LONDON: America has voted and now the Middle East waits to discover who has won — and, crucially, what that victory will mean for a region with which the US has had a complex relationship ever since President Franklin D. Roosevelt and Saudi Arabia’s King Abdulaziz bin Saud met for historic talks on a US warship in the Suez Canal in 1945.
Whichever way CNN and the other big US channels have called the result of the US presidential election, it could be days, or even weeks, before America’s arcane electoral process reaches its final conclusion and the winner is formally declared.
Although they have ticked the box on their ballot papers alongside their preferred candidate, America’s voters have not actually voted directly for Kamala Harris, Donald Trump or any of the four other runners.
Instead, in proportion to its number of representatives in Congress, each state appoints electors to the Electoral College, the combined membership of which votes for the president and the vice president.
It is rare, but not unknown, for electors to disregard the popular vote. But either way, to become president, a candidate needs the votes of at least 270 of the college’s 538 electors.
Their votes will be counted, and the winner announced, in a joint session of Congress on Jan. 6. The president-elect is then sworn into office on Monday, Jan. 20 — and, as first days at work go, these promise to be intense.

A poll worker waits for voters at a polling station in New York City on Election Day, November 5, 2024. (AFP)
There will be many issues, domestic and foreign, clamoring for the attention of the new president and their team.
But of all the in-trays jostling for attention, it is the one labeled “Middle East” that will weigh most heavily on the Resolute desk in the Oval Office and on the mind of the incoming president.
Depending on how they are handled, the sum of the challenges contained in that in-tray could add up either to an opportunity to achieve something no American president has achieved before, or an invitation to a disastrous, legacy-shredding encounter with some of the world’s most pressing and intractable problems.
Palestine and Israel
In November 2016, then-President-Elect Donald Trump declared: “I would love to be able to be the one that made peace with Israel and the Palestinians.” A lot of “really great people” had told him that “it’s impossible — you can’t do it.”
But he added: “I disagree … I have reason to believe I can do it.”
As recent history attests, he could not do it.
Every US president since Jimmy Carter, who led the Camp David talks that culminated in a peace agreement between Egypt and Israel in 1979, has been drawn inexorably into the maelstrom of Middle East politics — partly through economic and political necessity, but also because of the Nobel-winning allure of going down in history as the greatest peacemaker the world has ever known.
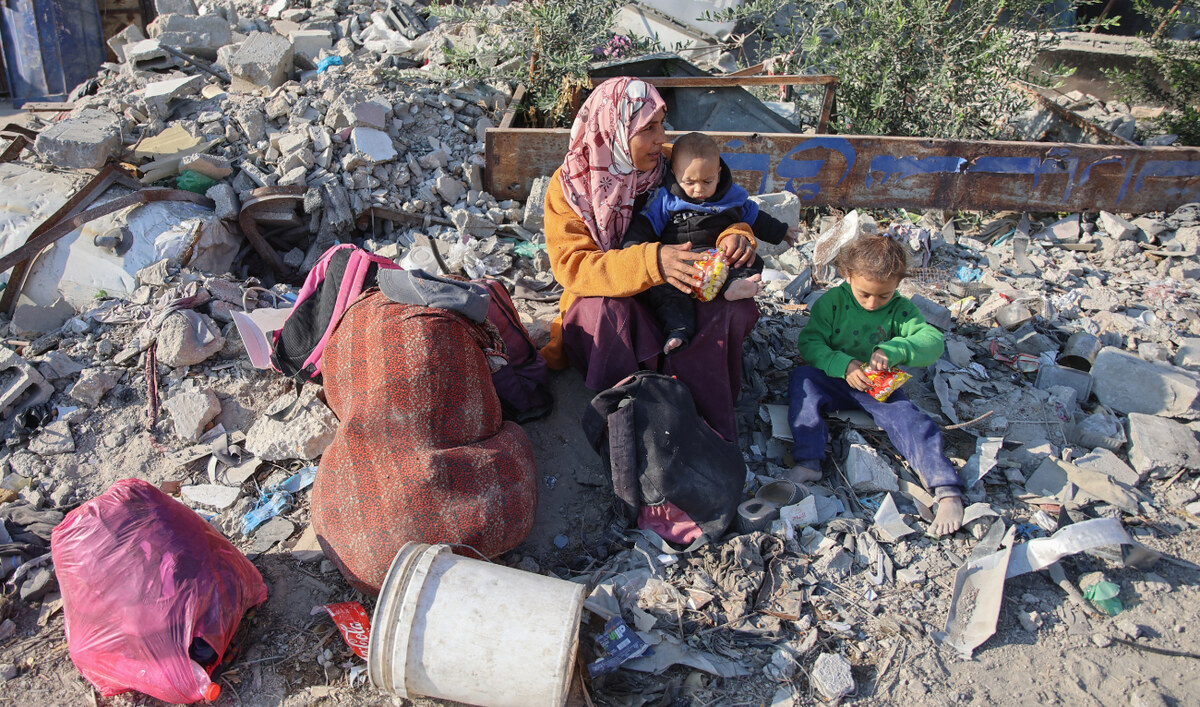

A woman rests with her children as displaced Palestinians flee Beit Lahia in the northern Gaza Strip on November 5, 2024. (AFP)
Not for nothing, however, is the Israel-Palestine issue known in diplomatic circles as “the graveyard of US peacemaking.”
