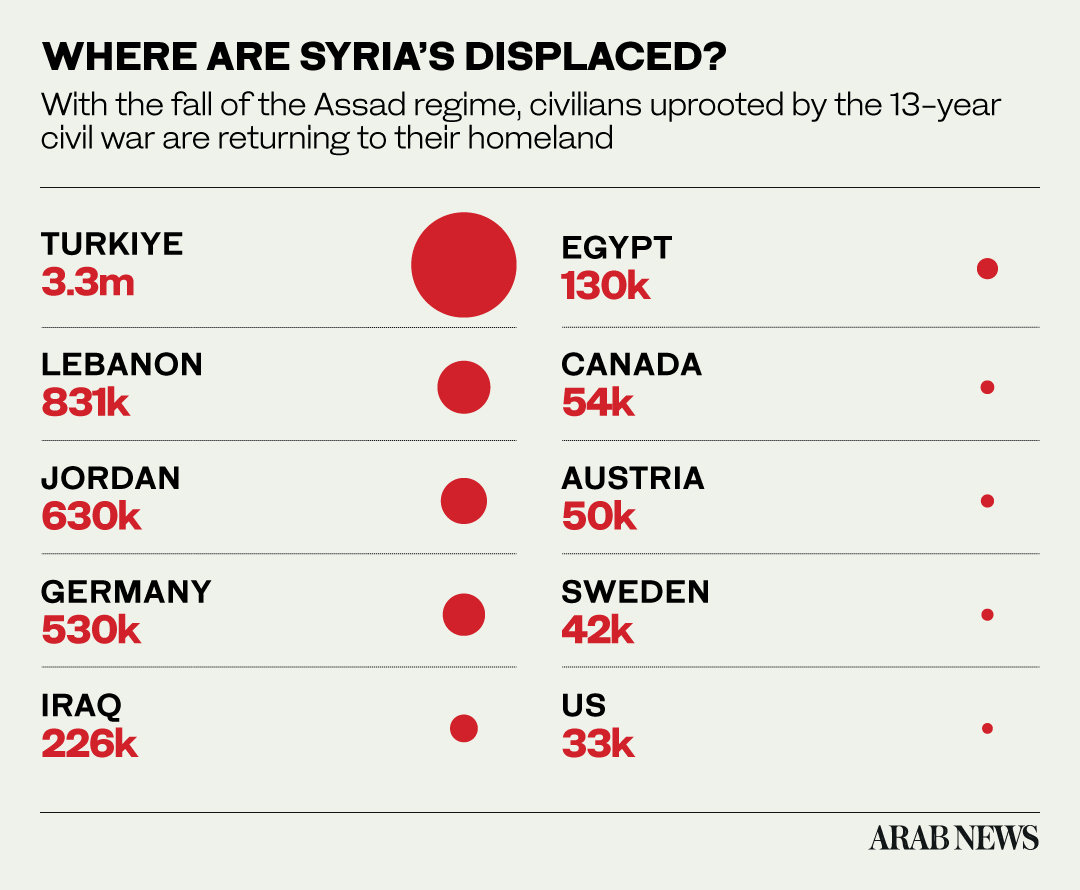
LONDON: Brought to the brink of collapse by more than a decade of civil war, fragmentation, sanctions, and the displacement of countless medical professionals, the Syrian Arab Republic’s health system is on life support.
With the fall of the Bashar Assad regime in December and the rise of a fledgling transitional authority, Syria now faces the daunting task of rebuilding a unified and resilient health sector from amid the ruins.
Data from the World Health Organization shows that just 57 percent of Syria’s hospitals and 37 percent of its primary health centers are fully operational. However, even these suffer severe shortages, leaving millions unable to access basic services.
“Hospitals are outdated, primary health care centers lack essential services, technology is obsolete, and there is no health insurance, funding, or digitization,” Dr. Zaher Sahloul, head of the US-based medical charity MedGlobal, told Arab News.
