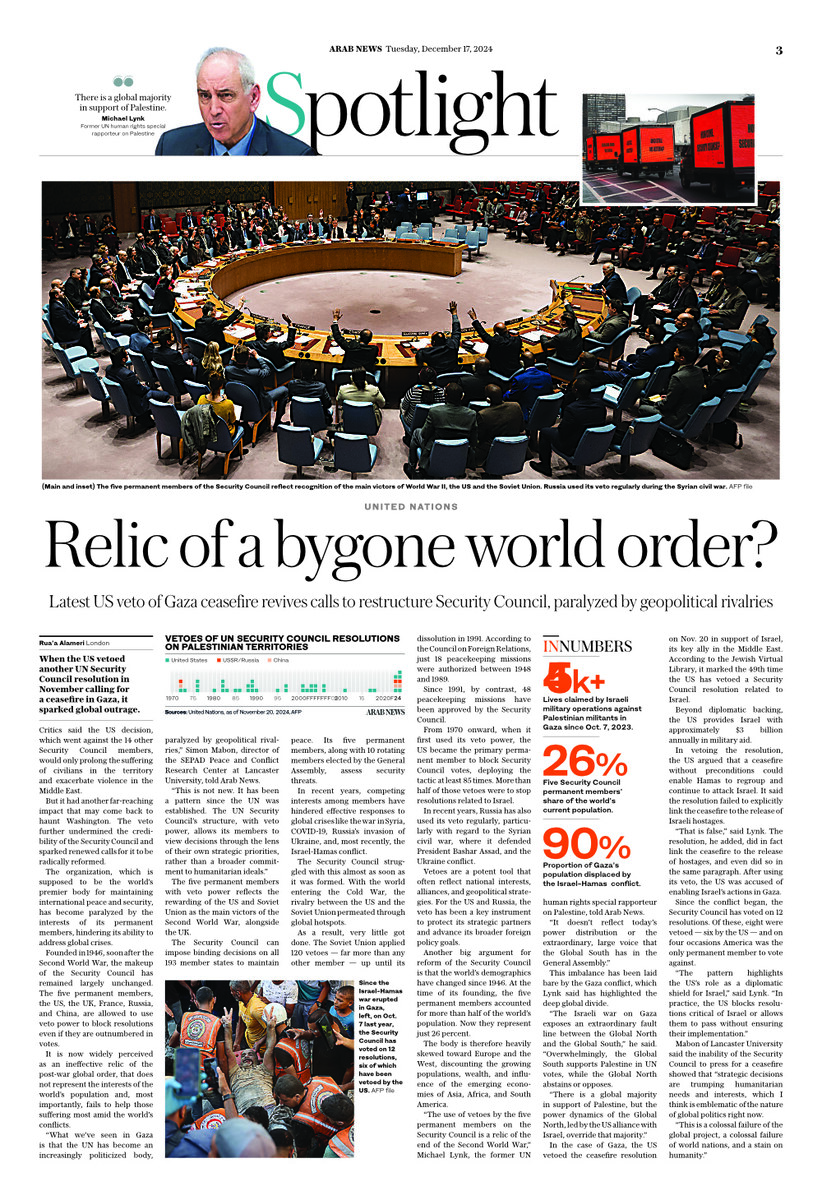
LONDON: When the US vetoed another UN Security Council resolution in November calling for a ceasefire in Gaza, it sparked global outrage.
Critics said the US decision, which went against the 14 other Security Council members, would only prolong the suffering of civilians in the territory and exacerbate violence in the Middle East.
But it had another far-reaching impact that may come back to haunt Washington. The veto further undermined the credibility of the Security Council and sparked renewed calls for it to be restructured.

Inspired by the Oscar-nominated film "Three Billboards Outside Ebbing, Missouri", three billboards circle the United Nations on February 22, 2018 for three hours to demand action on Syria in advance of a Security Council vote in New York. (AFP)
The organization, which is supposed to be the world’s premier body for maintaining international peace and security, has become paralyzed by the interests of its permanent members, hindering its ability to address global crises.
