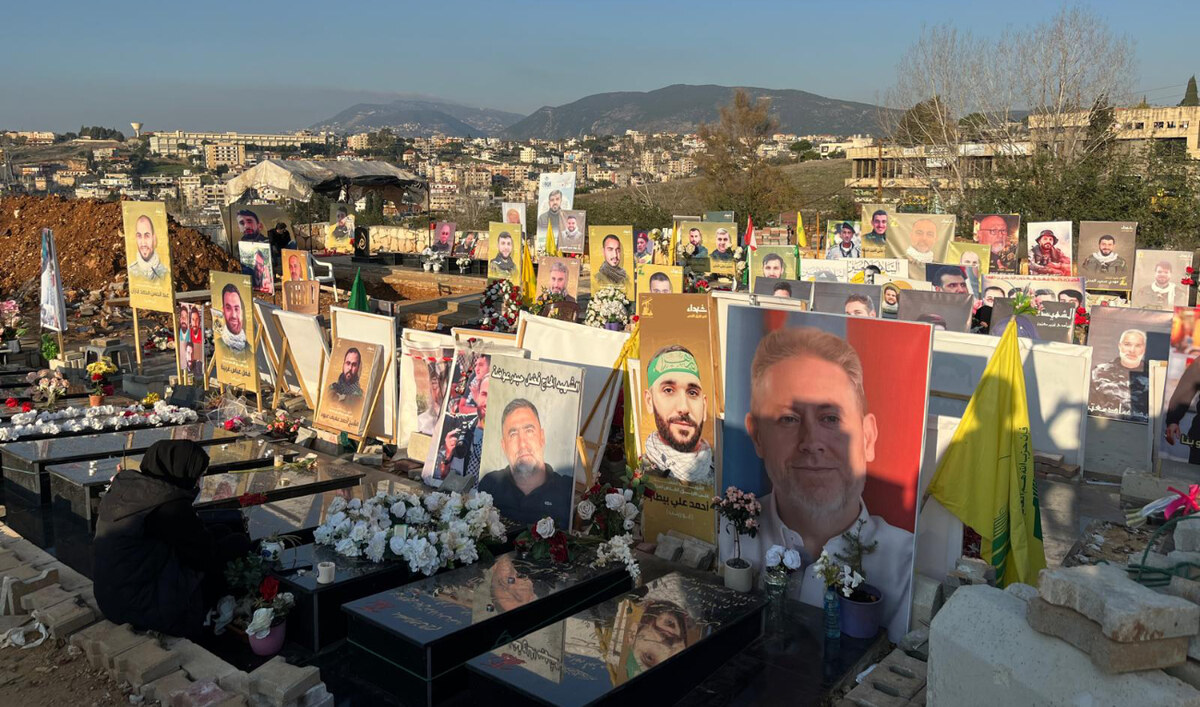
LONDON: At precisely 3:30 p.m. local time on Tuesday, an estimated 3,000 pagers carried by Hezbollah members beeped several times before exploding simultaneously, killing at least 12 people and injuring thousands more across Lebanon and parts of Syria.
At least eight of the dead were reportedly members of Iran-backed Hezbollah, and the many wounded included Mojtaba Amini, Iran’s ambassador to Lebanon, who may have lost at least one eye.
But clips from security cameras in shops in Beirut and other locations, circulated on social media, illustrated the dangerously indiscriminate nature of the attack.
Many civilians going about their day also fell victim to the blasts as pagers exploded in supermarkets, on the streets, and in cars and homes. Among the dead were two children who were in the wrong place at the wrong time.
Fleets of ambulances ferried a reported 2,700 wounded to hospitals across Lebanon, where overwhelmed medics struggled to cope with multiple victims suffering serious wounds, mainly to their hips, where pagers are generally worn on belts, and to hands and eyes.
On Wednesday afternoon, further blasts were reported across Lebanon, this time reportedly involving hand-held radios, causing at least three further fatalities and a hundred more wounded, according to Lebanese state media.
Israel has neither confirmed nor denied responsibility for the attack. But on Wednesday a US official told AP that Israel had briefed Washington on the attack after it had been carried out and, with no other feasible suspect in the frame, there is little doubt that it was the handiwork of Mossad, Israel’s lethally inventive foreign intelligence agency.
It is also clear that, figuratively and literally, the pager attack was both designed and timed to send a message.
The opportunity to use pagers as an offensive weapon arose in February when Hezbollah leader Hassan Nasrallah publicly warned members to stop using cell phones, which are easily bugged and traced and have been linked with many assassinations executed by missile attacks.
According to a senior Lebanese security source quoted by The Times of Israel, Hezbollah then ordered 5,000 pagers, which were imported into Lebanon earlier this year.
Initial speculation was that Israel had somehow infected the pagers with code designed to cause lithium batteries inside them to overheat and explode. However, it has since emerged that the pagers used only ordinary AAA batteries.
Besides, the near-instantaneous and synchronized detonations, apparently triggered by incoming messages, suggest the pagers had all been fitted with a small amount of explosive and a miniature electronic detonator.

On Tuesday, a senior Lebanese security source told Reuters: “The Mossad injected a board inside of the device that has explosive material that receives a code. It’s very hard to detect it through any means, even with any device or scanner.”
On Wednesday, Gold Apollo, the Taiwanese firm whose brand name was found on the pagers used in the attack, denied involvement, saying the AR-924 models widely identified after the blasts had been made under license by a Budapest-based company, BAC Consulting KFT.