“The Ministry of Health is tasked with resuscitating the healthcare system with a very limited capacity and a small cadre of health administrators. The whole healthcare system needs to be rebuilt.”
A senior Syrian health official recently told the Iraq-based Shafaq News that interim authorities have devised “a short-term emergency plan spanning three to six months, prioritizing fuel, electricity, and vital medical supplies.
Zuhair Qarat, director of planning and international cooperation at Syria’s Ministry of Health, said the country is experiencing critical shortages of essential medical supplies, fuel, and even food for patients and staff.
To pave the way for recovery, local nongovernmental organizations and international aid groups have launched their own initiatives, like MedGlobal’s “Rebuilding Syria” campaign, to help address these shortages.
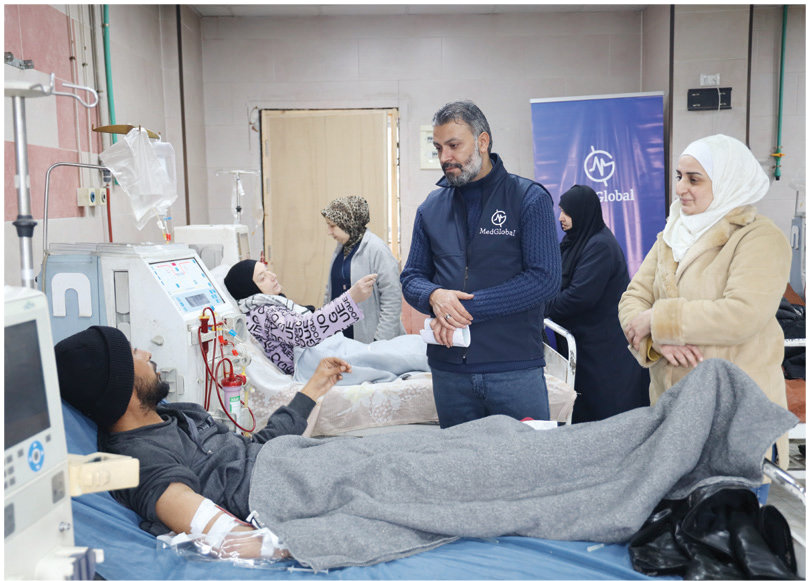
MedGlobal, a US-based medical charity, has launched the “Rebuilding Syria” campaign to help address shortages in health care services. (Photo courtesy of MedGlobal)
Their efforts come as Muslims in Syria observe their first Ramadan since the fall of the regime. Food shortages during the fasting month have only intensified the suffering and highlighted the need for additional aid.
A recent report by the World Food Programme found that more than half of Syria’s population — 12.9 million people — are food insecure, with about 3 million facing acute hunger. Malnutrition, especially in children, weakens the immune system and can lead to a range of health problems.
MedGlobal’s Sahloul said that although Syrian doctors “are very capable, working against all odds,” the average salary for a doctor is just $25 a month — barely enough to cover three days of food and transportation.
“The needs are immense, while the funding is limited, especially with the persistence of sanctions,” he said.
