LONDON: After nearly half a century of Assad family rule in Syria, there is a glimmer of hope for neighboring Lebanon, which for decades endured military occupation, persistent interference in its political affairs, and a legacy of assassinations linked to the regime.
Bashar Assad, who succeeded his father Hafez in 2000, was overthrown on Dec. 8, marking the conclusion of a devastating 13-year civil war. His ousting is likely to have major implications for neighboring countries — few perhaps more so than Lebanon.

The Assad regime’s interest in Lebanon dates back to the period after the 1973 Arab-Israeli war, when it became part of Syria’s strategy to avoid being flanked by Israel through the Bekaa Valley, according to a 2005 paper by Bassel Salloukh of the Lebanese American University.
But Israel was not the only perceived existential threat. The late Hafez Assad, who seized power in 1970, “lived in constant fear of coup and conspiracy,” Syrian historian Sami Moubayed told Arab News. “Lebanon was where many of his worst threats had been based.”
These threats included Yasser Arafat’s Palestinian Liberation Organization, the Palestinian Fatah Movement, the Iraq-backed Fatah Revolutionary Command Council, and Assad’s comrade turned rival, Mohammad Umran, believed to have been killed by Syrian intelligence in 1972.
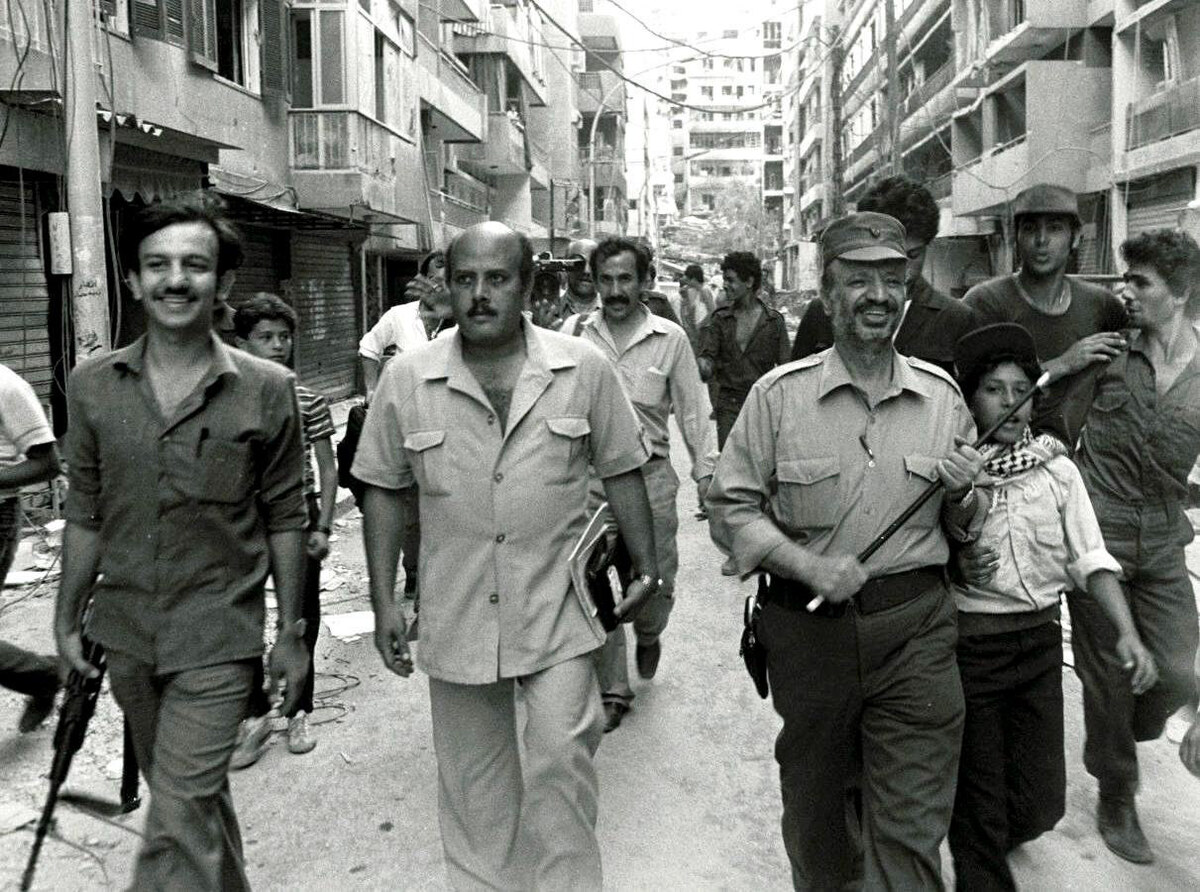

Palestinian leader Yasser Arafat (R) with his supporters in Beirut during the early days of the 1982 Israeli invasion of Lebanon. (AFP)
In addition, Iraqi dictator Saddam Hussein “invested heavily in Lebanon and would go on to support Michel Aoun’s War of Liberation against Syria during the last stage of the civil war,” Moubayed said.