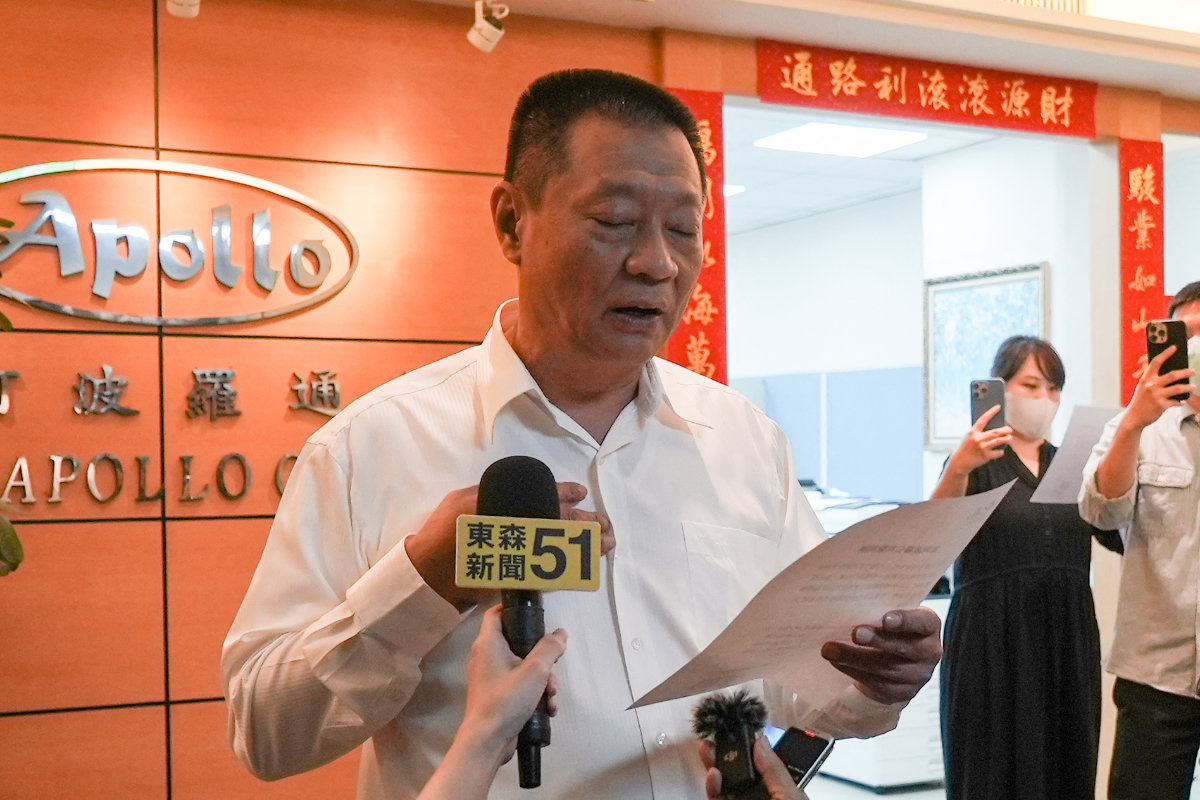

Hsu Ching-kuang, head of Taiwanese company Gold Apollo, speaks to the media outside the company's office in New Taipei City on Sept. 18, 2024, saying his company had nothing to do with the pager explosion attack in Lebanon. (AFP)
In a statement issued at 1:40 p.m. Taiwan time on Wednesday, Gold Apollo said: “This model is produced and sold by BAC. Our company only provides the brand trademark authorization and is not involved in the design or manufacturing of this product.”
Images of BAC’s headquarters — a modest, semi-detached building on Szonyi Street in the north of Budapest — have spread on social media, but BAC has yet to comment. Its website went offline on Wednesday and the profile of its owner and managing director was deleted from LinkedIn.
It is, however, extremely unlikely that any genuine company would knowingly take part in such an operation, risking Hezbollah’s wrath, knowing full well that the devices would be easily traced back to it. This has provoked some speculation that BAC, established only in 2022, might have been a front company operated by Israeli intelligence.
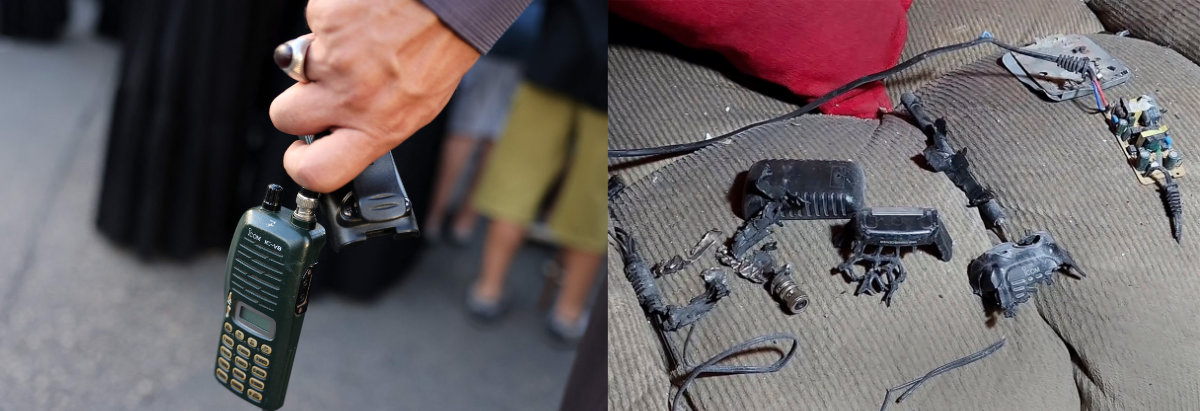

Combo image showing a walkie-talkie (right frame) that was exploded inside a house in Baalbek, east Lebanon, on Sept. 17, 2024, and a man holding a walkie talkie device after he removed the battery following the pager explosions. (AP/AFP)
A more likely scenario is that the batch of pagers ordered by Hezbollah were intercepted en route to Lebanon by Israeli agents — most probably at a port or airport, where typical customs and shipping delays may have given agents, working with local collaborators, enough time to meddle with the devices.