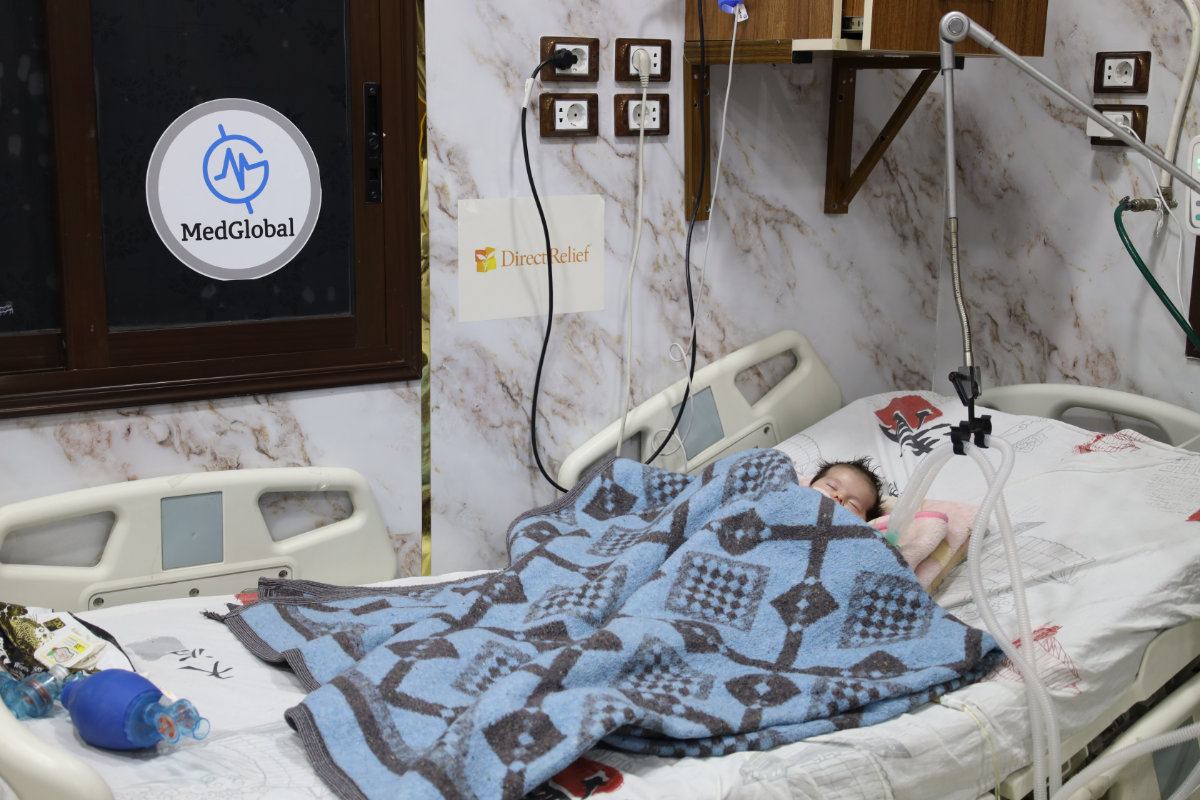
About 3 million Syrians are facing acute hunger, and children are the most vulnerable, according to a recent report by the World Food Programme. (Photo courtesy of MedGlobal)
Coinciding with the Muslim holy month, MedGlobal has launched a special appeal for donations.
“In Ramadan, we are ramping up our fundraising campaign for the many programs we are offering, especially lifesaving dialysis services, medications for poor patients with chronic diseases, and supporting lifesaving heart procedures to patients with cardiac disease in public hospitals,” said Sahloul.
“We also started a new program to provide meals to patients and medical staff in two public hospitals in Homs.”
MedGlobal has been working to address medical supply shortages by ramping up its in-kind donation programs to Syrian hospitals.
“We recently sent a shipment of medical supplies worth $20 million, to be distributed to hospitals in coordination with the Ministry of Health,” said Sahloul.