As such, Moubayed said, Hafez “simply could not afford to lose Lebanon.”
“Due to its proximity with Syria and lax borders, anything could be smuggled to and from Lebanon; arms, spies, saboteurs, assassins, and revolutionary ideas,” he said. “If Lebanon fell to any of Assad’s abovementioned enemies, then his regime in Damascus would become endangered.”
Rooted in Assad’s paranoia, the regime’s involvement escalated and became more pronounced with the Syrian army’s intervention in the Lebanese civil war, eventually leading to a 29-year Syrian occupation of Lebanon.
In late spring 1976, a year into Lebanon’s 15-year civil war, Assad deployed troops to rescue the Maronite Christian militias under attack by the PLO and the Lebanese National Movement.
The National Movement coalition, formed in 1969 and dissolved in 1982, included leftist, pan-Arabist and pro-Syria groups. It was led by Druze leader Kamal Jumblatt, whose killing on March 16, 1977, is widely attributed to Assad’s brother Rifaat.
Assad’s alliance with the Maronite militias against the National Movement and the PLO might seem perplexing given the regime’s anti-Israel stance at the time. Indeed, Syria’s actions appeared to align with Israel’s main objectives in its 1982 invasion of Lebanon; destroying the PLO and installing a Maronite-led government.

Syrian President Bashar al-Assad (L) meets with Lebanese Druze leader Walid Jumblatt in Damascus on September 13, 2000. Jumblatt, who had vowed to seek the redeployment of Syria's 35,000 troops in Lebanon, said Lebanon still needed the presence of the Syrian army as a "pressure" tool to "disarm peacefully the Palestinian camps." (AFP)
But Assad’s concerns about, and enmity toward, the National Movement had deep and complex roots, which ultimately led to his brief alliance with the Maronites.
“The National Alliance actually predates the Lebanese civil war, and so does Hafez Assad’s annoyance with it,” Moubayed said. “On paper, however, they ought to have been inseparable allies, given their mutual support for the Palestinians.
“There were many components in the National Alliance that Assad never liked, like Lebanese Baathists backed by Iraq and Kamal Jumblatt’s Progressive Socialist Party.”
Moubayed added: “The Lebanese civil war came at a time when Assad was in the midst of a major standoff with the Iraq Baath, which had a spillover into Lebanon.
“In mid-1975, and while the war was just starting to unfold in Lebanon, Iraq had mobilized its army and threatened to invade Syria (over water rights). Assad suspected that then Vice President Saddam Hussein would use the National Alliance to create trouble for Syria.”