Budapest, the capital of Hungary, is a major transport hub on the River Danube and is home to Csepel Freeport, the country’s principal port.
Wherever the devices were tampered with, “the use of pagers bears the hallmark of Israel weaponizing digital technology to achieve political ends,” Ibrahim Al-Marashi, associate professor in the Department of History at California State University San Marcos, told Arab News.
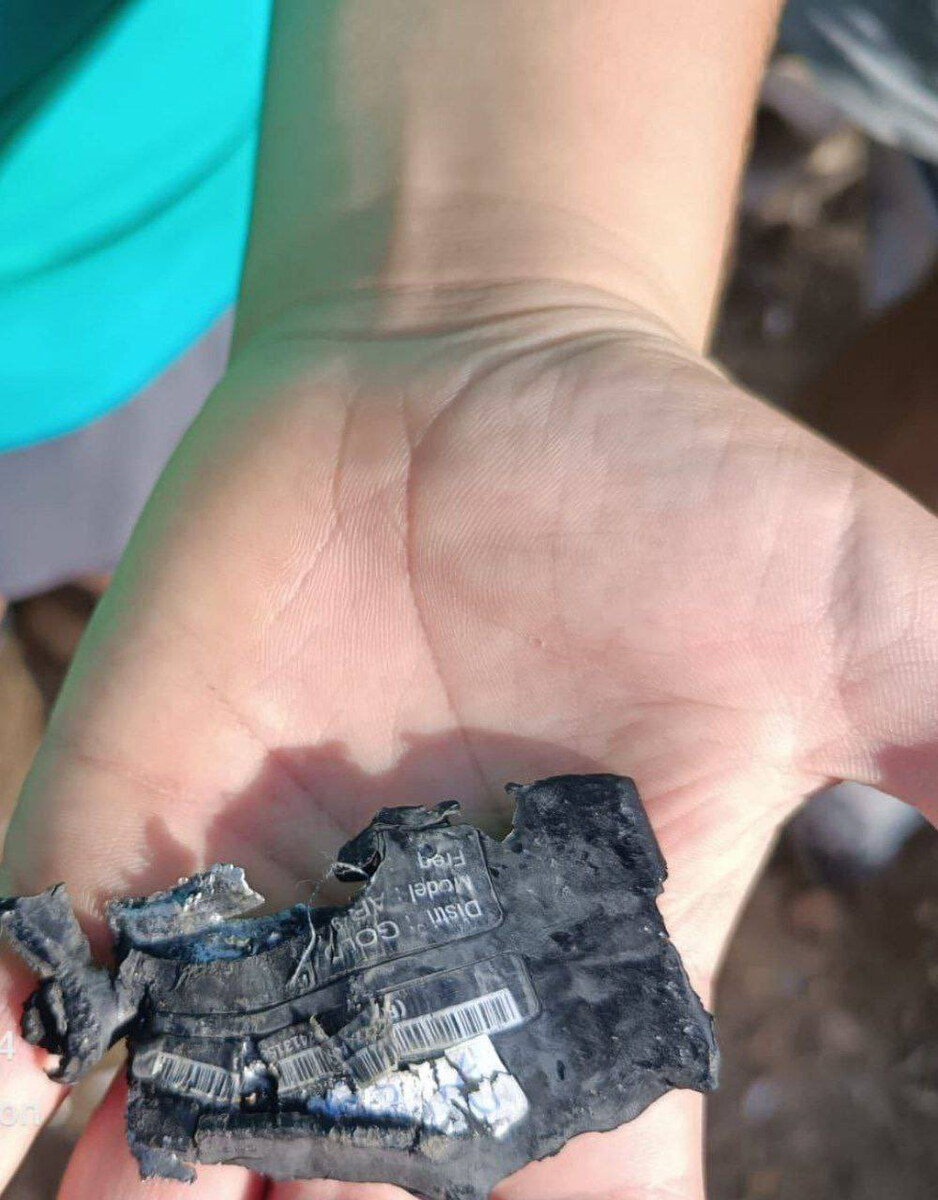

Social media photo showing a pager battery that exploded during an apparent Israeli attack on Sept. 17, 2024 against users of the device in southern Lebanon. (AFP)
Israel has “form” in such warfare. In 2010, “a code known as Stuxnet, snuck into a USB drive, caused Iranian centrifuges to accelerate to the point that they destroyed themselves.”
In 1996, Hamas bombmaker Yahya Ayyash was killed when explosives hidden inside his cell phone were triggered remotely by Israeli agents.
“The advantage of the most recent attack in Lebanon is that it allows Israel to strike from a distance while claiming plausible deniability, avoiding a US rebuke at a time when Washington has pressured Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu not to strike Hezbollah,” said Al-Marashi.
But the pager attack, he warned, could lead to a dangerous escalation.