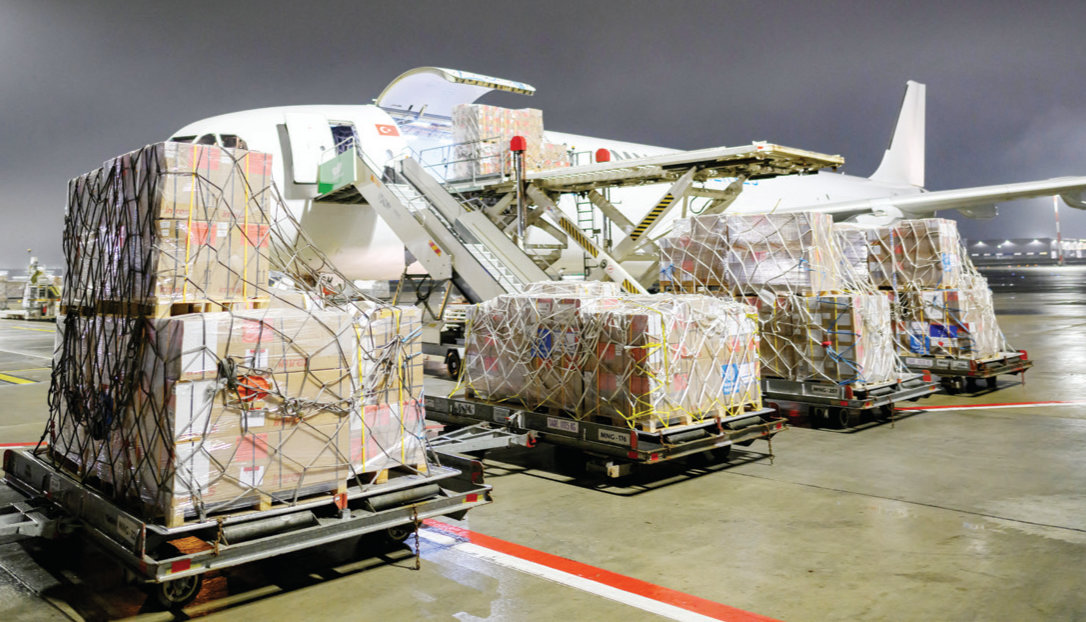

Workers unload medical and health supplies to Syria, delivered by the World Health Organization at the Istanbul International Airport in Turkiye on December 26, 2024. (AFP)
In addition to donations, MedGlobal and its partners are engaging Syrian expatriates in postwar recovery. One key effort is REViVE, launched by Syrian experts in global health, healthcare administration, public health, economics, informatics, and mental health.
Another initiative, the Homs Healthcare Recovery, also known as Taafi Homs, employs 625 Syrian doctors in the diaspora to develop a plan to support public hospitals.
“Through the initiative, we activated the only cardiac catheterization center in Homs at Al-Walid Hospital, launched a mental health program to support victims of torture and freed prisoners, and provided training to recent psychiatry graduates in coordination with the University of Illinois at Chicago,” said Sahloul.
IN NUMBERS
• 14.9 million Syrians in need of healthcare services. * $56.4m
• $56.4 million Funds required to address health needs.
(Source: WHO)
“We also procured critical medical equipment, including an eye echo machine for the city’s only public eye hospital and a neurosurgical microscope for the university hospital. Additionally, we delivered 1,000 life-saving dialysis kits to three hospitals and dialysis centers.
“Similar initiatives have begun in Deir ez-Zor and rural Damascus.”
And while these initiatives are providing Syrians with much-needed health services, Sahloul stressed that the full collaboration of the new health authorities remains key to their success.
Although the fall of the Assad regime has opened a path for the health sector’s recovery, significant challenges remain. These include the absence of a state-led transition strategy, the continued brain drain of health professionals, and US sanctions.