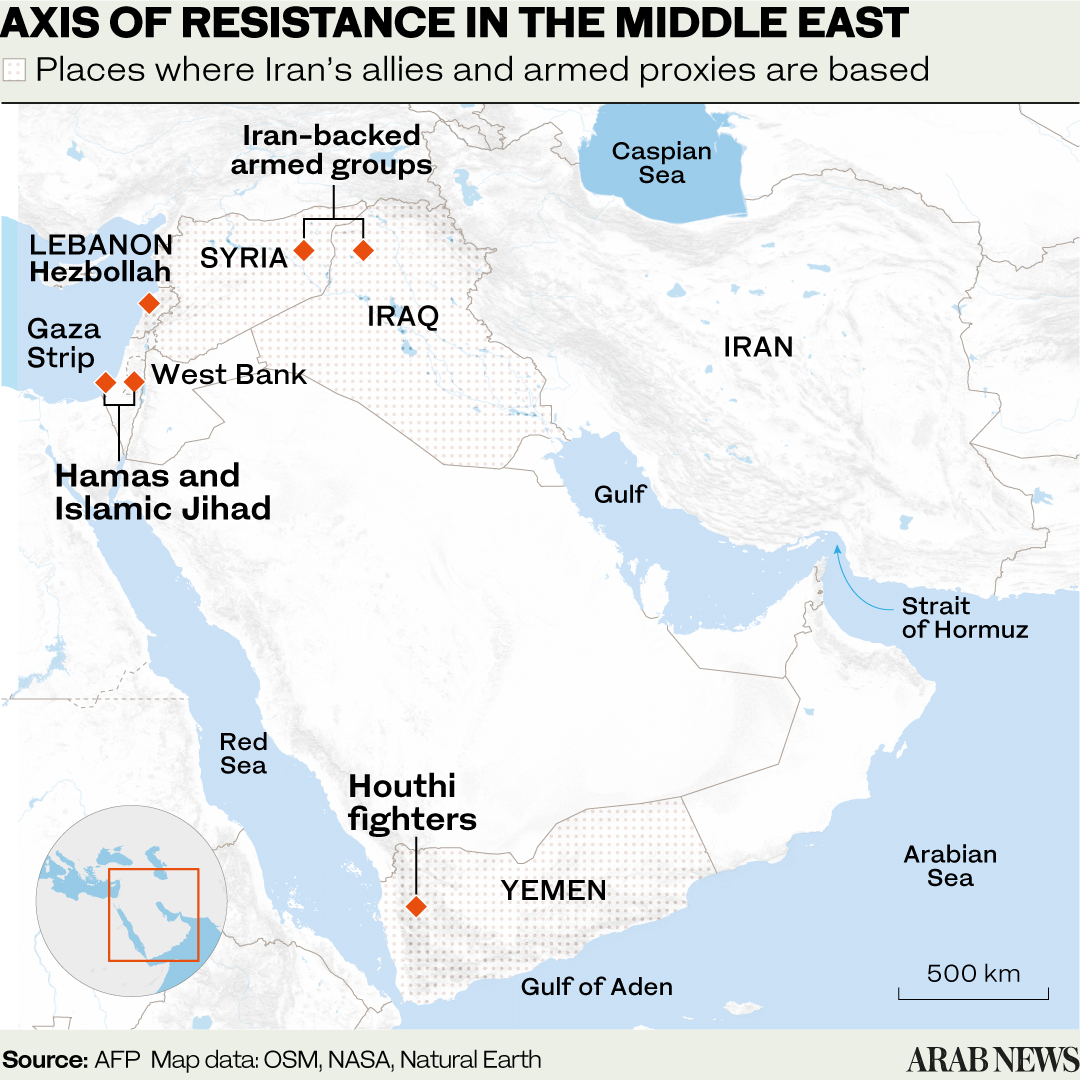
Since Oct. 7, 2023, and Israel’s onslaught on Hamas and other Palestinian militant groups in Gaza and Iran-backed Hezbollah in Lebanon, a crisis long deemed intractable appears to have degenerated even further to a point of no return.
