LONDON: Lebanon’s healthcare system, already crippled by years of economic crisis, has been brought to the brink of collapse since Israel’s unprecedented attack on Hezbollah’s communications network in mid-September and the wave of airstrikes targeting its leaders and weapons caches.
According to some reports, several health facilities have been damaged by Israeli airstrikes. Last month, the World Health Organization said the “escalation of violence” since Sept. 23 had forced at least 37 health centers to close their doors.
Lebanon’s Health Ministry also said dozens of medical workers have been killed, with the WHO reporting 28 deaths in a single 24-hour period last week.
Lebanon was rocked last month by two attacks on Hezbollah’s communications network, which saw pagers and walkie-talkies carried by militia members explode simultaneously.
The devices, reportedly booby-trapped by Israel, exploded in public areas, killing 20 people, including children, and injuring 450 others, according to the Health Ministry, overwhelming hospitals across Lebanon.
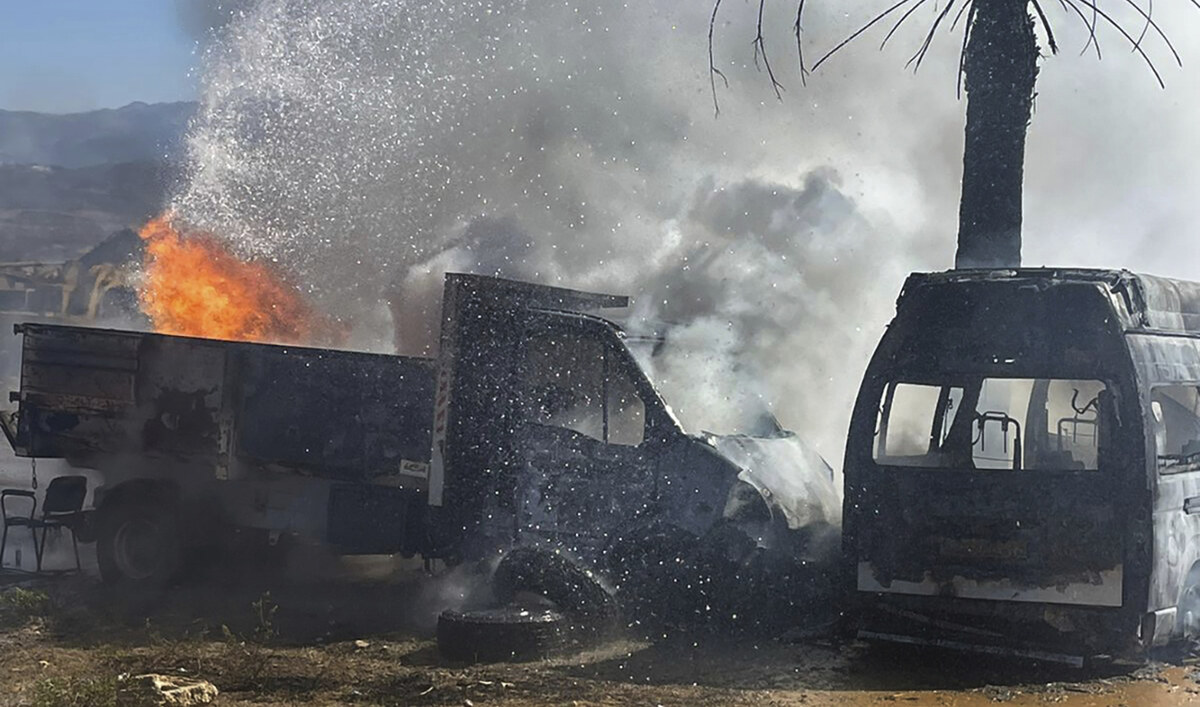

A truck and ambulance burn after Israeli airstrikes hit a group of paramedics outside a hospital in Marjayoun, south Lebanon, Friday, Oct. 4, 2024. (AP)
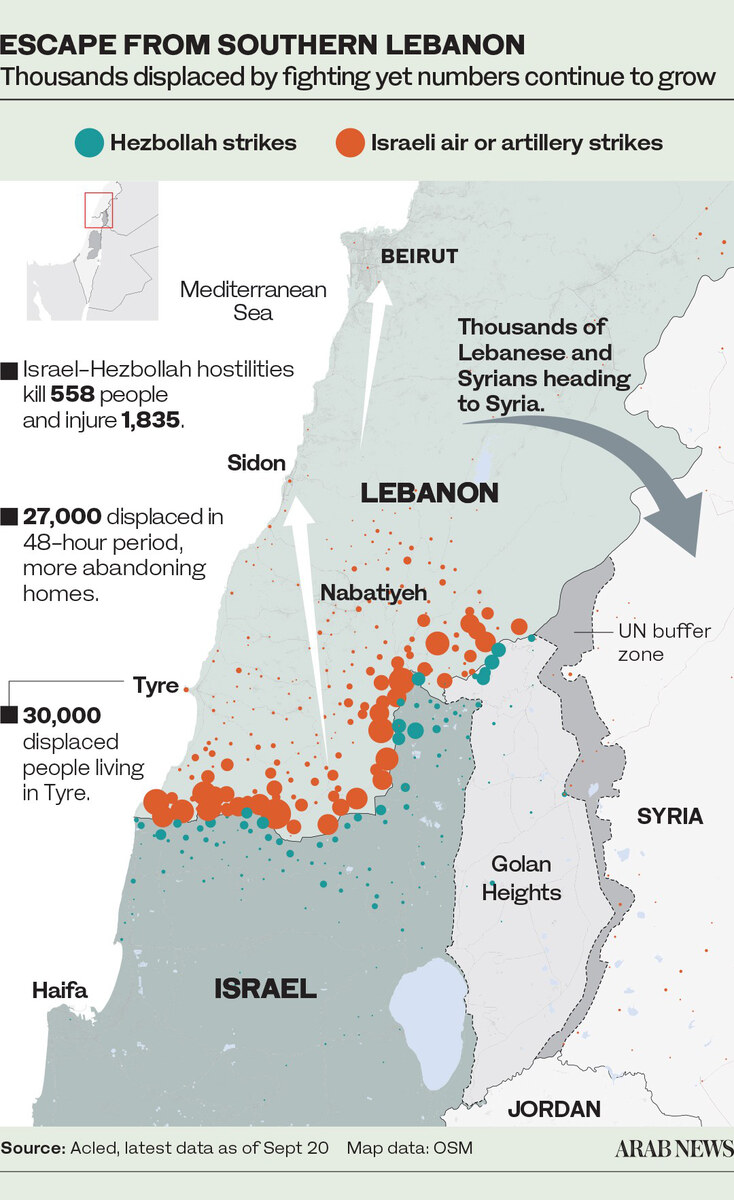
Soon afterward, Israel began pounding Lebanon in its pursuit of Hezbollah, its leadership, and its weapons. The relentless airstrikes have killed at least 1,250 people and injured more than 5,000, according to Lebanon’s Health Ministry.
Israel and Hezbollah began trading fire along the Lebanese border on Oct. 8, a day after the Hamas-led attack on southern Israel that killed 1,200 and saw 250 taken hostage, prompting Israel’s retaliatory operation in Gaza.