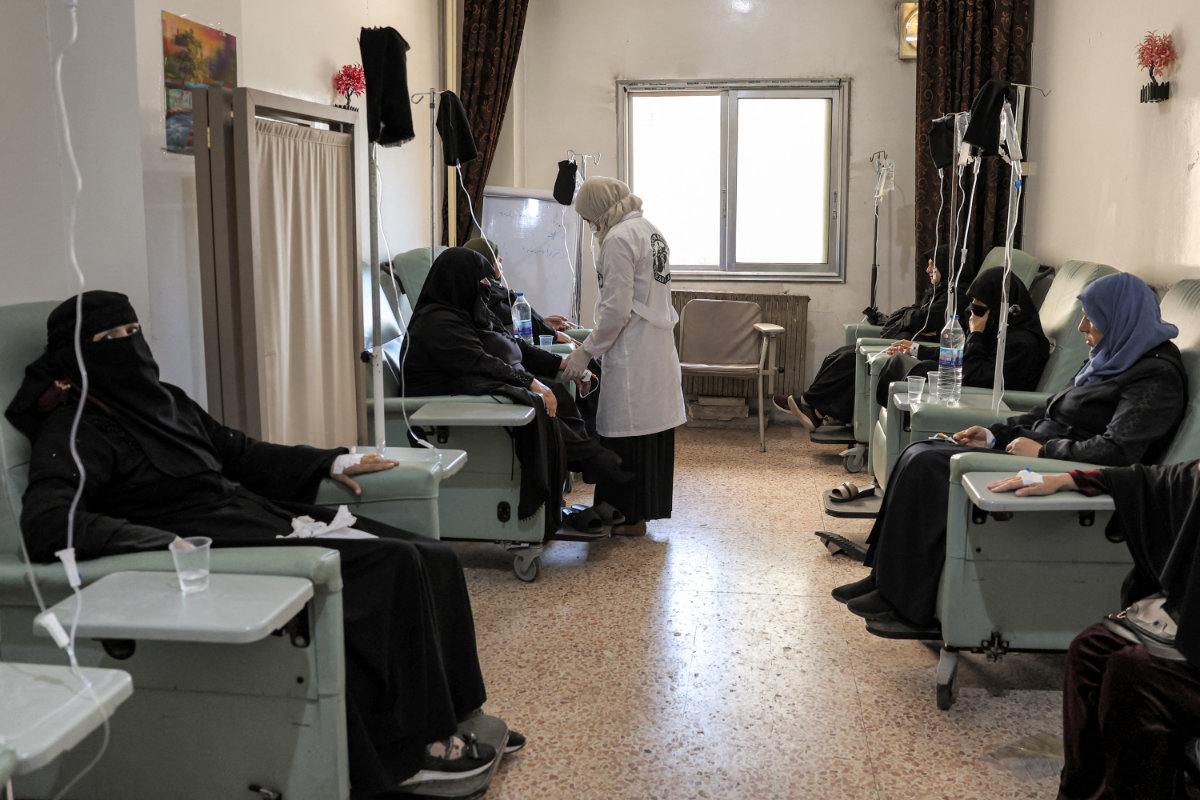

In this picture taken on May 2, 2023, female patients receive treatment at the Hematology and Oncology department run by the Syrian American Medical Society (SAMS) at Idlib Central Hospital in the rebel-held northwestern Syrian city. (AFP/file)
“At this early stage, the focus is only on immediate and urgent needs and stopping the bleeding,” Sahloul said. “This is necessary but is not enough.
“A new strategy must be drafted to address health governance, human resources, health information systems, training, and education. It should place the Ministry of Health and related ministries at the center, supported by local and international NGOs, as well as UN agencies.
“There should be greater coordination and collaboration between the Ministry of Health, NGOs, and UN agencies. This is not happening at present for many reasons.”
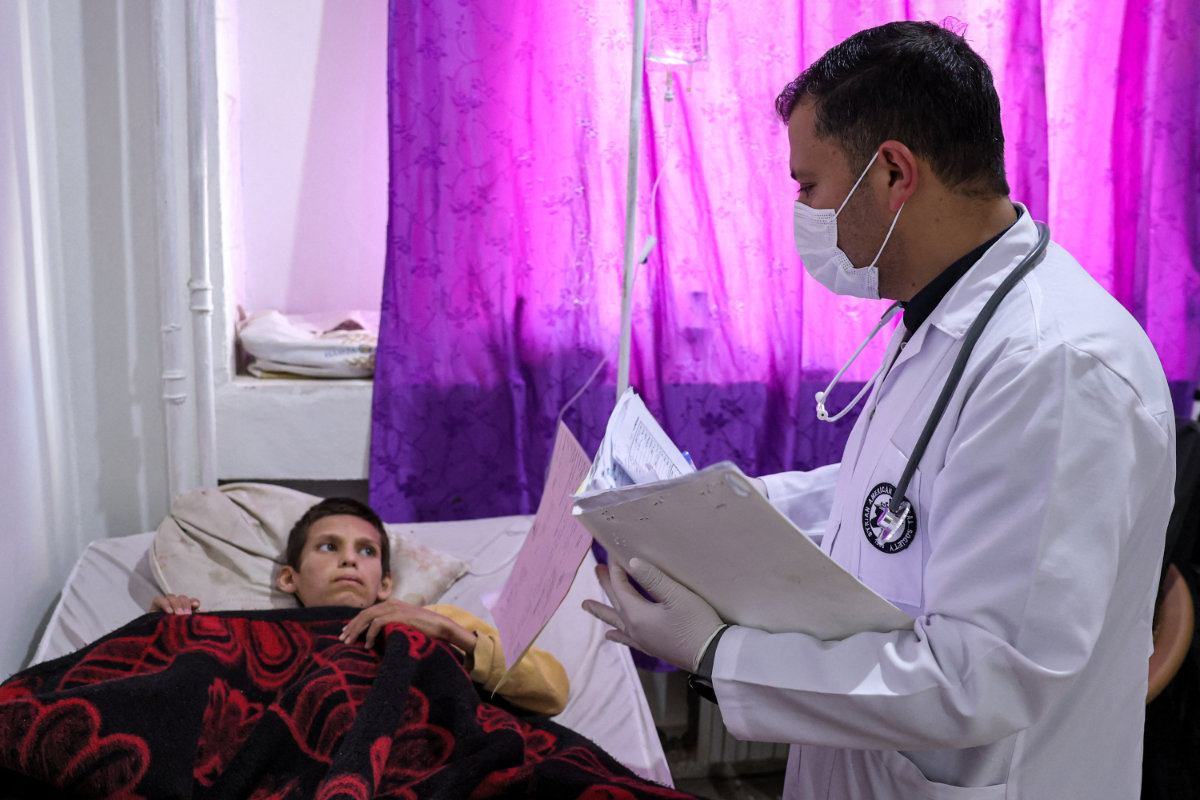

In this picture taken on May 2, 2023, Rabie, a teenage cancer patient, speaks with his physician oncologist Abdel-Razek Bakkour as he lies in a bed at the Hematology and Oncology department run by the Syrian American Medical Society (SAMS) at Idlib Central Hospital in Syria. (AFP/file)
Failing to develop a clear strategy amid ongoing shortages of basic services and limited resources “will further cripple the healthcare system, drive more brain drain, worsen healthcare outcomes more than the war’s impact, and allow disease outbreaks,” he added.