All the talk throughout the election by both of the main candidates, calculated to walk the electoral tightrope between pro-Israel and pro-Palestinian voters, will now be forgotten.
All that matters now is action — careful, considered action, addressing issues including the desperate need for a permanent ceasefire in Gaza and the reopening of the much-cratered pathway to a two-state solution.
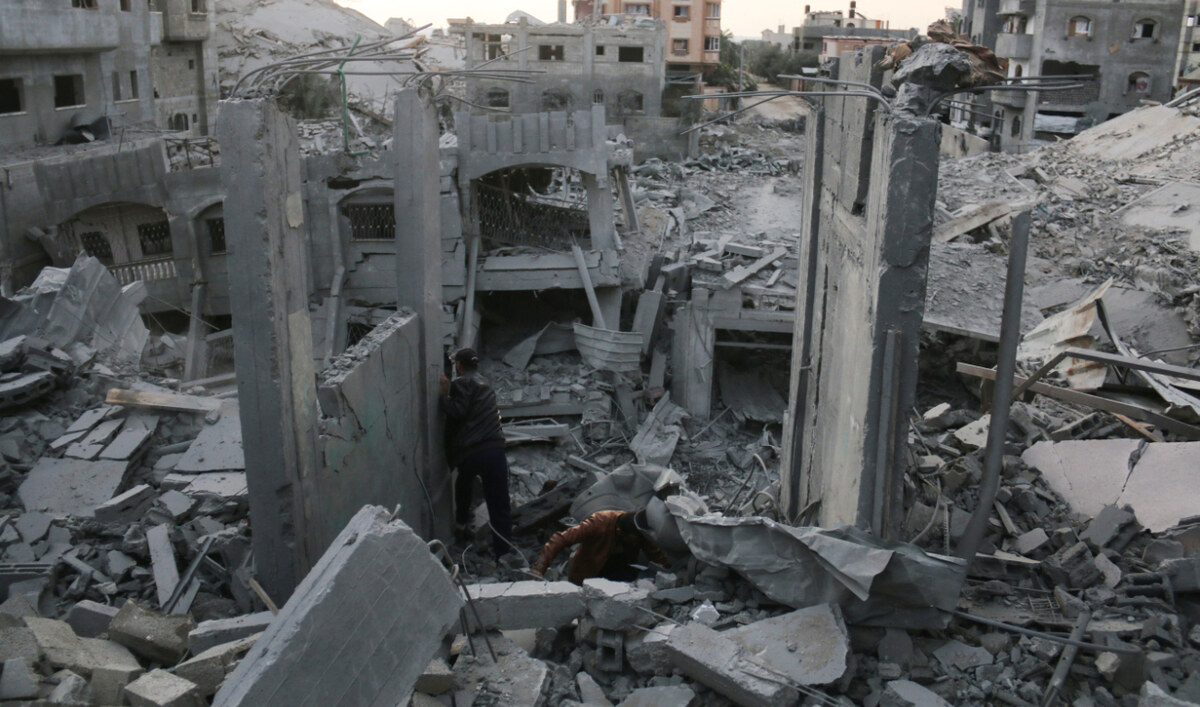

Palestinians search through the rubble following Israeli strikes in Nuseirat refugee camp in the central Gaza Strip, on November 1, 2024. (AFP)
Epitomizing the hypocrisy that has so infuriated millions, including the many Arab American voters who have switched their allegiance from the Democrats to the Republicans in this election, the Biden-Harris administration has bemoaned the deaths of tens of thousands of innocent Palestinians while simultaneously supplying Israel with the munitions that killed them.