Founded in 1946, soon after the Second World War, the makeup of the Security Council has remained largely unchanged. The five permanent members, the US, the UK, France, Russia, and China, are allowed to use veto power to block resolutions even if they are outnumbered in votes.
It is now widely perceived as an ineffective relic of the post-war global order, that does not represent the interests of the world’s population and, most importantly, fails to help those suffering most amid the world’s conflicts.
INNUMBERS
• 45k+
Lives claimed by Israeli military operations against Palestinian militants in Gaza since Oct. 7, 2023.
• 26%
Share of world’s current population by five permanent members of the UN Security Council.
• 90%
Proportion of Gaza’s population displaced by the Israel-Hamas conflict.
• 8
UNSC resolutions related to Gaza war that have been vetoed by the US.
• 49
UNSC resolutions related to Israel vetoed by the US since 1970.
“What we’ve seen in Gaza is that the UN has become an increasingly politicized body, paralyzed by geopolitical rivalries,” Simon Mabon, director of the SEPAD Peace and Conflict Research Center at Lancaster University, told Arab News.

A man runs with the body of a child victim that was rescued from the rubble following Israeli bombardment on the four-storey Muqat family house in the Zarqa neighbourhood in the north of Gaza City on October 26, 2024 amid the ongoing war in the Palestinian territory between Israel and Hamas. (AFP)
“This is not new. It has been a pattern since the UN was established. The UN Security Council’s structure, with veto power, allows its members to view decisions through the lens of their own strategic priorities, rather than a broader commitment to humanitarian ideals.”
The five permanent members with veto power reflect the recognition of the US and Soviet Union as the main victors of the Second World War, alongside the UK.
“The US pushed for China’s inclusion, while the UK advocated for France to create a European counterbalance to potential German or Soviet threats,” said Ephrem Kossaify, UN correspondent at Arab News.

Ambassador Robert Wood, Alternate Representative of the U.S. for Special Political Affairs in the UN, raises his hands to veto a draft resolution during a United Nations Security Council meeting on the situation in the Middle East, including the Palestinian question at the UN headquarters on November 20, 2024 in New York City. (AFP)
“However, this structure has remained unchanged since then, leading to mounting calls for Security Council reforms to reflect the realities of today’s world order.”
The Security Council can impose binding decisions on all 193 member states to maintain peace. Its five permanent members, along with 10 rotating members elected by the General Assembly, assess security threats.
In recent years, competing interests among members have hindered effective responses to global crises like the war in Syria, COVID-19, Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, and, most recently, the Israel-Hamas conflict.
The Security Council struggled with this almost as soon as it was formed. With the world entering the Cold War, the rivalry between the US and the Soviet Union permeated through global hotspots.
As a result, very little got done. The Soviet Union applied 120 vetoes — far more than any other member — up until its dissolution in 1991. According to the Council on Foreign Relations, just 18 peacekeeping missions were authorized between 1948 and 1989.
Since 1991, by contrast, 48 peacekeeping missions have been approved by the Security Council.