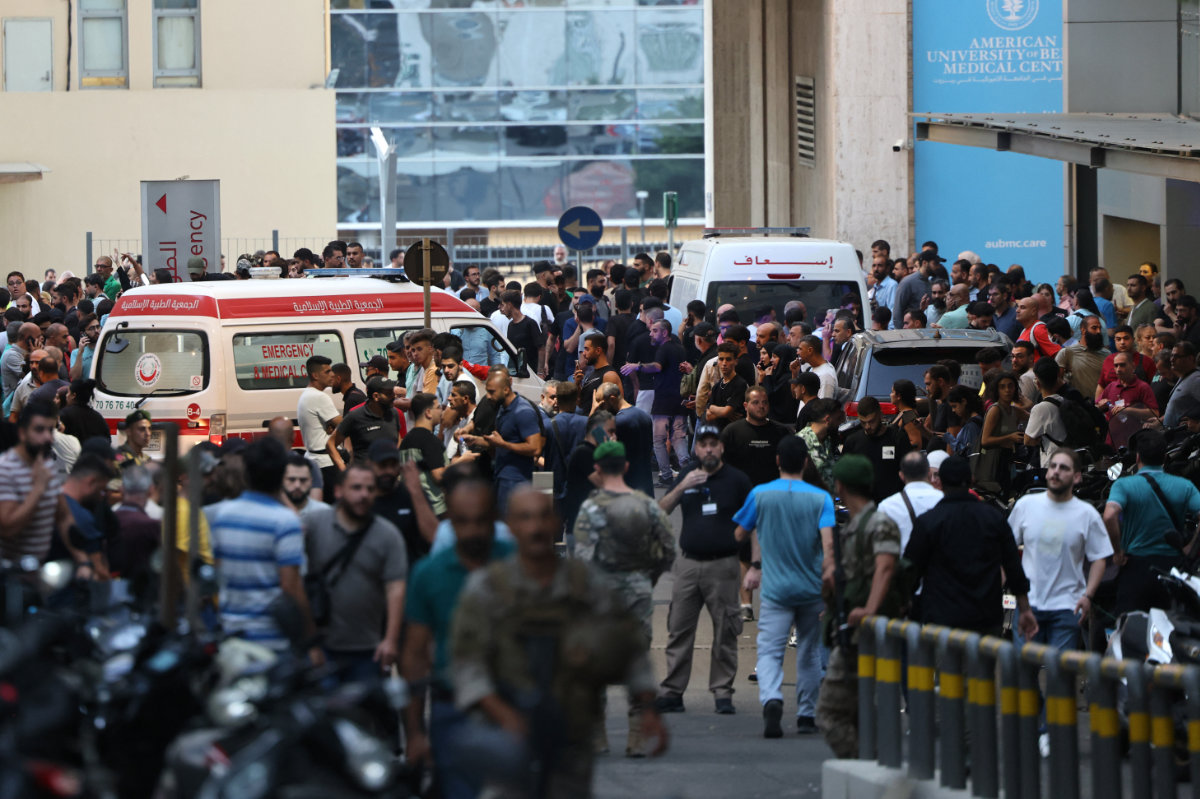

Ambulances are surrounded by people at the entrance of the American University of Beirut Medical Center, on Sept.17, 2024, after explosions hit locations in several Hezbollah strongholds around Lebanon. (AFP)
“Hezbollah does have the ability to weaponize the digital in retaliation, raising the possibility that violent non-state actors might even pursue artificial intelligence to retaliate against their adversaries.”
Given the complexities of the operation, and the sheer workload involved in sabotaging thousands of devices, there is little doubt that the attack would have been weeks, if not months, in the planning.
But it is the timing of the attack that sends the most worrying signal.
The day after Hamas attacked Israel on Oct. 7, its ally Hezbollah began firing missiles into northern Israel — a near-daily bombardment that has increased steadily in intensity, forcing the evacuation of thousands of Israelis from the border region.
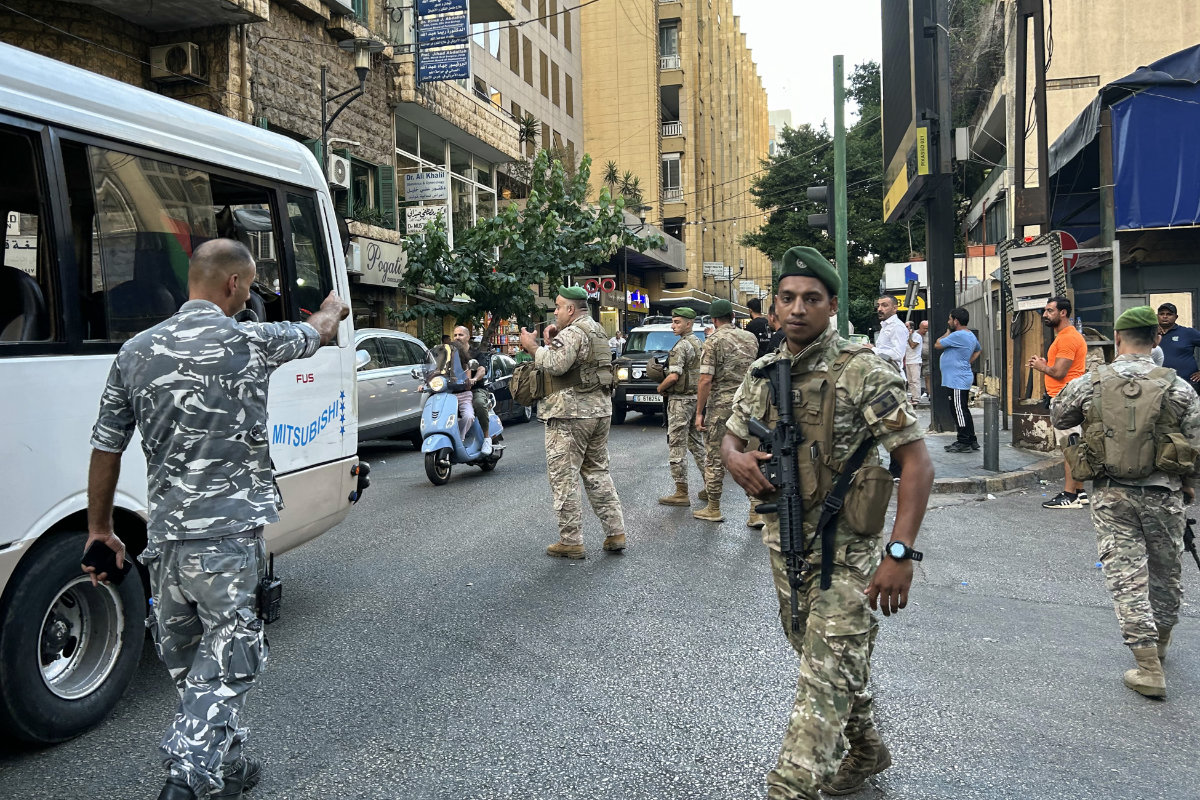

Lebanese army soldiers stand guard in Beirut on September 17, 2024, after an Israeli pager device attack against the Hezbollah in southern Lebanon on September 17. (AFP
After a meeting of its Security Cabinet on Monday night, barely 12 hours before the pagers were detonated, Netanyahu’s office announced that “the Security Cabinet has updated the objectives of the war to include the following: Returning the residents of the north securely to their homes. Israel will continue to act to implement this objective.”