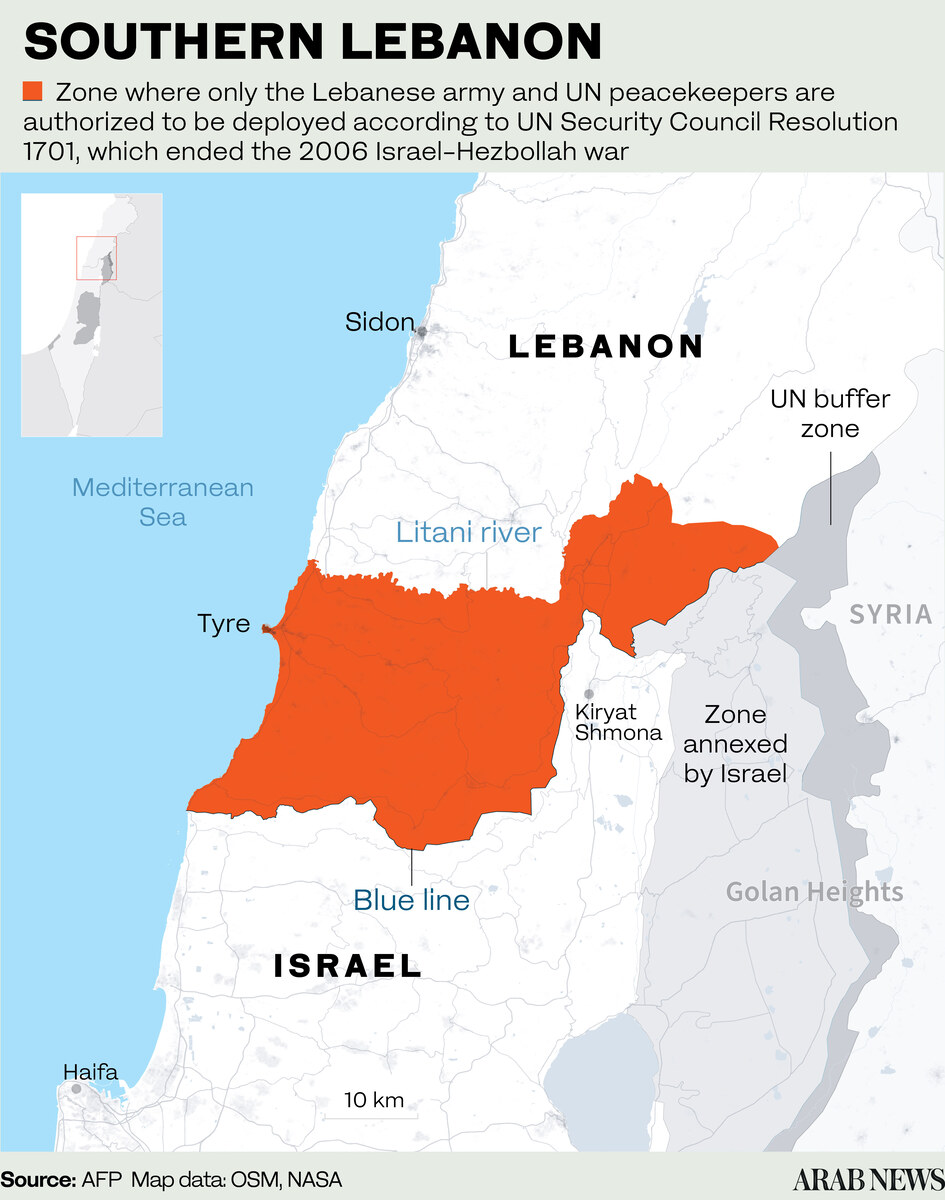
Hezbollah rocket fire has displaced nearly 60,000 people from Israel’s north. The Israeli government says its aim is to push Hezbollah back to the Litani River, about 18 km from the Israeli border, which would allow displaced Israeli civilians to return to their homes.
Over the past two weeks, there have been reports of damage to healthcare facilities in Lebanon. In one such incident earlier this month, an airstrike on Marjayoun Hospital in the south knocked the facility out of service and killed dozens of staff.