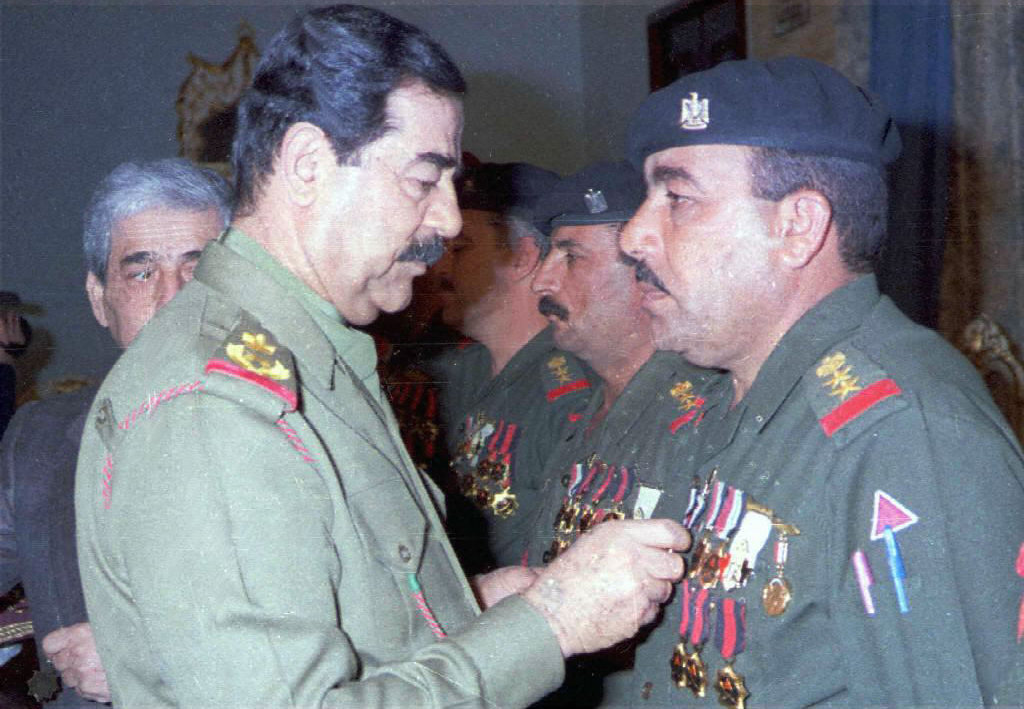

Iraq’s President Saddam Hussein decorates army officers loyal to his regime in this photo taken in 1998. Fear of Saddam trying “to corner him from both Iraq and Lebanon” was said to have helped influence Syrian President Hafez Assad's decision to continue meddling in the affairs of Lebanon. (INA/AFP file)
Moreover, according to Moubayed, the National Alliance’s relationship with Yasser Arafat was “troubling” for Assad, who feared a “Palestinian mini-state in Lebanon” could provoke Israeli intervention and allow Saddam Hussein “to corner him from both Iraq and Lebanon.”
“When Christian leaders came seeking his help to clip the wings of Arafat in Lebanon, Assad saw it as a lifetime opportunity to destroy Abu Ammar (Arafat).”
This may explain why Assad quickly turned against two Christian factions that defied Damascus by demanding its withdrawal and collaborating with Israel against a common Palestinian and Muslim enemy.
In the summer of 1978, Syria launched rockets and artillery at the East Beirut strongholds of two Christian factions, the Phalangists and followers of former President Camille Chamoun, The New York Times reported.

Lebanese right-wing leader and founder of Lebanon's Phalangist Party Pierre Gemayel (L) with with Lebanon's Christian Maronite Kataeb (Phalange) party leader and former Lebanese president Camille Chamoun (R) during a military parade in East Beirut May 25, 1980. (AFP file photo)
A third faction, led by former Lebanese President Suleiman K. Frangieh, broke with the others over their alliance with Israel.
Israel came to its Maronite allies’ rescue, then soon retreated, leaving behind a buffer zone controlled by the Southern Lebanon Army.
Fearing a similar alliance between the Lebanese Forces in Zahle, eastern Lebanon, and local allies that could threaten the Syrian army’s presence in the nearby Bekaa Valley, Assad cracked down on the LF. This led to the Battle of Zahle, which lasted from December 1980 to June 1981.
Israel invaded Lebanon again in 1982, capturing Beirut and forcing Syrian troops to retreat to the Bekaa Valley. The majority of the PLO, including its leader Arafat, were expelled on Aug. 30 that year as part of an international agreement to end the violence.

Israeli soldiers on watch in an armored vehicle in Beirut on July 21, 1982. (AFP)
Meanwhile, Assad, who used the rhetoric of resistance against Israel to strengthen his rule, seized the opportunity to gain control of the Palestinian issue in Lebanon.
For Assad, Moubayed said, controlling Lebanon was “almost as important as controlling Syria itself, and if it came at the expense of the Palestinians, then this was a price he was willing to pay.”
In late 1982, Arafat’s stance was reportedly becoming more moderate toward Israel, and PLO dissidents in Lebanon’s northern city of Tripoli began organizing with Assad’s support.
Within a year, and after Arafat returned to Lebanon, the Battle of Tripoli erupted between pro-Syrian Palestinian militant factions and the PLO. Arafat accused Assad of orchestrating the rebellion against him among PLO forces in Lebanon.