At the same time, reports suggested Netanyahu was on the brink of buckling to the extremist elements in his cabinet by sacking his Defense Minister Yoav Gallant, who has criticized him for having no postwar plan for Gaza, and replacing him with Gideon Saar, leader of the New Hope — The United Right party.
On Wednesday, the day after the pager attack, reports in Israeli and other media, citing anonymous US and Israeli officials, suggested it had been planned originally as “an opening blow in an all-out war against Hezbollah.”
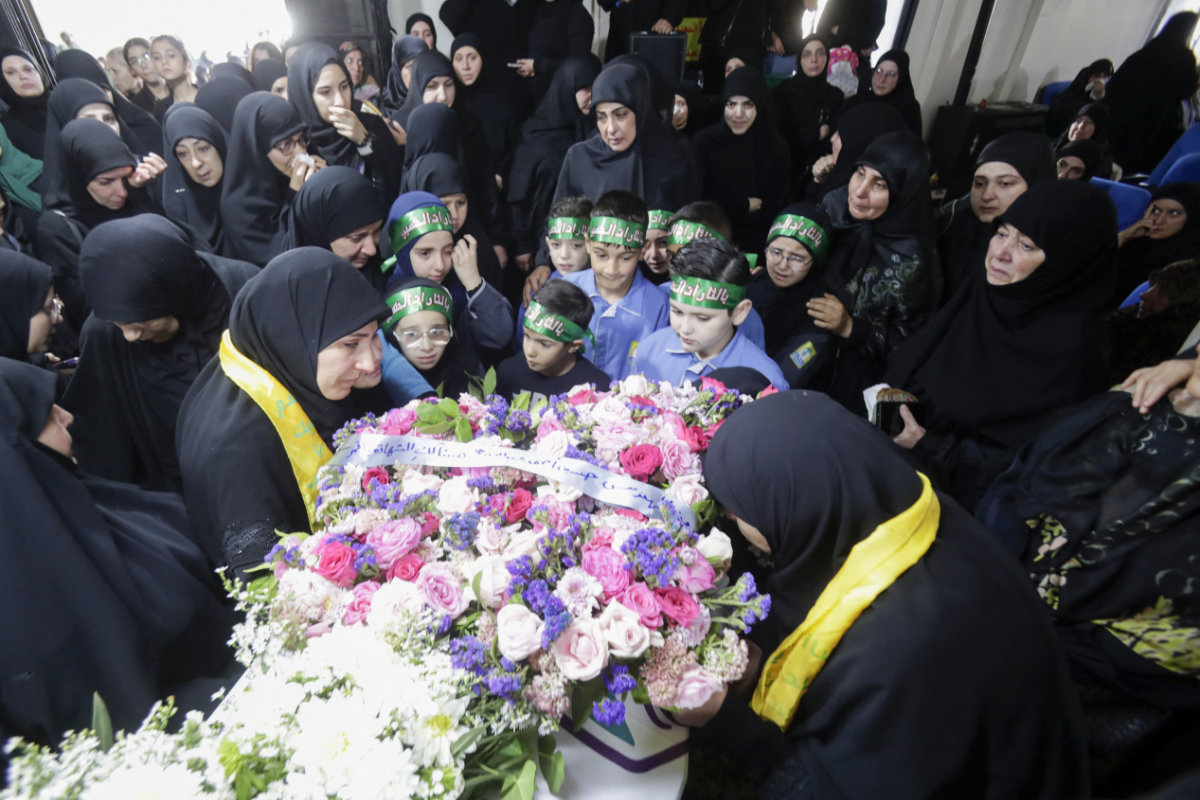

Relatives mourn Fatima Abdallah — a 10-year-old girl killed in Israel's pager device attack — during her funeral in the village of Saraain in the Bekaa valley on September 18, 2024. (AFP)
According to The Times of Israel, a Hezbollah operative “had come to suspect the devices had been tampered with.” He was killed before he could alert his superiors, but the decision was taken to detonate the pagers before the plot was uncovered.
The question now is whether Israel is poised to follow up the pager attack, perhaps as was planned, with an all-out assault against Hezbollah in Lebanon.
“We have been teetering on the brink of a wider war for many months now,” Sanam Vakil, director of the Middle East and North Africa program at the London-based Royal United Services Institute, told Arab News.
“Hezbollah and Iran have made it clear they don’t want this broader conflict to erupt, but Israel cannot end the war in Gaza without addressing the security crisis on its northern borders with Iran, Lebanon and Syria.