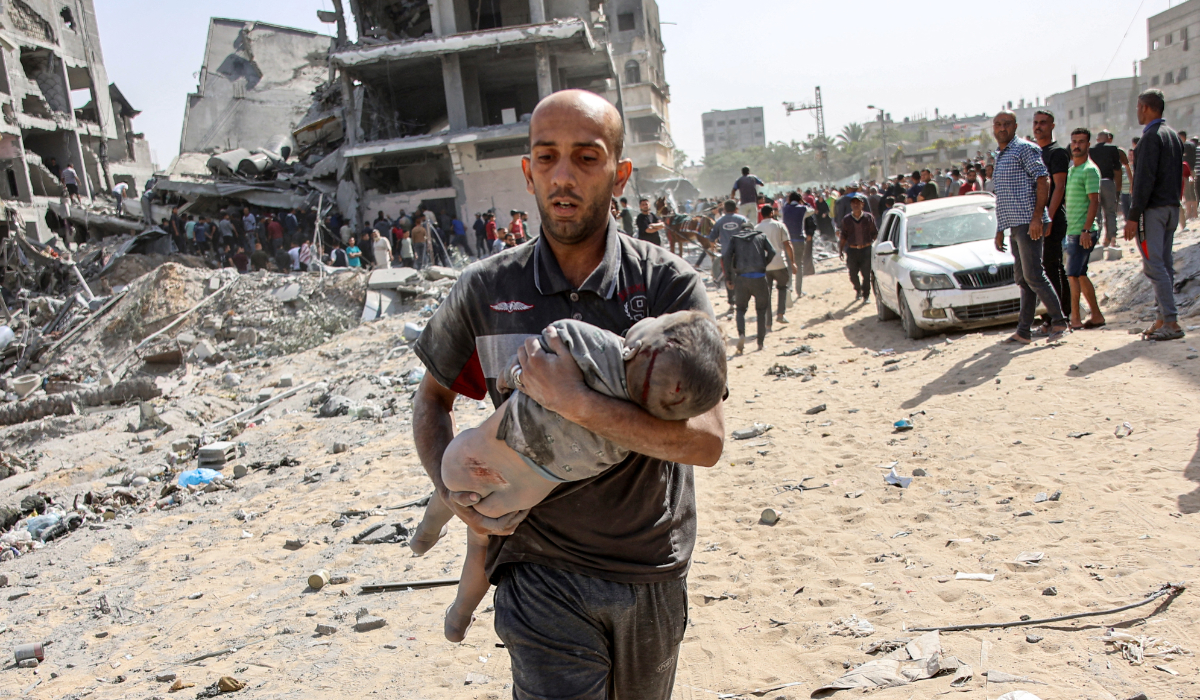
A young Palestinian girl reacts in the courtyard of the al-Shifa hospital in Gaza City after the bodies of victims were transported there, following an Israeli strike that hit a school-turned-shelter in the Al-Shati refugee camp on November 7, 2024, amid the ongoing war between Israel and the Hamas militant group. (AFP)
From 1970 onward, when it first used its veto power, the US became the primary permanent member to block Security Council votes, deploying the tactic at least 85 times. More than half of those vetoes were to stop resolutions related to Israel.
In recent years, Russia has also used its veto regularly, particularly with regard to the Syrian civil war, where it defended President Bashar Assad, and the Ukraine conflict.
Vetoes are a potent tool that often reflect national interests, alliances, and geopolitical strategies. For the US and Russia, the veto has been a key instrument to protect its strategic partners and advance its broader foreign policy goals.

Michael Lynk, Former UN human rights special rapporteur on Palestine
Another big argument for reform of the Security Council is that the world’s demographics have changed since 1946. At the time of its founding, the five permanent members accounted for more than half of the world’s population. Now they represent just 26 percent.
The body is therefore heavily skewed toward Europe and the West, discounting the growing populations, wealth, and influence of the emerging economies of Asia, Africa, and South America.
“The use of vetoes by the five permanent members on the Security Council is a relic of the end of the Second World War,” Michael Lynk, the former UN human rights special rapporteur on Palestine, told Arab News.
There is a global majority in support of Palestine.
Michael Lynk, Former UN human rights special rapporteur on Palestine
“It doesn’t reflect today’s power distribution or the extraordinary, large voice that the Global South has in the General Assembly.”
This imbalance has been laid bare by the Gaza conflict, which Lynk said has highlighted the deep global divide.