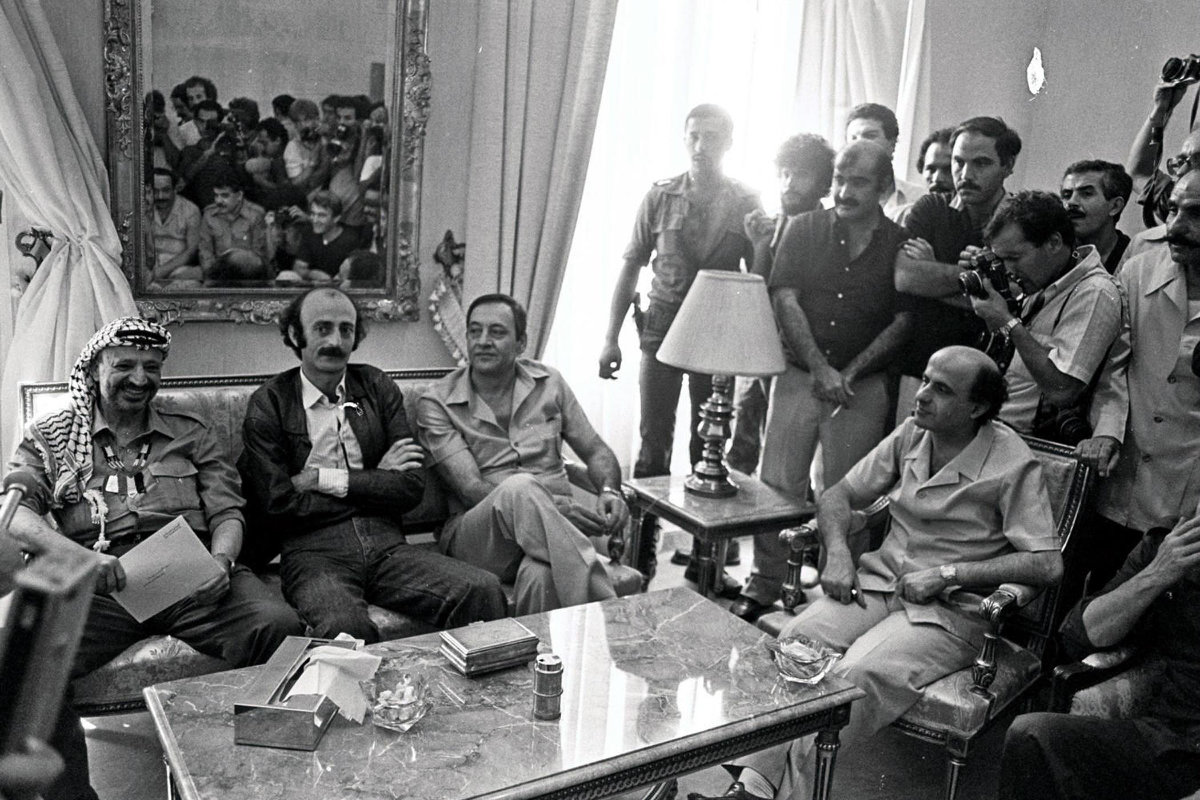

Palestinian leader Yasser Arafat (L), Lebanese Druze leader Walid Jumblatt (2nd L), Shiite Muslim Amal Movement chief Nabih Berri (3rd L) and the head of the Communist Action Organization Mohsen Ibrahim (R) are seen in a picture dated August 30, 1982 during a farewell gathering in Beirut before the Palestinian leader left the Israeli-occupied city to Tunis the same day. (AFP file)
The conflict ended the PLO’s involvement in the Lebanese civil war.
“For Assad, it was as much about controlling the Palestinian issue as it was about controlling Lebanon,” Lebanese economist and political adviser Nadim Shehadi told Arab News. “Control of Lebanon gave Assad leverage over the resolution of the Palestinian-Israeli conflict. He held the cards and controlled the camps.
“After Israel’s withdrawal in 1983 and the departure of the PLO, Syria systematically took control of PLO assets and organizations. Every party (in Lebanon) saw this, even the Kataeb (Phalangist) Party.
