LONDON: In a bid to protect the rights of children, Kuwait recently raised the minimum age of marriage to 18. However, the fight against child marriage across the Arab world remains an uphill battle, particularly in conflict-ridden regions.
In mid-February, Kuwait amended its Personal Status Law No. 51/1984 and Jaafari Personal Status Law No. 124/2019, citing alarming rates of child marriage. In 2024 alone, 1,145 underage marriages were registered, including 1,079 girls and 66 boys.
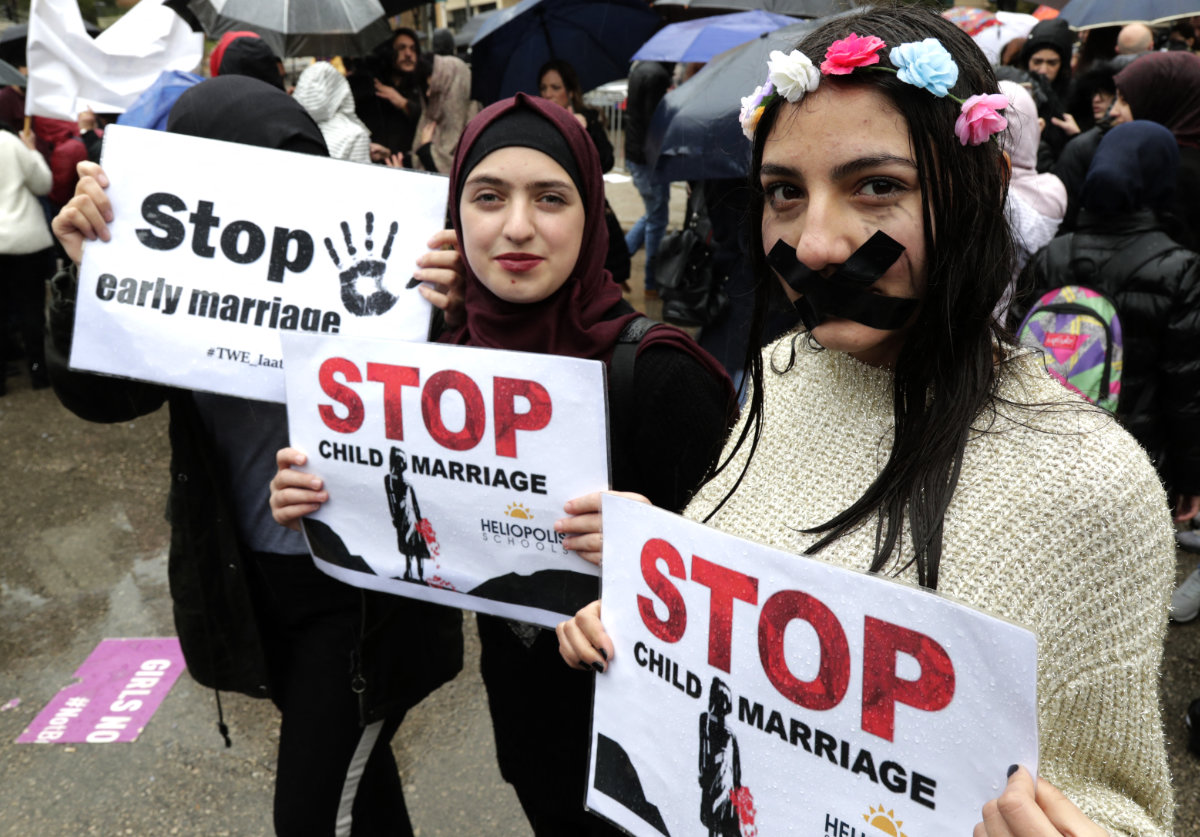

Lebanese women participate in a march against marriage before the age of 18, in Beirut on March 2, 2019. (AFP/file)
The move aligns with the Gulf state’s international commitments, including the Convention on the Rights of the Child and the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women.
Under the principles of both conventions and other international treaties, child marriage is widely recognized as a harmful practice, and a violation of human rights that only deepens gender inequality, particularly as it affects girls more than boys.
“Child marriage is a human rights violation,” Hadeel Qazzaz, Oxfam’s Middle East North Africa regional gender coordinator, told Arab News. “It impacts the life of the child.”