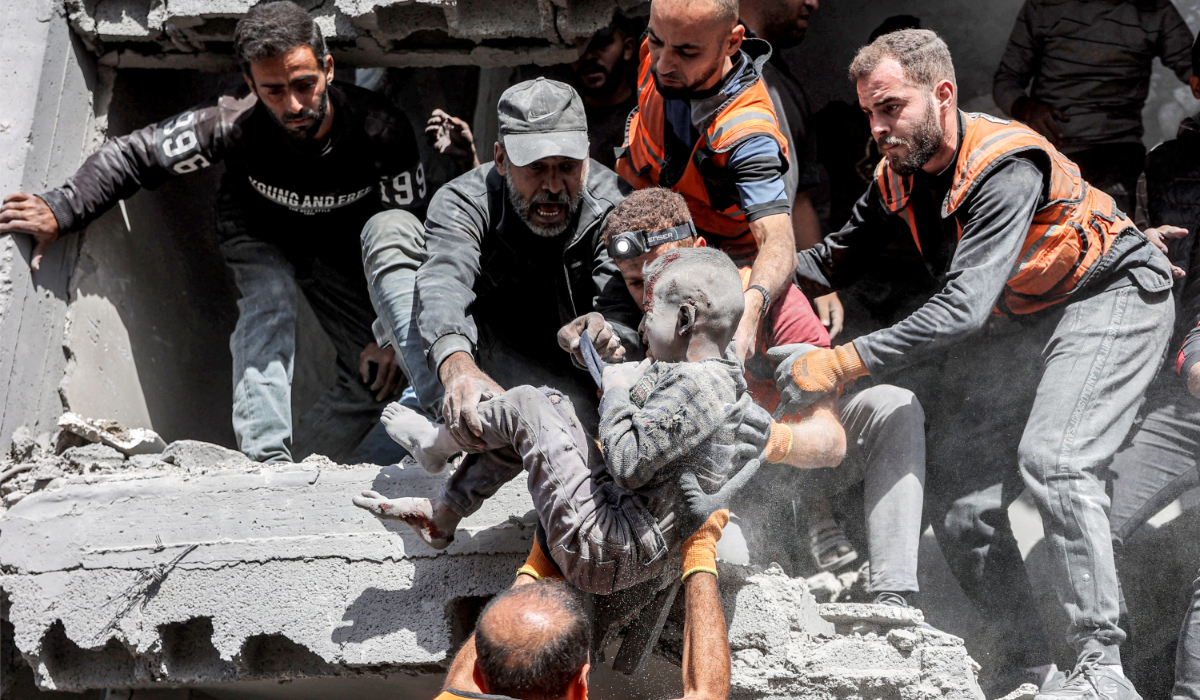

Palestinian civil defence members hand over to each other a child that was rescued following Israeli bombardment on the four-storey Muqat family house in the Zarqa neighbourhood in the north of Gaza City on October 26, 2024 amid the ongoing war in the Palestinian territory between Israel and Hamas. (AFP)
“The Israeli war on Gaza exposes an extraordinary fault line between the Global North and the Global South,” he said. “Overwhelmingly, the Global South supports Palestine in UN votes, while the Global North abstains or opposes.
“There is a global majority in support of Palestine, but the power dynamics of the Global North, led by the US alliance with Israel, override that majority.”
In the case of Gaza, the US vetoed the ceasefire resolution on Nov. 20 in support of Israel, its key ally in the Middle East. According to the Jewish Virtual Library, it marked the 49th time the US has vetoed a Security Council resolution related to Israel.