“In each institution, pro-Fatah/PLO members were replaced by pro-Syrian ones,” he added, highlighting that this had culminated in the War of the Camps, the War of Brothers, and the takeover of Ras Beirut by the Amal Movement and pro-Syrian factions.
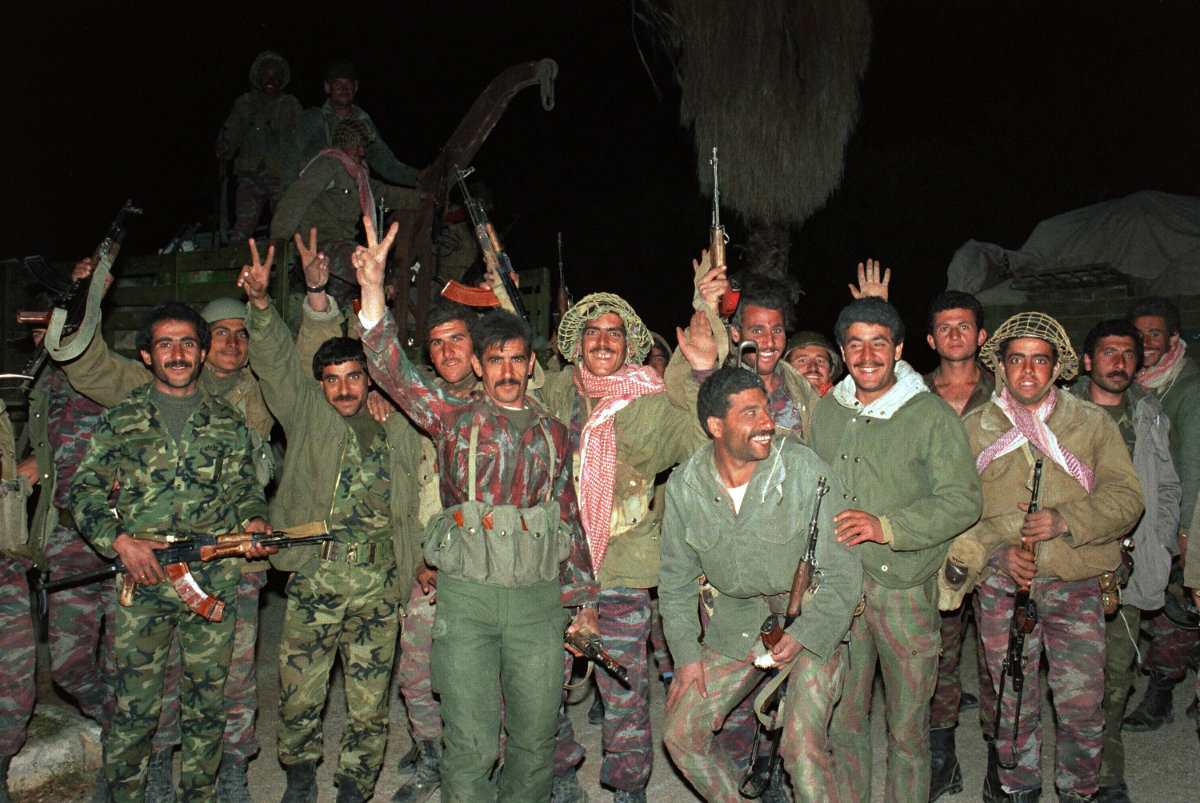

Syrian soldiers and members of the Amal militia, the first political organization of Lebanon's Shi'ite Muslim, celebrate the arrival of Syrian troops in west Beirut February 22, 1987. (AFP file)
Having influence over the resolution of the Palestinian-Israeli conflict means that “Assad would hold the key variables, and no peace process would succeed without his conditions, approval, or the right price being extracted,” Shehadi said.
“It gives him power over the region. This was demonstrated by the privileges he received in Lebanon through the Taif Agreement and the concessions made for Syria’s participation in the Gulf War coalition to expel Saddam from Kuwait.
“In a nutshell, it gives him veto power and blocking power.”
The Taif Accord, negotiated in Saudi Arabia in September 1989 and approved by Lebanon’s Parliament in November 1989, ended the civil war in 1990. While it called for the withdrawal of all foreign troops, it allowed Assad to impose a de facto protectorate over Lebanon and its political life.