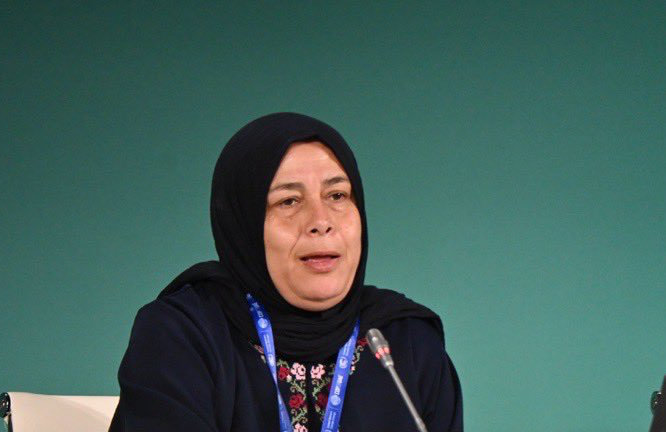

Hadeel Qazzaz, Oxfam’s gender coordinator for MENA region. (Supplied)
She explained that child marriage denies girls the chance to pursue education or employment, strips them of decision-making power, and denies them both bodily autonomy and reproductive choice.
“It does not only impact the child’s life but also the life of her family and her future children,” said Qazzaz. “Girl brides are more likely to be subjected to different forms of gender-based violence and to be less engaged at the family, community, or society levels.”
According to New York-based monitor Human Rights Watch, research shows that underage brides are at a higher risk of experiencing domestic violence, marital rape, and restricted access to reproductive healthcare and education.
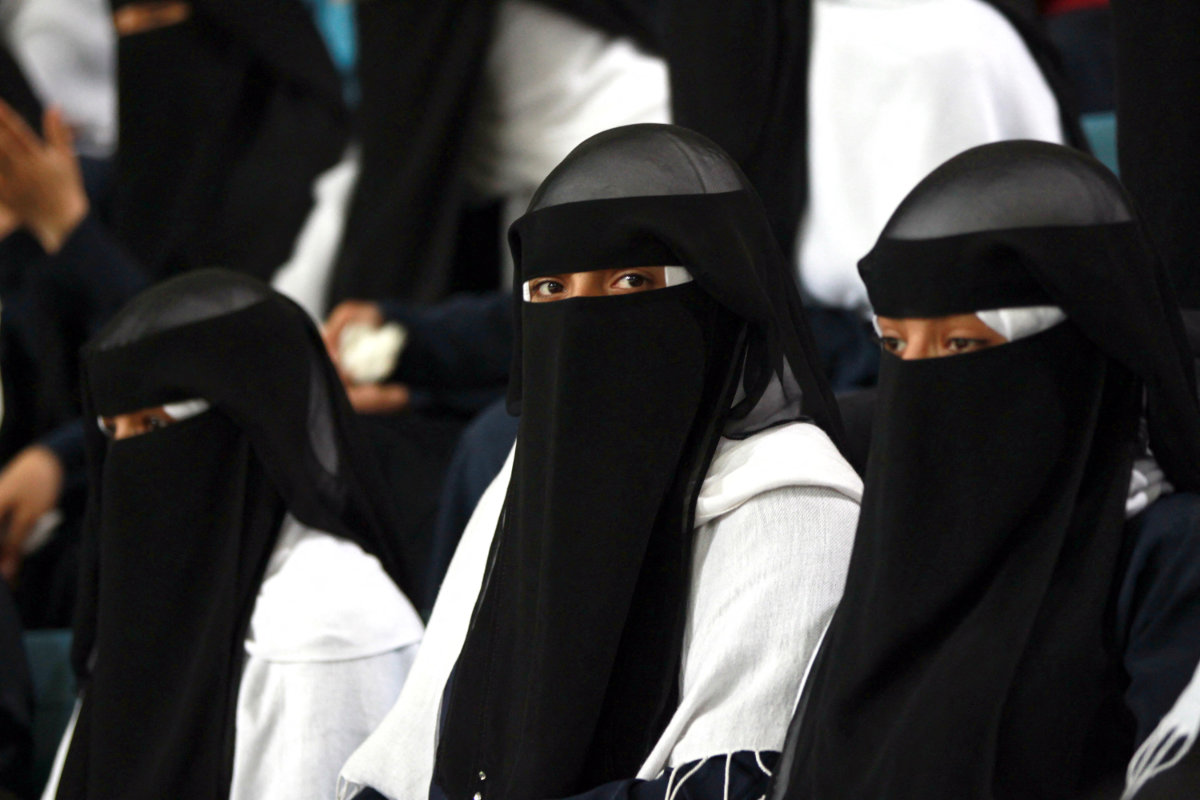

Child brides," or "death brides" as they are sometimes called, are quite common in poor tribal Yemen, where barely pubescent girls are forced into marriage, often to much older men. (AFP file photo)
UN agencies say a staggering 70 percent of married girls aged 15 to 19 experience physical or other forms of violence at the hands of their husbands.