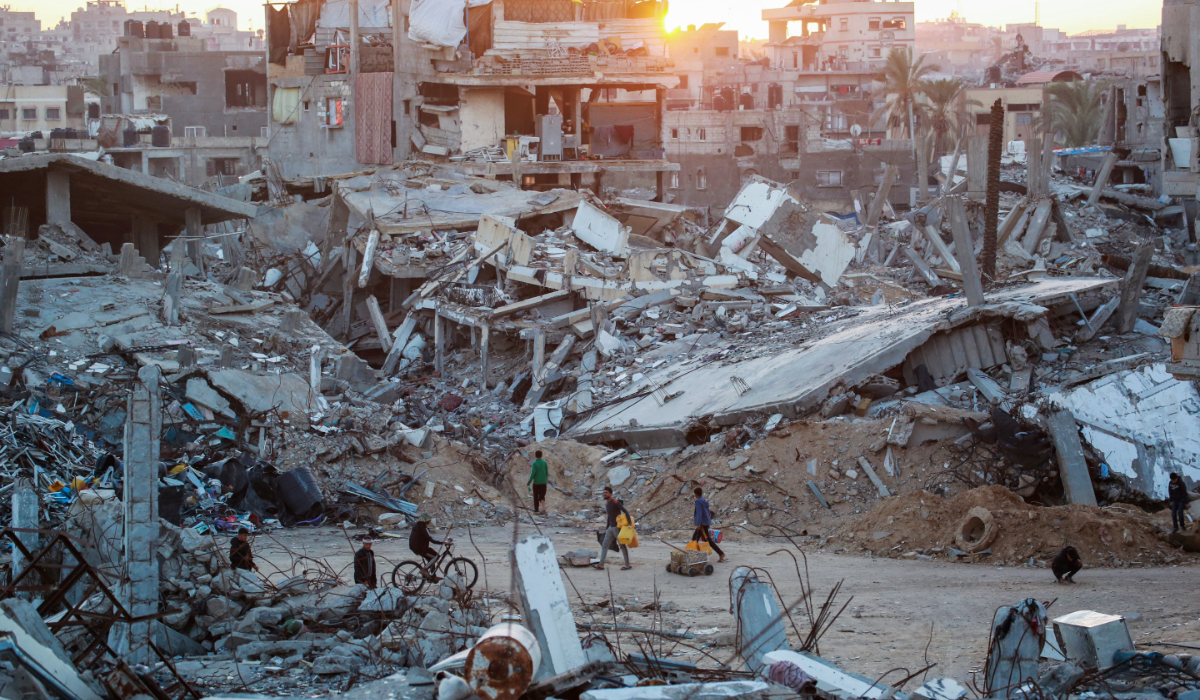

Palestinians walk in a devastated neighbourhood due to Israeli strikes in the southern Gaza Strip city of Khan Yunis on December 2, 2024, amid the ongoing war between Israel and the Palestinian Hamas movement. (AFP)
Beyond diplomatic backing, the US provides Israel with approximately $3 billion annually in military aid.
But the veto risks alienating other key US allies in the Middle East and damaging Washington’s diplomatic standing, particularly with the Gulf Cooperation Council, which recently called for an end to Israeli war crimes in Gaza.
The resolution called for an immediate, permanent ceasefire in Gaza, the unconditional release of all hostages seized during the Hamas-led attack of Oct. 7, 2023, and unrestricted humanitarian aid.
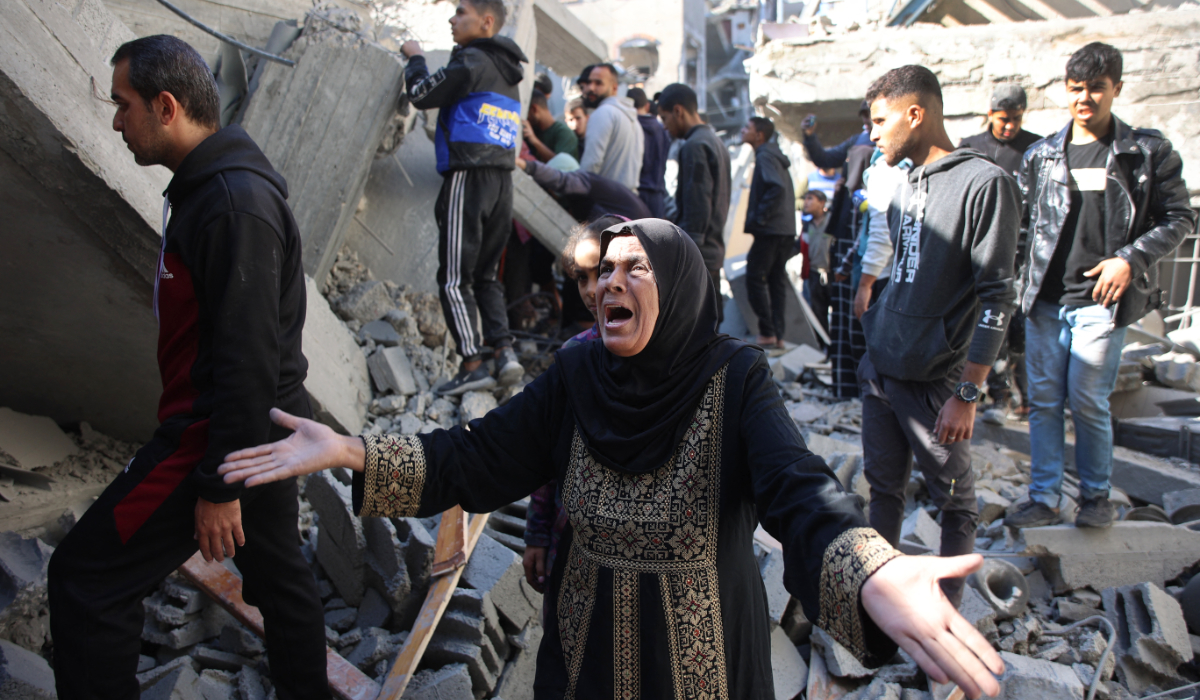

A Palestinian woman reacts as she stands amid the rubble of a building destroyed in an Israeli strike on the Shujaiyah neighbourhood in Gaza City in the northern Gaza Strip on November 30, 2024, during the ongoing war between Israel and the Hamas militant group. (AFP)
It aimed to address the humanitarian crisis by ensuring access to essential services like food, water and medical care. It would have forced Israel to stop restricting aid access to the territory, which has been pulverized by 14 months of military operations that have killed almost 45,000 Palestinians, including combatants.
In vetoing the resolution, the US argued that a ceasefire without preconditions could enable Hamas to regroup and continue to attack Israel. Robert Wood, the US deputy ambassador to the UN, criticized the resolution’s failure to explicitly link the ceasefire to the release of Israeli hostages.
“That is false,” said Lynk. The resolution, he added, did in fact link the ceasefire to the release of hostages, and even did so in the same paragraph. After using its veto, the US was accused of enabling Israel’s actions in Gaza.
Since the conflict began, the Security Council has voted on 12 resolutions. Of these, eight were vetoed — six by the US — and on four occasions America was the only permanent member to vote against.