Sahloul also stressed the “urgent need” to lift “crippling” US sanctions, which had been imposed on the Assad regime but continue to weigh on the new government, to achieve a full recovery for the medical sector.
“Humanitarian and emergency aid won’t be enough,” he said.
In addition to destroyed infrastructure, funding shortfalls, and supply shortages, the exodus of medical professionals has devastated Syria’s health system.

Girls sits near damaged buildings in the devastated Hajar al-Aswad area near the Yarmuk camp for Palestinian refugees on the southern outskirts of Damascus on December 23, 2024. (AFP)
The conflict, which began in 2011 following Assad’s brutal crackdown on anti-government protests, led to a loss of more than 70 percent of Syria’s health workforce. By 2021, the International Rescue Committee said there was just one doctor for every 10,000 people.
“The resourceful Syrian diaspora should be embraced and allowed to help,” said Sahloul, noting that “there are more than 12,000 Syrian-American doctors and a similar number in Germany.”
Syrians now make up the largest group of foreign doctors in Germany, The Associated Press reported in December. German officials have even said Syrian physicians are “indispensable” to the nation’s health system.
Sahloul said stopping the brain drain must be the top priority. “Every young doctor or new graduate I met in Syria is thinking of leaving,” he said. “This is not good for the future of the country and its health.”