Compounding the issue, complications from pregnancy and childbirth are the leading cause of death among adolescent girls aged 15 to 19 in developing countries. Girls aged 15 to 20 are twice as likely to die in childbirth as those in their 20s, while girls under 15 face a fivefold risk.
Pregnancy and domestic responsibilities often prevent girls from ever returning to education, Human Rights Watch warned. This lack of education limits their choices and opportunities throughout their lives, often leading to poverty.

Girls who marry young face many adverse effects that negatively impact their health and well-being, says the UNFPA. (AFP file photo)
The impact of child marriage extends beyond the individuals themselves, affecting the region’s economy as well.
A 2020 study by the International Monetary Fund found that eliminating child marriage could boost annual per capita gross domestic product growth in emerging and developing countries by 1.05 percentage points in the long term.
Nevertheless, child marriage remains a scourge across the Middle East and North Africa, hitting war zones and post-conflict societies the hardest.
The MENA region is home to 40 million child brides, with one in five marrying before the age of 18 and one in 25 before 15, according to the UN children’s agency, UNICEF. In recent years, girls have been married off at a rate of around 700,000 per year.
“These are alarming figures that can increase with fragility, conflicts, and natural disasters,” said Oxfam’s Qazzaz.
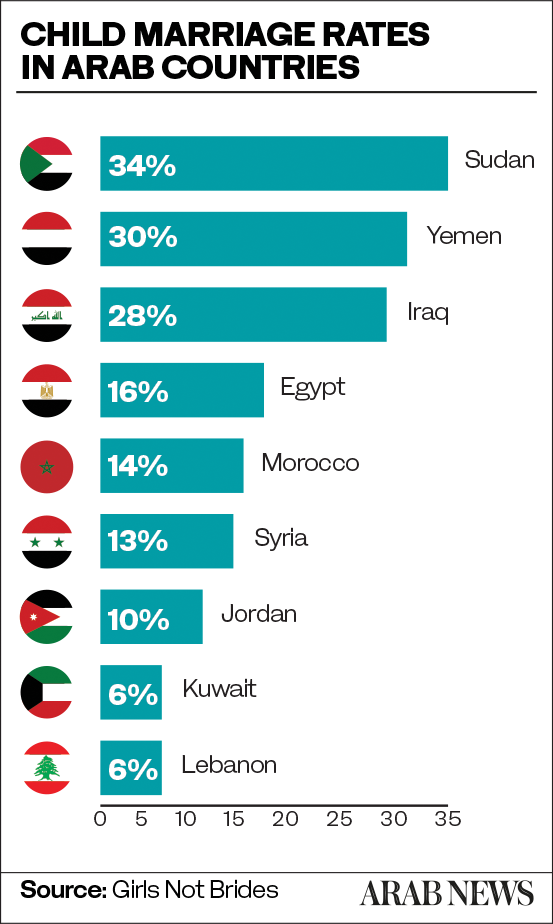
The five countries with the highest child marriage rates in the region are Yemen at 30 percent, Iraq at 28 percent, Iran at 17 percent, Egypt at 16 percent, and Morocco at 14 percent.
According to the UN Economic and Social Commission for Western Asia, the lack of legal protections, the impact of societal norms, poverty, and deep-rooted gender inequality are the key drivers of child marriage in the Arab world.
Many countries in the region have set the minimum age of marriage at 18, with some allowing exceptions based on judicial or parental consent. But even where minimum-age laws exist, exceptions often undermine their effectiveness.