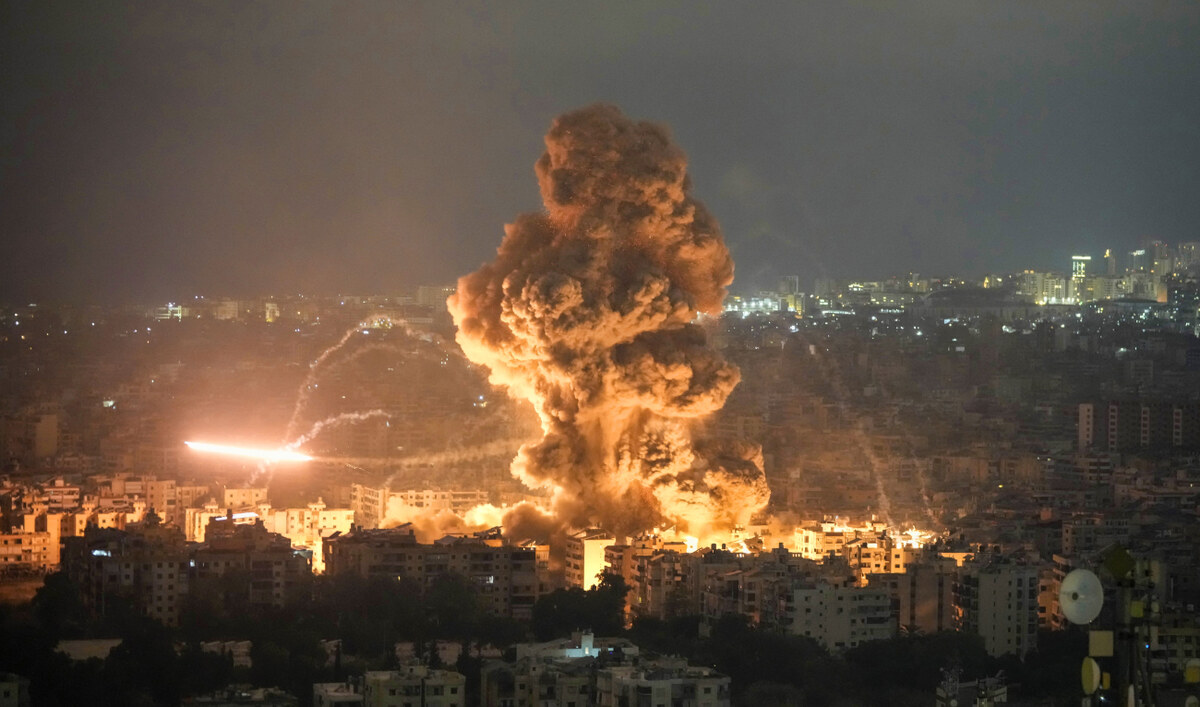

Flames and smoke rise from an Israeli airstrike on Lebanon’s Dahiyeh, Sunday, Oct. 6, 2024. (AP)
Mounes Kalakesh, Marjayoun’s director, told AP news agency that the Israeli military did not warn the government hospital before the strike. Emergency Director Shoshana Mazraani described the facility’s ensuing closure as a “tragedy for the region.”
Israel’s Arabic-language military spokesman, Avichay Adraee, accused Hezbollah of using ambulances to transport weapons and fighters, but he did not provide evidence to support the claim.
Lebanon’s Health Ministry said on Oct. 3 that 40 paramedics, firefighters and health workers had been killed in Israeli attacks over a period of three days.
Last week, the International Lebanese Medical Association appealed to the WHO to pressure Israel to halt what it called a “massacre” of Lebanon’s health workers.
IN NUMBERS
- 37 Lebanese health facilities forced to close owing to Israeli strikes, according to WHO.
- 97 Rescue workers killed since last October, according to Lebanon’s health minister.
Tania Baban, the Lebanon country director of the US-based charity MedGlobal, said the healthcare situation in Lebanon today is almost indescribable.
“The healthcare system is in a very difficult situation,” she told Arab News, stressing that if further hospitals are knocked out of action, the sector may not be able to respond to the mounting number of wounded.
“Even if they don’t get targeted, if there are still going to be attacks that are this intense on the south and in Dahieh (Beirut’s southern suburbs), that’s going to create a strain.”
Lebanon has suffered successive blows since the 2019 financial crisis, which severely impacted the provision of essential public services.