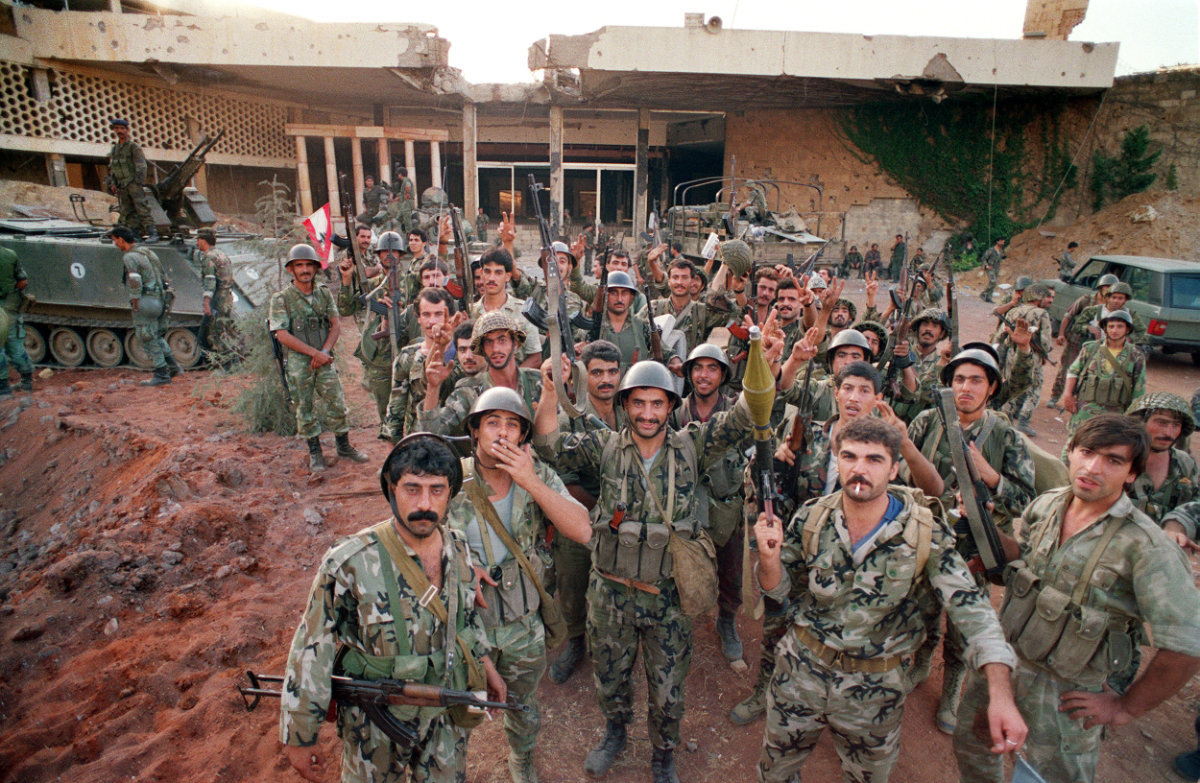

Syrian soldiers celebrate on October 13, 1990, in front of Baabda presidential palace in Beirut, taking over Christian areas formerly controlled by troops loyal to General Michel Aoun, who was forced to lay down his arms before a Lebanese-Syrian military coalition. (AFP)
Between 1991 and 2005, the Assad regime had total control over Lebanon’s domestic and foreign policies. It capitalized on the leeway it was given, skillfully balancing relations between Lebanon’s many sects and factions and playing a key role in fueling many of the tensions that persist today.
The Assads’ involvement in Lebanon was marked by a series of attacks that killed or wounded many anti-Syrian journalists and politicians. In 2005, during Bashar Assad’s reign, the wave of killings intensified. Under international pressure, the last Syrian soldiers withdrew from Lebanon on April 26 that year.
In 2005 alone, at least six anti-Syrian Lebanese figures were assassinated, including former Prime Minister Rafik Hariri, who was killed in a car bombing. His death, along with 21 others, was investigated by a UN-backed tribunal, which found no evidence linking Hezbollah’s leadership or Syria to the attack.

However, the assassination occurred as Hariri and his political allies were debating whether to call for Syria’s withdrawal of forces from Lebanon, the AP news agency reported.