In Iraq, for example, the problem is expected to worsen after authorities passed amendments to the personal status law in January, which indirectly legalize the marriage of girls as young as 9, sparking condemnation both domestically and abroad.

A girl joins a protest rally over a proposed amendment to the Iraqi Personal Status Law, which activists said would abet efemale child marriages. (AFP)
Although Iraqi law sets 18 as the minimum age of marriage, the amendments give Islamic courts greater authority to decide. Clerics could interpret Islamic law to allow such marriages under the Jaafari school followed by many religious authorities in Iraq.
Equality Now, a global feminist advocacy organization, warned that the amendments risk exacerbating existing gaps in Iraq’s 1959 Personal Status Law.
The group said the shift would create a fragmented legal system, with protections for children and women varying significantly across communities.
According to UNICEF, child marriage rates in Iraq vary widely by region, with Missan (43.5 percent), Najaf (37.2 percent), and Karbala (36.8 percent) reporting the highest rates.
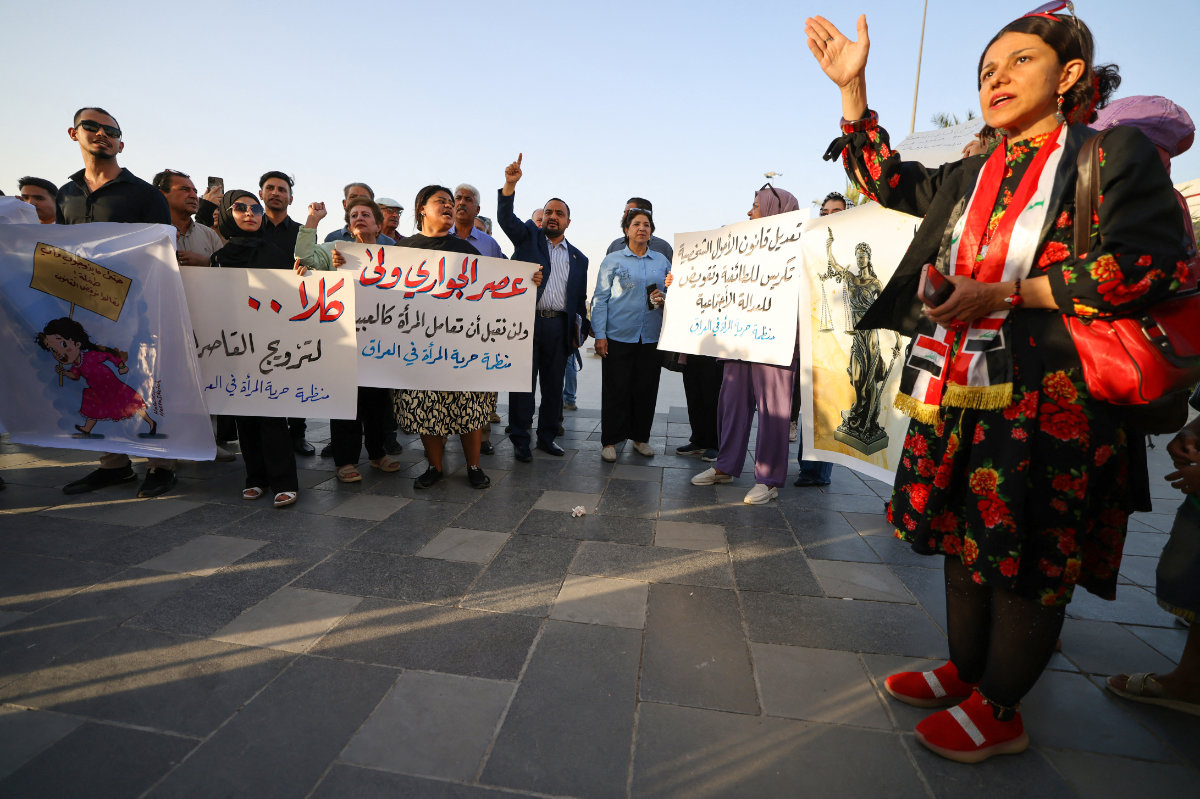

Activists demonstrate against female child marriages in Tahrir Square in central Baghdad on July 28, 2024, amid parliamentary discussion over a proposed amendment to the Iraqi Personal Status Law. (AFP)
“Fragmentation of laws creates loopholes that undermine the welfare of the most vulnerable, particularly girls, and weakens the state’s ability to uphold international human rights commitments,” Dima Dabbous, Equality Now’s MENA representative, said in a statement.
