical Students Associations estimates that 829,000 deaths annually are linked to diseases caused by contaminated war and poor standards of sanitation and hygiene.
As Sudan grapples with cholera, mpox and a humanitarian catastrophe, the country’s people await an end to the violence that continues to fuel this public health disaster.
