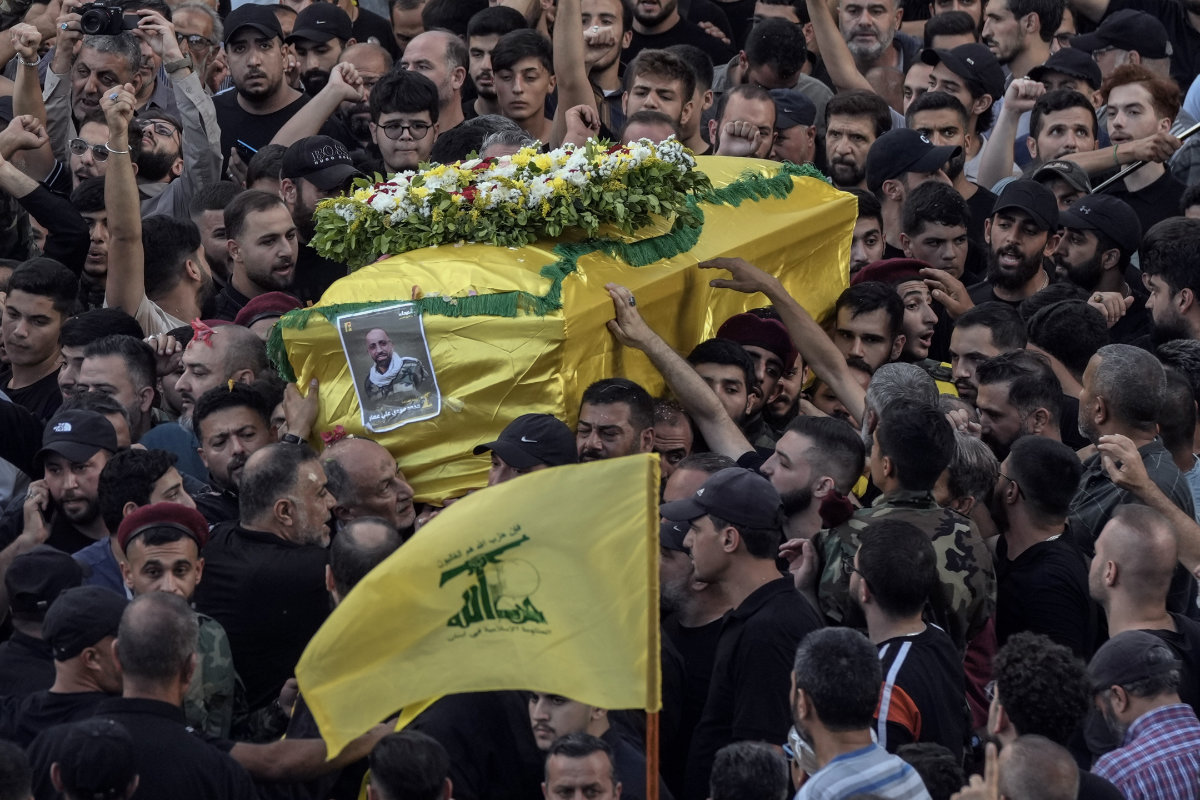

Mourners carry the coffin of Mohammed Mahdi, son of Hezbollah legislator Ali Ammar, who was killed Tuesday after his handheld pager exploded, in the southern suburb of Beirut, Lebanon, on Sept. 18, 2024. (AP)
“In order to address this security imbalance, which puts at risk the safety of the broader population but also that of those displaced since the war began, Israel is trying to target and degrade the ‘Axis of Resistance’ to stave off further threats,” she said, referring to the loose network of Iranian proxies throughout the region.
“But this strategy could certainly push the groups and Iran to respond and eventually draw in regional states and above all the US.”
Most Israelis, said Daniel Seidemann, an Israeli lawyer and founder of the nongovernmental organization Terrestrial Jerusalem, “will tell you that war with Hezbollah is inevitable, but a large percentage say: ‘Not now.’
“The priorities for many are a ceasefire in Gaza, release of the hostages and dialing down the tension in Lebanon. Hezbollah can wait,” he told Arab News.
“Hezbollah, actively backed by Iran, is a much greater threat to Israel than Hamas and the general perception is that there will eventually be a war with Hezbollah, but Israelis know this will be much different than what we have witnessed in the past. It would mean years of war and vast devastation.
“But Netanyahu has a vested interest in the perpetuation of the war, which would be good for Netanyahu but intolerable for Israel.”
What happens next, added Seidemann, “is not only an Israeli decision. Will the US provide the munitions and the rest of the world the legitimization to pursue a protracted war in Lebanon?
“The bottom line is that right now, anything can happen.”
For Al-Marashi, “there are a lot of variables in regard to further escalation that make predictions difficult, more difficult than at any time in analyzing systemic conflicts in the Middle East.
“Despite US sanctions on Iran, news emerged over the weekend that Iran has launched a satellite into space and allegedly has provided ballistic missiles to Russia.
“Second, the Houthis in Yemen have overcome a technical hurdle, launching a ballistic missile against Israel and having it hit Israeli soil, meaning Israel’s system that intercepts such missiles failed.