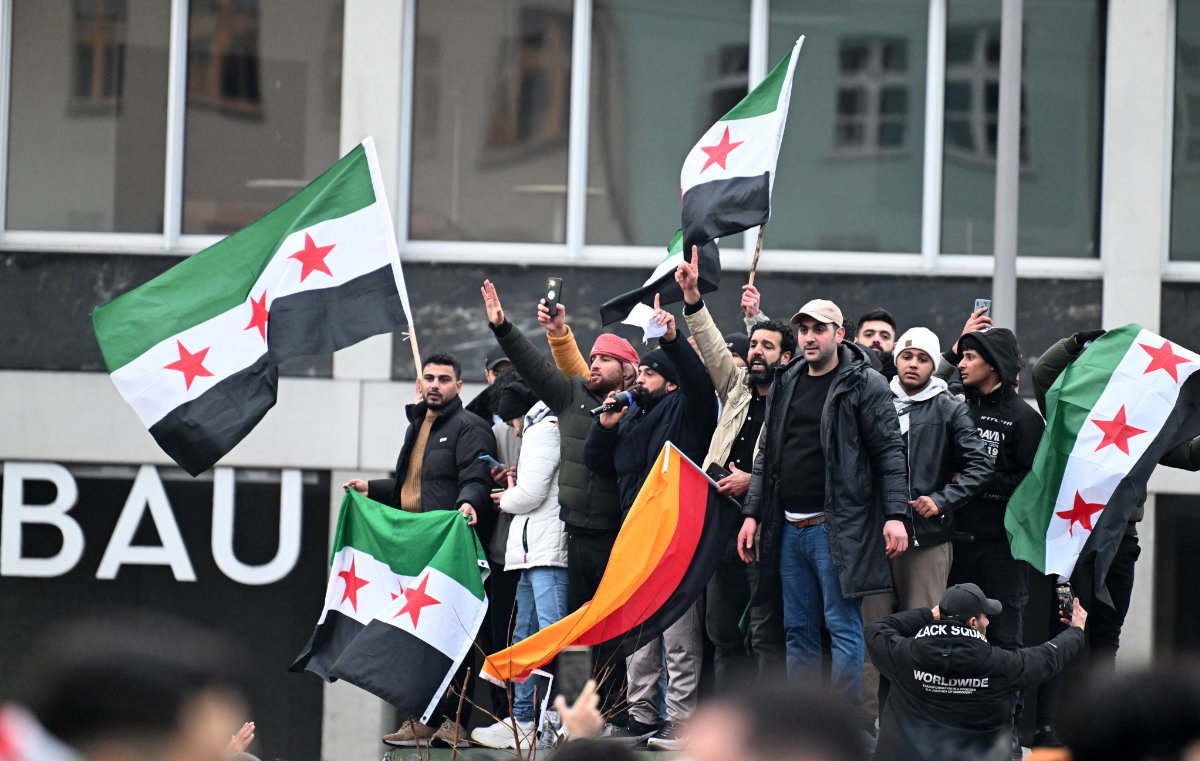

Members of the Syrian community rally in Berlin, Germany, on Dec. 8, 2024, to celebrate the end of Syrian dictator Bashar al-Assad's rule. The Syrian war has resulted in an acute shortage of health workers in the country. (AFP/File)
However, he added, “retention of healthcare workers requires improving compensation first and foremost, improving training and education, updating technology, and updating hospitals.”
In the meantime, NGOs are finding ways to leverage Syrian expatriates to aid the recovery. “Attracting Syrian specialists back is a challenge, but there are always creative solutions,” said Sahloul.
“Syrian expatriate physicians volunteering within MedGlobal and other diaspora NGOs are ready to contribute to medical and surgical missions, as well as tele-health, tele-psych, and online education and training — initiatives we’ve implemented across various regions over the past 14 years.”

Syria's yearslong war has resulted in an acute shortage in health care manpower. (Photo courtesy of MedGlobal)
Meanwhile, Syria faces multiple public health crises, including the rise of multidrug-resistant bacteria due to unchecked antibiotic use and limited lab testing.
Sahloul said a mental health crisis is also unfolding. This has been fueled by torture survivors, the families of the forcibly disappeared, victims of violence and displacement, returning refugees, and drug addiction linked to the production of the amphetamine-type stimulant captagon.