For Trump, regaining the White House would be a second chance at peacemaker immortality and, perhaps, the Nobel Peace Prize he felt he deserved for his 2020 Abraham Accords initiative.
Last time around, Trump did achieve the breakthrough of establishing diplomatic relations between Israel and the UAE and Bahrain. The big prize, which eluded him in 2020, was bringing Saudi Arabia on board. The Kingdom has made it clear that for that to happen, one condition must be fulfilled — the opening of a meaningful path to Palestinian statehood. This, therefore, could well be on the to-do list of a Trump administration in 2025.
For Harris, the presidency would be a chance to step out from under the shadow of the Biden administration, which has so spectacularly failed to restrain Israel, its client state, and in the process has only deepened the crisis in the Middle East and undermined trust in the US in the region.
The West Bank
If America has equivocated over events in Palestine and Lebanon, the Biden administration has not turned a blind eye to the provocative, destabilizing activities of extremist Jewish settler groups in the West Bank.
In February, the White House issued an executive order imposing sanctions on “persons undermining peace, security, and stability in the West Bank.” The order, signed by President Joe Biden, condemned the “high levels of extremist settler violence, forced displacement of people and villages, and property destruction,” which had “reached intolerable levels” and constituted “a serious threat to the peace, security, and stability of the West Bank and Gaza, Israel, and the broader Middle East region.”
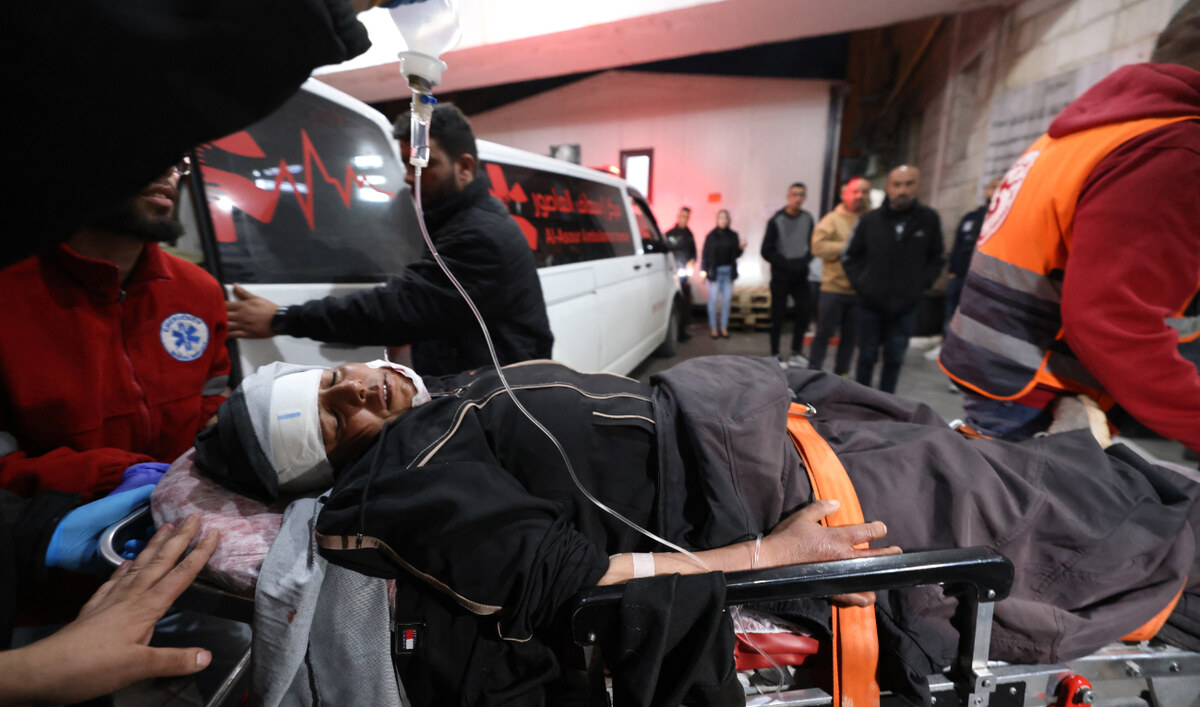

A wounded Palestinian man arrives for treatment for injuries sustained in clashes with Israeli settlers in the village of Mughayir, at a hospital in Ramallah in the occupied West Bank on April 12, 2024. (AFP)
So far, the US, reluctant to act against members of an ally’s government, has stopped short of sanctioning Israel’s far-right ministers Bezalel Smotrich and Itamar Ben Gvir, the chief settler rabble-rousers in Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu’s cabinet.