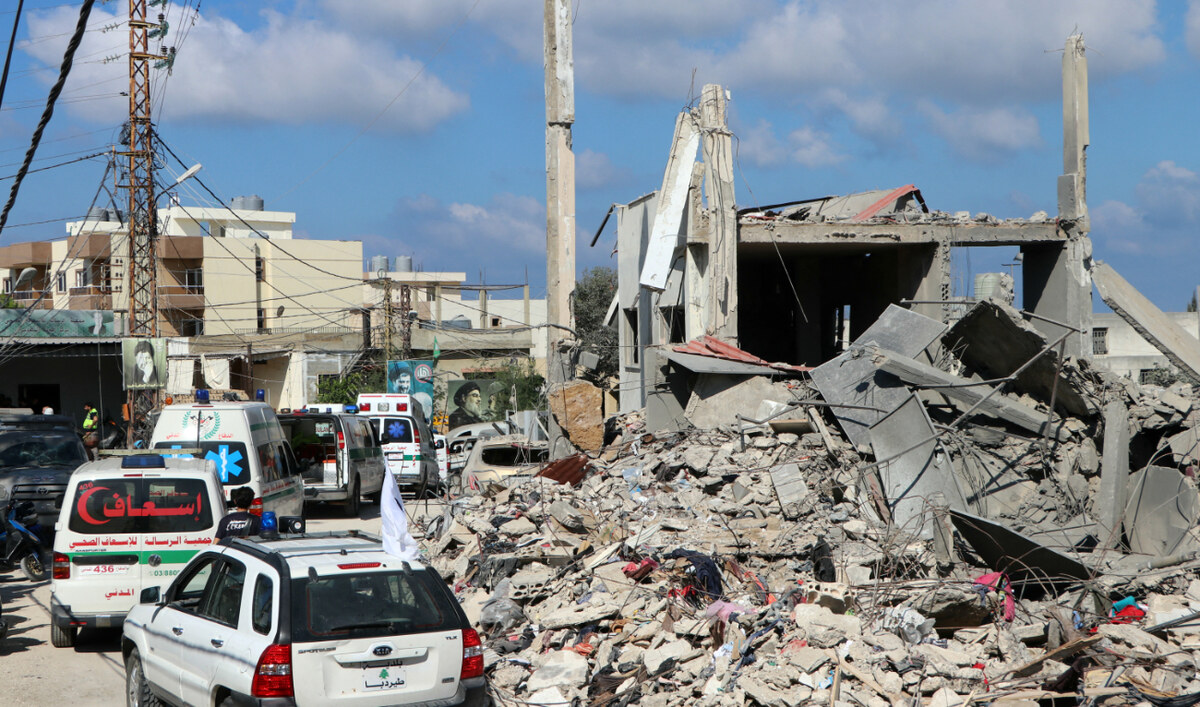

Ambulances carrying the bodies of civil defense workers killed in an Israeli strike drive amid the destruction in the southern Lebanese town of Tayr Dibba, on September 29, 2024. (AFP)
“The economic crisis caused the devaluation of the local currency and inflation, which caused some serious problems in the procurement of medical equipment and supplies as well as medications,” said Baban.
“When the government announced bankruptcy, it wasn’t able to purchase supplies for the hospitals, so the hospitals were not able to cater for the patients,” she added.
The economic situation also impacted livelihoods, leaving many people in Lebanon unable to afford private medical care.
Lebanon has been in the grips of a financial crisis since late 2019, brought on in part by the mountain of debt the government had built up since the end of the civil war in 1990. In April 2022, Deputy Prime Minister Saade Chami declared the state and its central bank bankrupt.