The 2005 attacks on prominent anti-Syria figures also targeted journalists who were vocal in criticizing Assad’s policies in Lebanon, including history professor Samir Kassir; former MP Gebran Tueni, the editor and publisher of Annahar newspaper; and TV anchor May Chidiac, who survived an assassination attempt but lost an arm and a leg.
Throughout their rule, both Hafez and Bashar Assad were notorious for maintaining tight control over the media, a practice that became especially evident during Syria’s civil war, which began in 2011. Although less pronounced, this strategy also extended to Lebanon during their reign.
“Repressive regimes often struggle to accept criticism, as they excel in obstructing the truth and silencing messengers,” Jad Shahrour, the spokesperson for the Samir Kassir Foundation, told Arab News via email from Beirut.
“Under the Assad family’s rule, journalists faced significant repercussions for critical reporting, including detention and torture.”
The atrocities uncovered in Sednaya after Assad’s fall serve as evidence of the fate faced by those who opposed the regime.
“Similar tactics were used in Lebanon during Syria’s military presence from 1976 to 2005, leading to the targeting of journalists like Gebran Tueni and Samir Kassir,” Shahrour said. “Although Syria’s direct control lessened after 2005, it continued to influence Lebanese media through allies.
“This repression shaped a polarized media landscape in both Syria and Lebanon, creating a dangerous environment for journalists and silencing dissent.”
Shahrour added: “The driving force behind the silencing of dissenters is rooted in fear; criminals within the regime are terrified of the truth.
“Their credibility is tightly bound to their hold on power, which, in turn, is maintained through their criminal actions.”
The withdrawal of Syrian troops from Lebanon, nonetheless, did not end Assad’s influence over political life in Lebanon.
Opinion
This section contains relevant reference points, placed in (Opinion field)
In a speech announcing the move, Bashar Assad said: “Syria’s withdrawal from Lebanon does not mean the absence of a Syrian role. This role is governed by many geographic and political and other factors. On the contrary, we (will be) more at liberty and more forthcoming in our dealings with Lebanon.”
Through strategic political and military alliances, including with the Iran-backed Hezbollah and the Amal Movement, and under the guise of resistance against Israel, the Assad regime maintained significant influence over Lebanon’s domestic and foreign policies.
In 2011, Lebanon found itself with a mainly pro-Syrian cabinet. The formation of this government came months after the eruption of anti-regime protests in Syria, making it critical for Assad to secure a friendly cabinet in Beirut.
Although Assad’s demise signals a potential turning point for Lebanon as it approaches a long-awaited conclusion to its presidential election — ongoing since 2022 and potentially concluding on Jan. 9 — decades of Assad interference still loom large over Lebanese politics.
The Syrian regime “cloned itself in Lebanon” by penetrating “every institution and political party, including ministries, the army, the security services and even religious organizations,” Shehadi wrote in a recent op-ed for Arab News.
“Syria also facilitated the creation of Hezbollah, sponsored by its ally Iran, and balanced it out with Prime Minister Rafik Hariri.”
And despite Hezbollah being weakened by its recent war with Israel and the waning of Iran’s regional influence since Assad’s downfall, Shehadi predicts “a crisis over the formation of the Cabinet and the ministerial declaration following the election of a president.”

Lebanon's caretaker Prime Minister Najib Mikati (2nd-L) and Lebanese army commander, General Joseph Aoun (2nd-R), visit the southern Lebanese village of Khiam on December 23, 2024, after the withdrawal of Israeli forces from the area under a ceasefire deal with Hezbollah. (AFP)
He told Arab News: “The main variable here would be whether the Amal Movement can act independently of Hezbollah. I personally doubt it can, or that (Parliament Speaker) Nabih Berri would take the risk.
“The ministerial declaration upon the formation of the new government will have to address Hezbollah’s arms and the army’s prerogatives to take over and prevent rearming in south Lebanon.”
It will also “have to reference (UN Security Council) Resolutions 1559,” which calls for the disbanding and disarmament of all militias in Lebanon. “Hezbollah will try to block this, and it will take a long time to find a suitable language that satisfies all parties.”
Although the Assads are gone, their legacy is likely to linger. “For over 50 years, the Assad regime flourished by creating problems for its neighbors,” Shehadi said. “It will not be missed.”










