Whether Harris would continue with, or even strengthen the sanctions policy, remains to be seen, but the settlers believe that Trump would let them off the hook. “If Trump takes the election, there will be no sanctions,” Israel Ganz, chairman of one of the main settler groups, told Reuters last week.
“If Trump loses the election, we will in the state of Israel … have a problem with sanctions that the government over here has to deal with.”
It was, after all, Trump who recognized Jerusalem as the capital of Israel, undoing decades of US foreign policy, and moved the US Embassy there from Tel Aviv.
Whoever wins, if they are truly interested in peace in the region, they will need to exert pressure on Netanyahu to bring the extremist right-wingers in his government to heel. It was Ben Gvir’s repeated incursions into the Al-Aqsa Mosque compound that Hamas cited as the main provocation that triggered its Oct. 7 attack on Israel last year.
Iran
Iran has been a thorn in the side of every US administration since the 1979 revolution, the roots of which can be traced back ultimately to the CIA-engineered overthrow of democratically elected Iranian Prime Minister Mohammad Mosaddegh in 1953.
The next US president faces two key, interrelated choices, both of which have far-reaching consequences. The first is how to deal with Iran’s President Masoud Pezeshkian, a heart surgeon who was elected in July and, so far, has given every appearance of being someone who is prepared to negotiate and compromise with the West and its regional allies.
In the hope of lifting the sanctions that have so badly hurt his countrymen, if not their leaders, Pezeshkian has offered to open fresh negotiations with the US over Iran’s nuclear program.
According to a recent Arab News/YouGov poll ahead of the presidential election, this would be appealing to many Arab Americans.
Asked how the incoming US administration should tackle the influence of Iran and its affiliated militant groups in the region, 41 percent said it should resort to diplomacy and incentives, with only 32 percent supporting a more aggressive stance and a harsher sanctions regime.
Here, a Harris victory might pave the way to progress. The Biden presidency has seen some sanctions lifted and moves made toward reopening the Iran nuclear deal, the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action.
In a move that infuriated supporters of Israel but brought some relief to a region that appeared to be teetering on the brink of all-out war, in October the Biden administration publicly warned Israel that it would not support a strike on Iranian nuclear facilities in retaliation for Tehran’s drone and missile attack on Israel.
Under a Trump administration, however, progress with Iran would seem unlikely. It was Trump who in 2020 ordered the assassination of Iran’s Revolutionary Guard Corps commander, Qassem Soleimani, and who in 2018 unilaterally pulled the US out of the JCPOA to the dismay of the other signatories, Iran and the five permanent members of the UN Security Council. It is difficult to see how he could revisit that decision.
The Houthis
In many ways, coming to an understanding with Iran could be the greatest contribution any US president could make to peace in the region, especially if that led to a defanging of Iran’s proxies, which have caused so much disruption in the Middle East.
The previous Trump administration backed Saudi Arabia’s war against the Houthi rebels in Yemen and designated the group as a foreign terrorist organization. In 2021, however, Biden reversed that decision and withdrew US support for the military interventions of the Coalition to Restore Legitimacy in Yemen against the rebels, who overthrew Yemen’s internationally recognized government, sparking the civil war, in 2015.