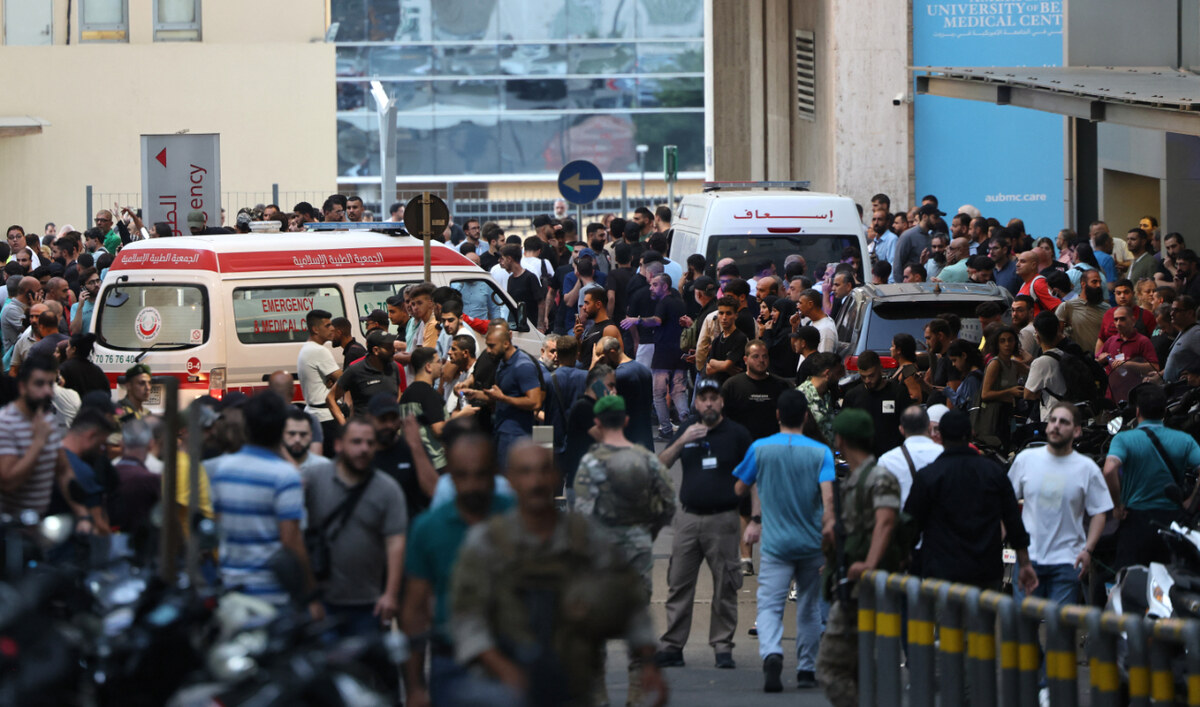

Ambulances are surrounded by people at the entrance of the American University of Beirut Medical Center, on September 17, 2024. (AFP)
The World Bank reclassified Lebanon as a lower-middle-income country, down from upper-middle-income status in July 2022, after the country’s gross domestic product per capita dropped by 36.5 percent between 2019 and 2021.
Aid agencies in Lebanon are also concerned about the welfare of the approximately 1.2 million people who have been displaced by Israeli strikes and incursions in the south, the Bekaa Valley, Beirut’s southern suburbs, and Baalbek.
MedGlobal’s Baban says the scale of displacement in Lebanon has further strained medical services. Inadequate shelter, overcrowding, and the onset of winter heighten the risk of disease outbreaks.
“We’re worried about infectious diseases,” she said. “Flu season is on the way, COVID, the possibility of hepatitis A if they don’t have access to clean drinking water, and the possibility of, God forbid, cholera.”