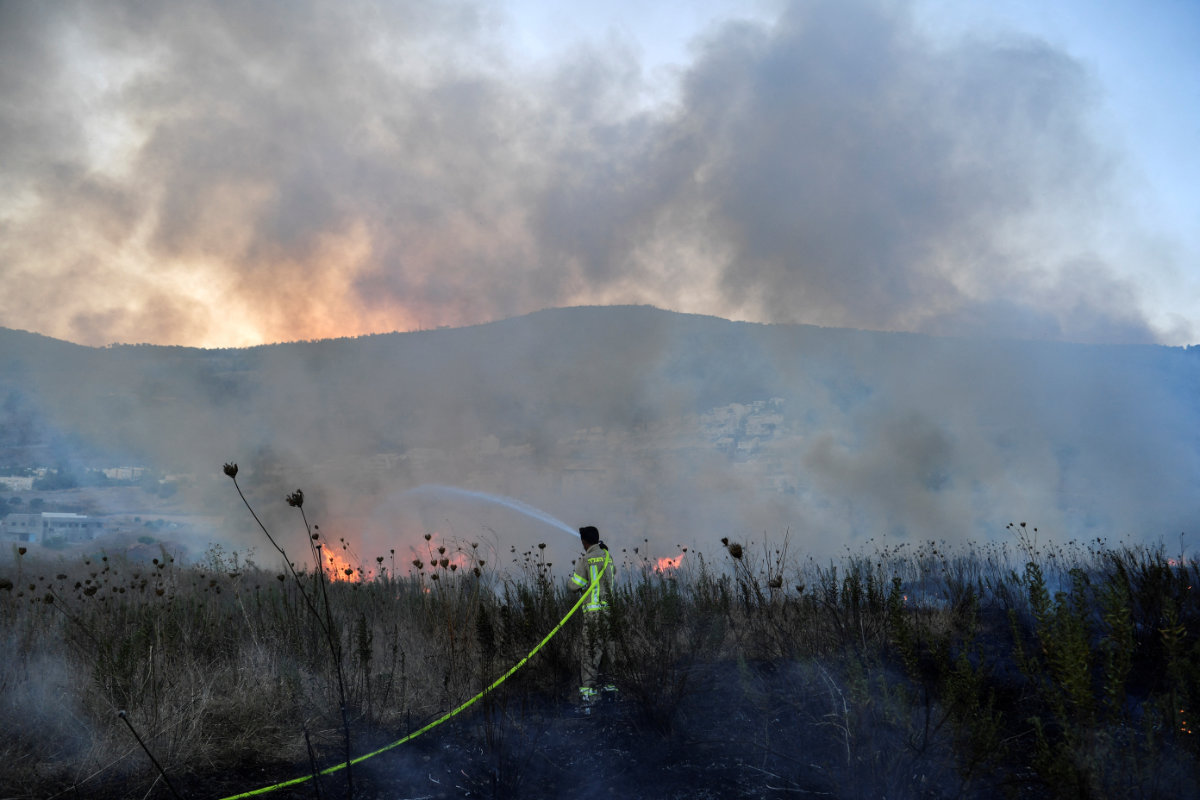

An Israeli firefighter works to put out a blaze after rockets were fired from Lebanon towards Israel, amid cross-border hostilities between Hezbollah and Israel, in Kiryat Shmona, Israel, on Sept. 18, 2024. (REUTERS)
“From that perspective, both Israeli adversaries have demonstrated they can overcome technical hurdles, signaling to Israel that it is not invulnerable.”
Were a regional war to escalate, he added, “it would put US positions in Bahrain and Iraq in the crosshairs of the Axis of Resistance. Biden, seeking to ensure a Kamala Harris victory in the US election, is most likely going to pressure Israel not to escalate matters prior to the election.
“At the same time, if war in the Middle East helped Donald Trump, that would work to the advantage of Netanyahu, who would prefer a Trump presidency.”
The Middle East, said Brian Katulis, senior fellow for US foreign policy at the Washington-based Middle East Institute, “has been teetering on the edge of a wider escalation for much of this past year, with the risk of nation-states going directly to war with one another growing.”
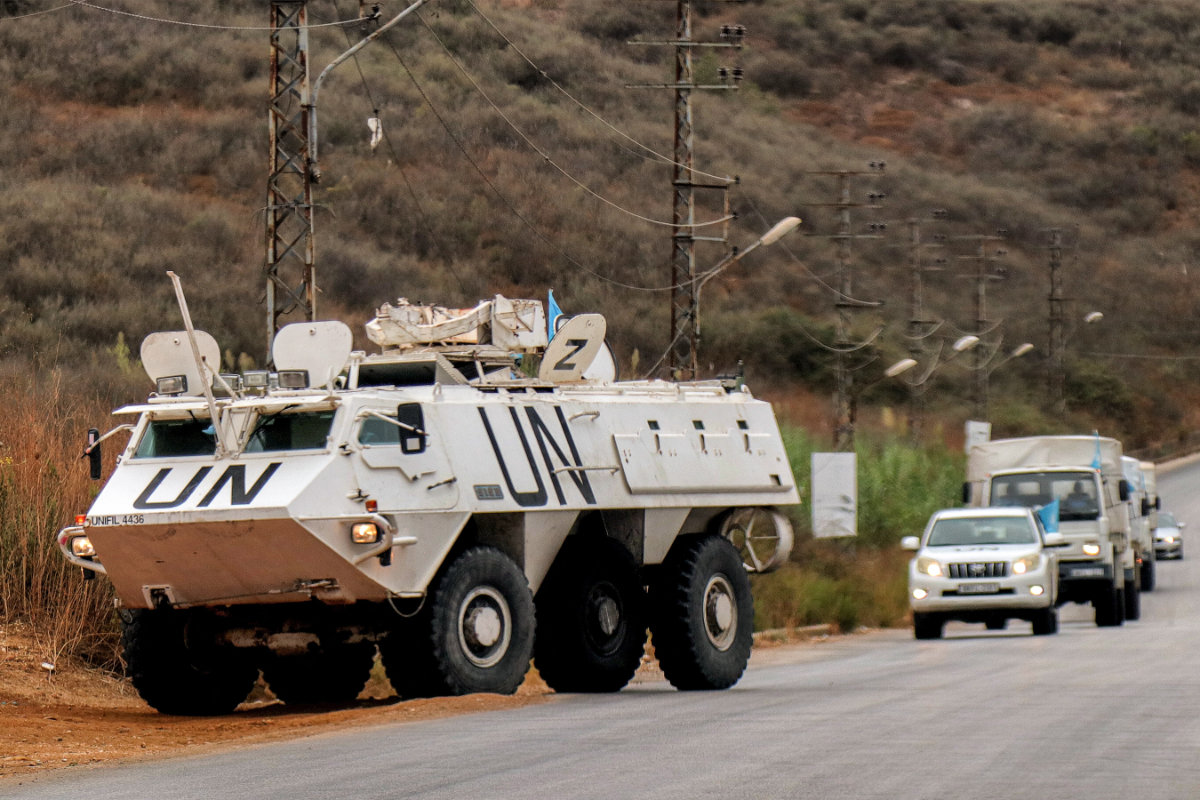

An armored personnel carrier of the United Nations Interim Force in Lebanon (UNIFIL) patrols along al-Khardali road along the Israel-Lebanon border on September 17, 2024. (PhotAFP)
It was, he told Arab News, important to keep in mind the two core drivers of events — “a regime in Iran that operates with a revolutionary ideology that seeks to upend the state order of the Middle East, and an increasingly right-wing Israeli government that rejects a two-state solution and is unable to see the historic opportunity it has in opening relations with key Arab states if it took steps to define a clear end to this war that leads to a State of Palestine.”