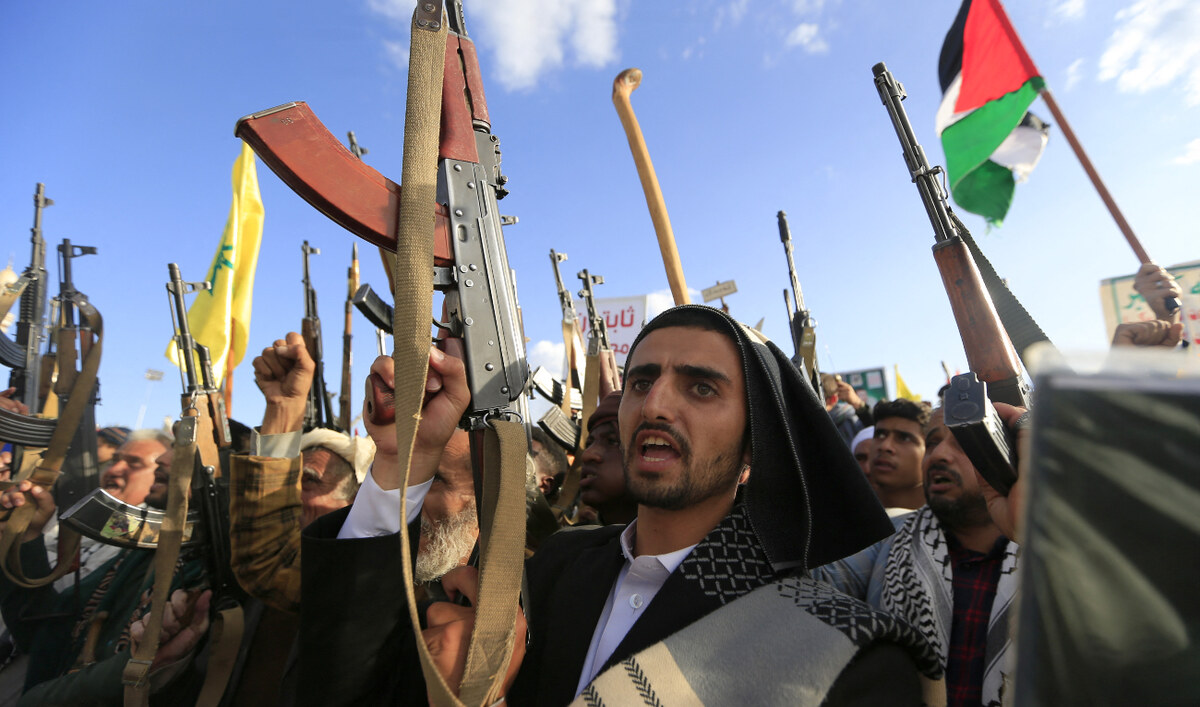

Houthi supporters attend an anti-Israel rally in solidarity with Gaza and Lebanon in the Houthi-controlled capital Sanaa on November 1, 2024. (AFP)
Since then, however, Houthi attacks on shipping in the Red Sea, and drone and missile assaults on Saudi Arabia, have opened Western eyes to the true nature of the rebel group, to the extent that in October Biden authorized the bombing of Houthi weapons stores by B2 stealth bombers.
For either candidate as president, apart from securing the all-important commercial navigation of the Red Sea, dealing with the Houthis offers the opportunity to mend bridges with Arab partners in the region (only Bahrain joined America’s Operation Prosperity Guardian, a naval mission to protect shipping).
But it is Trump, rather than the Biden-era tainted Harris, who is expected to come down hardest on the Houthis.
Hezbollah
Trump’s grasp of events in the Middle East has at times appeared tenuous. In a speech in October, for example, he boiled down the conflict between Israel and Hezbollah in Lebanon to “two kids fighting in the schoolyard.” As president, though, there seems little doubt that he would, once again, be Israel’s man in the White House.
In a recent call with Netanyahu, he appeared briefly to forget the importance of wooing the all-important Arab American swing-state votes and told the Israeli prime minister to “do what you have to do,” even as innocent civilians were dying at the hands of Israeli troops in Lebanon.