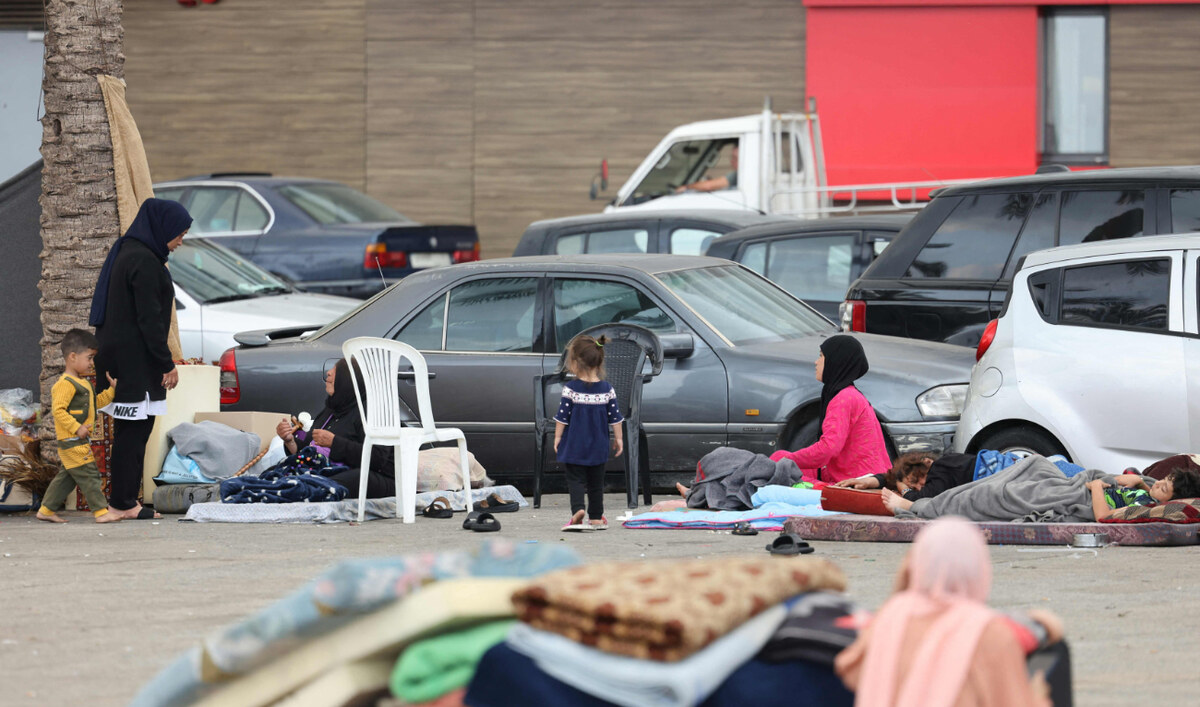

Displaced families take refuge on central Beirut's Ain Al-Mreisseh seaside promenade on October 7, 2024. (AFP)
Giacomo Baldini, the Lebanon country director of the non-profit Relief International, said that while his team is providing hygiene kits and medical outreach in Beirut, Tripoli, and the Bekaa Valley, “the need for clean water, hot food, and medical supplies is huge, and will only increase.”
He wrote in a first-hand account from Beirut shared with Arab News: “We are hoping to provide mental health support as soon as possible. There are simply not enough skilled professionals in Lebanon to provide the amount of support needed.”
Baban said: “The Ministry of Health is doing its best to reach out to stakeholders, including international NGOs such as MedGlobal, to bring in supplies from abroad.”
The ministry’s plan is to bring in additional resources while this is still possible, she said. “He (the health minister) doesn’t want people to procure and purchase supplies locally so as not to deplete the supplies we already have in the country.”