In this context, “the US and outside actors such as Europe, China, and Russia can play important roles in trying to shape the trajectory of events in the region, but the main drivers are the regional actors themselves.
“One interesting pivotal grouping is the Arab Gulf states, particularly Saudi Arabia, who do not want to see a wider regional escalation with Iran but do want to advance a two-state solution.”
Right now, however, even as uncertainty remains about Israel’s next move, much depends on how Hezbollah will respond to the extraordinary blow it suffered on Tuesday.
The attack, described by a Hezbollah official as “the targeting of an entire nation,” has been condemned as “an extremely concerning escalation” by Jeanine Hennis-Plasschaert, the UN special coordinator for Lebanon.
In the past year, Hezbollah has suffered the loss of more than 400 fighters, including senior commander Fuad Shukr, to Israeli airstrikes in Lebanon.
But the pager attack represents an embarrassing security breach on such a scale that if it is to save face, Hezbollah’s leadership has almost no choice but to respond with more than the usual daily delivery of a handful of rockets.
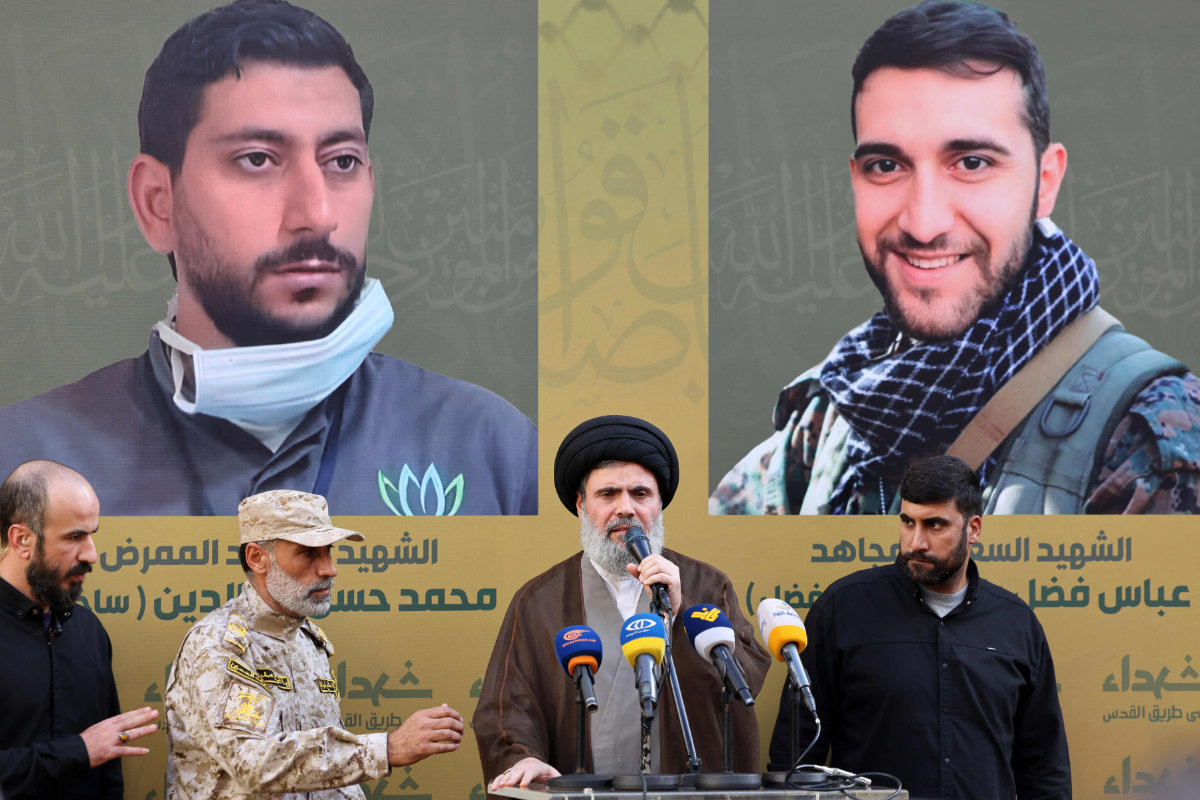

Hashim Safieddine, a Shiite Muslim cleric and the head of Hezbollah's Executive Council, speaks during the funeral of persons killed after hundreds of paging devices exploded in a deadly wave across Lebanon the previous day, in Beirut's southern suburbs on September 18, 2024. (AFP)
After Israel’s multiple airstrikes in southern Lebanon last week and now the pager attack, “we are more on the precipice of a regional war than ever,” Kelly Petillo, program manager for Middle East and North Africa at the European Council on Foreign Relations, told Arab News.
“We will have to see how Hezbollah will retaliate now, and the level of that response will determine where this goes. But these episodes are an indication that things are heating up and we are close to the precipice.”
As for Netanyahu, after almost a year of fighting in Gaza, the fear now is that his answer to growing domestic criticism over the apparent absence of a postwar plan may be an even more nightmarish scenario — more war, only this time in Lebanon.