Of course, no American government is going to defend Hezbollah or any of Iran’s proxies. But when Hezbollah’s leader, Hassan Nasrallah, was targeted in an Israeli airstrike in September, Harris released a statement that outlined a preference for diplomacy over continuing conflict.
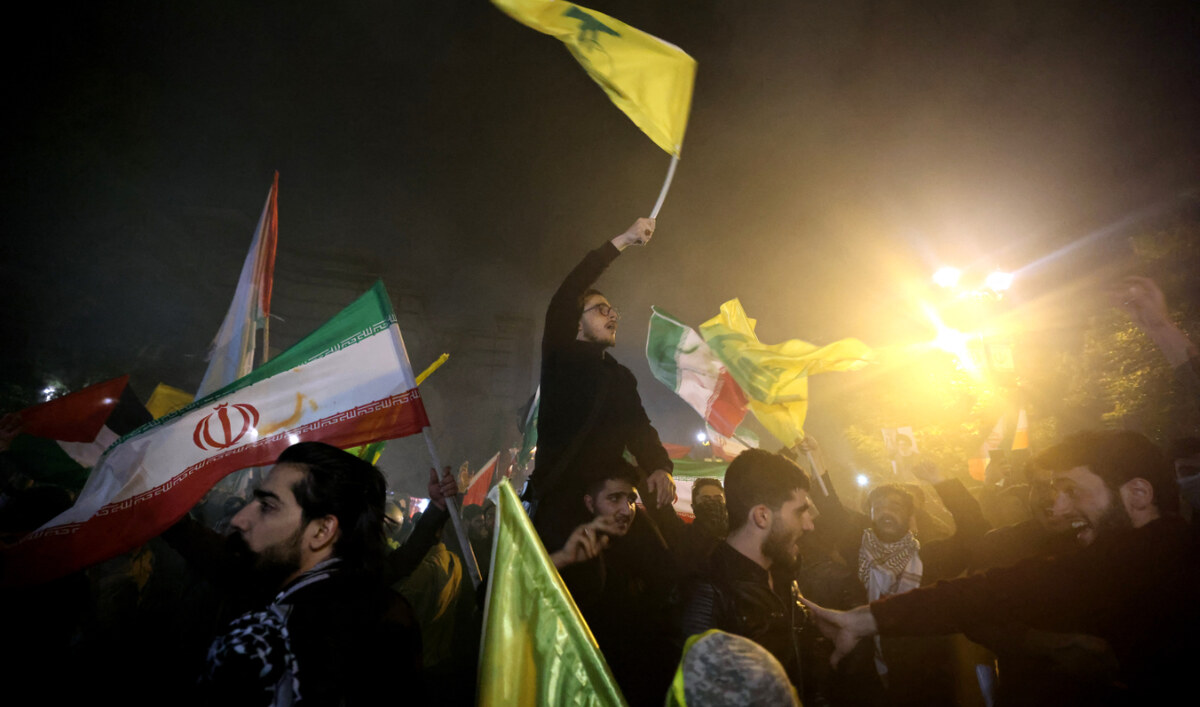

Demonstrators celebrate during a rally outside the British Embassy in Tehran on October 1, 2024, after Iran fired a barrage of missiles into Israel in response to the killing of Hezbollah leader Hassan Nasrallah. (AFP)
She had, she said, “an unwavering commitment to the security of Israel” and would “always support Israel’s right to defend itself against Iran and Iran-backed terrorist groups such as Hezbollah, Hamas, and the Houthis.”
But, she added, “I do not want to see conflict in the Middle East escalate into a broader regional war. We have been working on a diplomatic solution along the Israel-Lebanon border so that people can safely return home on both sides of that border. Diplomacy remains the best path forward to protect civilians and achieve lasting stability in the region.”
The US presence in the Middle East
One of the findings of the recent Arab News/YouGov poll of Arab Americans ahead of the election was that a sizable majority (52 percent) believed the US should either maintain its military presence in the Middle East (25 percent), or actually increase it (27 percent).