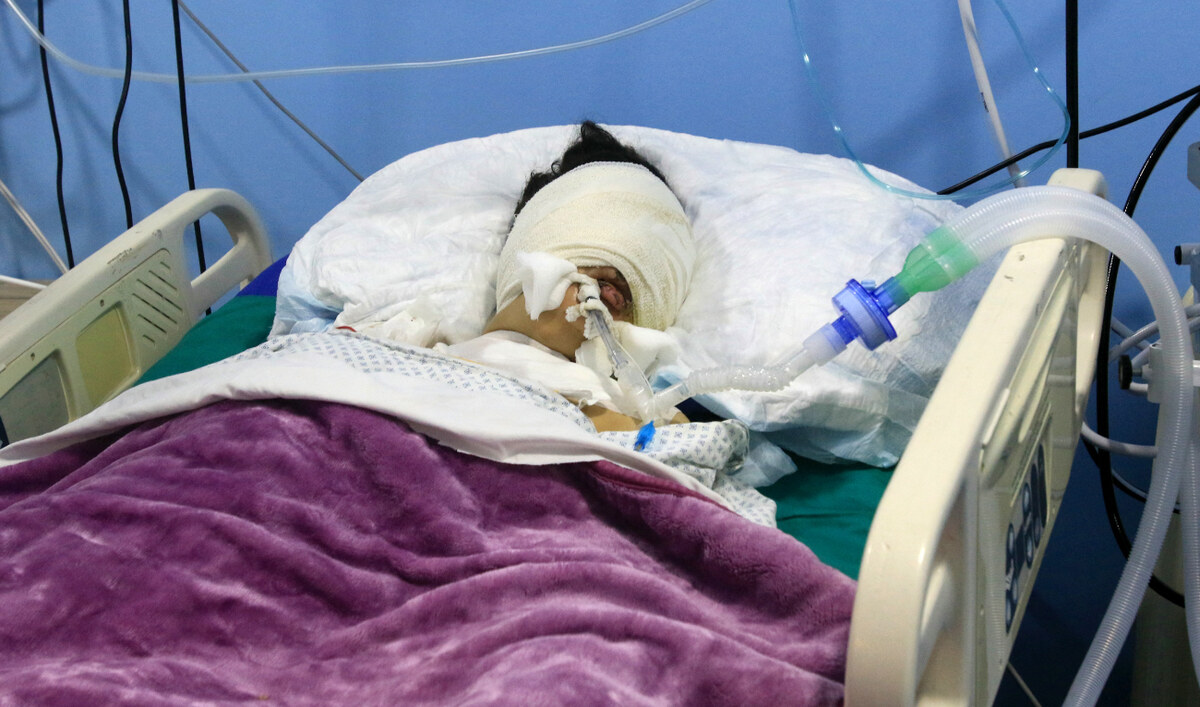
A child wounded during Israeli bombardment rests at a hospital in the southern Lebanese village of Saksaqiyeh on September 26, 2024. (AFP)
However, the intensifying Israeli strikes on southern Beirut, where part of the Beirut Rafic Hariri International Airport is situated, pose a significant risk to the delivery of supplies.
“The health system’s capacity in Lebanon is deteriorating,” WHO chief Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus said in a post on X on Oct. 3. “Medical supplies cannot be delivered due to the almost complete closure of Beirut’s airport.”
He called for the “urgent facilitation of flights to deliver health supplies to Lebanon” as “lives depend on it.”
Baban of MedGlobal said NGOs are struggling to raise sufficient funds to alleviate the pressure on Lebanon’s health system amid the escalating hostilities and worsening humanitarian crisis.
And while there are donors providing “shipments of medical supplies that can be shipped into the country,” the suspension of flights by many carriers has hindered the process.
Israeli airstrikes on the main border crossing between Syria and Lebanon have also obstructed the movement of supplies and medicines into Lebanon.
On Oct. 4, Israeli airstrikes targeted the Masnaa border crossing, impeding civilians trying to flee and disrupting humanitarian operations, the international monitor Human Rights Watch said in a statement.
One of the biggest challenges Lebanon’s hospitals could soon face is maintaining a consistent power supply. Most still have access to fuel for generators and many have installed solar panels. However, as the colder months approach, they may have more challenges.

A man rides his scooter as he drives on the debris of destroyed buildings that were hit by Israeli airstrikes in Dahiyeh, Beirut, Lebanon, Sunday, Oct. 6, 2024. (AP)
“So far, we’re okay with fuel, but if that changes or the prices go up, then it might create a problem because in winter, you can’t depend on solar panels,” said Baban. “If fuel prices go up, it will be expensive to purchase fuel to keep hospitals running.”
The people working tirelessly to keep hospitals operational are also at risk of exhaustion.
Baban warned that while many doctors remain in the country, “they’re obviously already on the brink of being overworked after these sharp and rapid escalations.”


