“The pattern highlights the US’s role as a diplomatic shield for Israel,” said Lynk. “In practice, the US blocks resolutions critical of Israel or allows them to pass without ensuring their implementation.”
In the Gulf, Saudi Arabia and Qatar said the veto showed the need for reform of the Security Council.
The body’s failure to take decisive action on Gaza reflects the broader issues plaguing global governance. Even UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres accepts this assessment.
In September he told Arab News: “We have no real power, let’s be honest. The body of the UN that has some power is the Security Council, and you know, the Security Council is paralyzed.”
Kossaify warned that such paralysis erodes public confidence in the UN.
“When the person in the street sees the Security Council unable to act in the most pressing situations that are threatening peace and security due to one member’s use of the prerogative, they lose faith in the entire organization,” he said.
Mabon of Lancaster University said the inability of the Security Council to press for a ceasefire showed that “strategic decisions are trumping humanitarian needs and interests, which I think is emblematic of the nature of global politics right now.
“This is a colossal failure of the global project, a colossal failure of world nations, and a stain on humanity.”
The international community’s response to Gaza highlights the growing consensus that reforms are needed in multilateral institutions like the UN.
In the years ahead, the effectiveness and legitimacy of the UN will continue to be debated, as the role of major powers in shaping global diplomacy is increasingly scrutinized.
Lynk suggests reforms that would allow the UN General Assembly to override a Security Council veto through a supermajority vote would introduce “democratic oversight to counter the P5’s stranglehold.”
The problem, of course, would be getting the permanent five members to consent to reforms that erode or remove their veto powers. “But reforms like this are worth fighting for,” said Lynk.
What is clear is that in today’s geopolitical landscape, the failure of the Security Council to protect lives in Gaza is likely to hasten moves towards overhauling the body that is meant to maintain international peace.