This will be one of the big issues facing the next president, whose administration’s ethos could be one of increasing isolationism or engagement.
America still has 2,500 troops in Iraq, for example, where talks are underway that could see all US and US-led coalition personnel withdrawn from the country by the end of 2026 — 23 years since the invasion of Iraq in 2003.
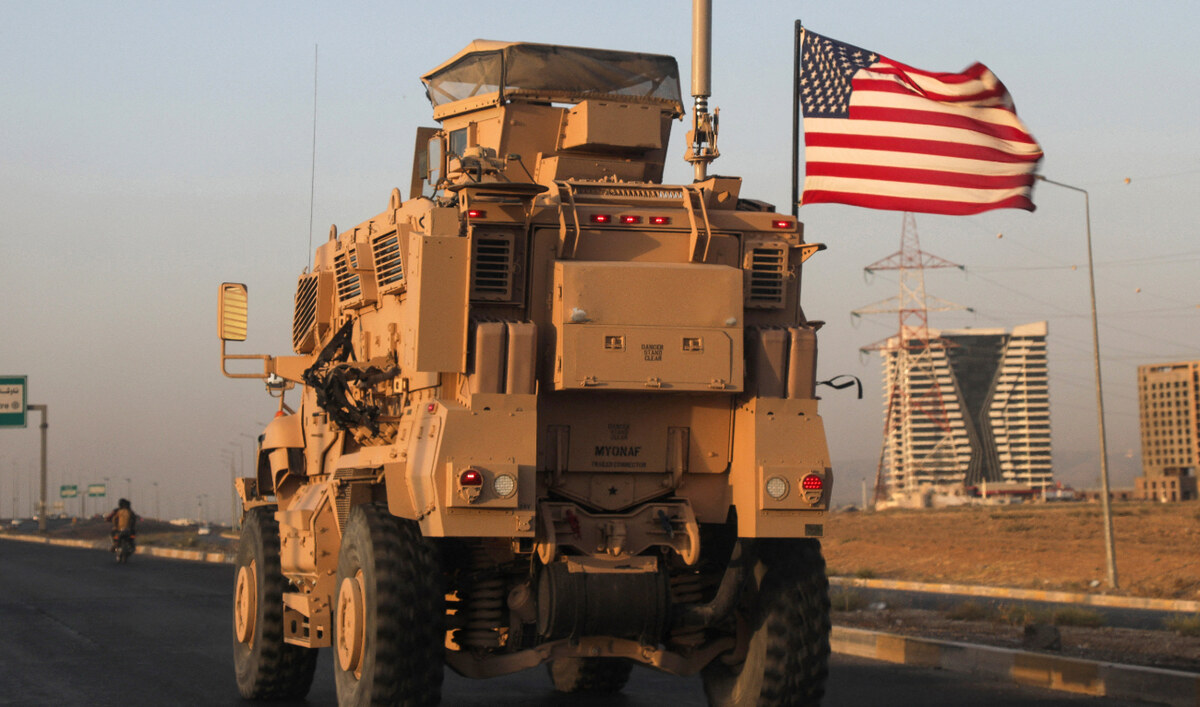

A vehicle part of a US military convoy drives in Arbil, the capital of the autonomous Kurdish region of northern Iraq, on September 17, 2024. (AFP)
In April, Biden and Iraqi Prime Minister Mohammed Shia Al-Sudani issued a joint statement affirming the intention to withdraw US troops, who now act mainly as advisers, and transition to a “bilateral security partnership.”
Trump, on the other hand, could go much further, and as president has a record of disengaging America from military commitments. In 2019, to the alarm of regional allies, he unilaterally ordered the sudden withdrawal of the stabilizing US military presence in northeastern Syria, and in 2020 withdrew hundreds of US troops who were supporting local forces battling against Al-Shabaab and Daesh militants in Somalia.
In the wake of his election defeat that year, he ordered the rapid withdrawal of all US troops from Afghanistan. The order was not carried out, but in September 2021, the Biden administration followed suit, ending America’s 20-year war and leading to the collapse of the Afghan National Security Forces and the takeover of the country by the Taliban.
