“There are very limited resources to manage the mental health crisis and festering drug addiction,” he said.
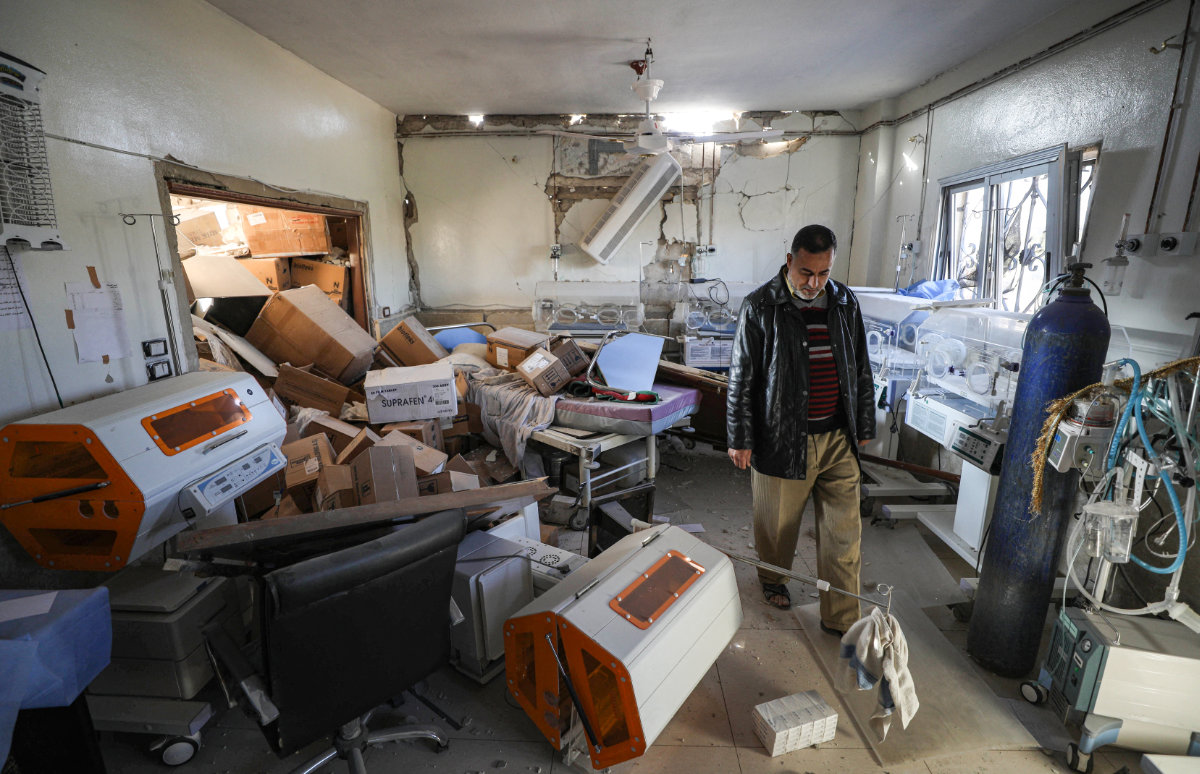

A man walks through a destroyed neonatal care ward at a hospital that was hit by a reported air strike in the Syrian village of Shinan, Idlib, on November 6, 2019. (AFP File)
Syria also faces an epidemic of noncommunicable diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, hypertension, obesity, chronic kidney disease, cancer, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
“Many patients cannot afford their medications — a problem compounded by one of the highest smoking rates in the world,” said Sahloul.
Although Assad’s portraits have been removed from hospitals in areas once under his regime’s control, anything beyond this surface level change remains unlikely without the lifting of US sanctions and a clear recovery strategy.
For now, Syria’s doctors will continue to fight an uphill battle, struggling to keep the lights on amid ongoing electricity and fuel shortages, and keeping themselves and their patients fed, let alone provide lifesaving care.






