Conflict and displacement across parts of the MENA region, including Syria, Yemen, Lebanon, Sudan, and the Palestinian territories, worsen inequalities that make girls vulnerable to child marriage and its consequences.
Oxfam’s Qazzaz pointed out that conflict is “one of the main reasons” for the rising rates across MENA countries. “In the Gaza Strip, where child marriage was less common, there is now a noticeable increase in the number of marriages,” she said.
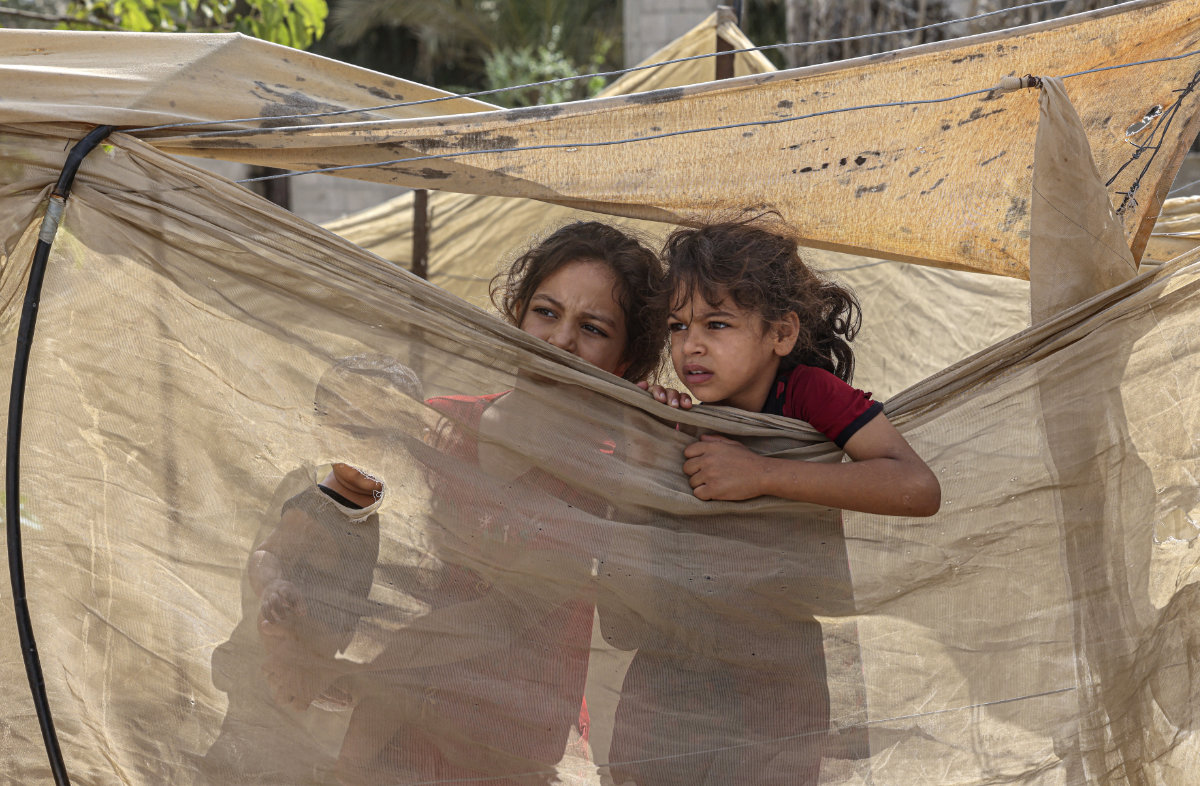

In the Gaza Strip, where child marriage was less common, there is now a noticeable increase in the number of marriages, says Oxfam. (AFP photo/file)
“The reasons vary from fear for the safety of the girl to scarcity of resources that force families to marry their daughters to others who can provide for them.”
Since the Oct. 7, 2023, Hamas-led attack on southern Israel, Gaza has been under intense Israeli bombardment and a strict blockade of humanitarian aid and consumer goods.
After 16 months of war, Gaza’s population — 90 percent of whom have been displaced — are now fully reliant on what limited aid can get through.
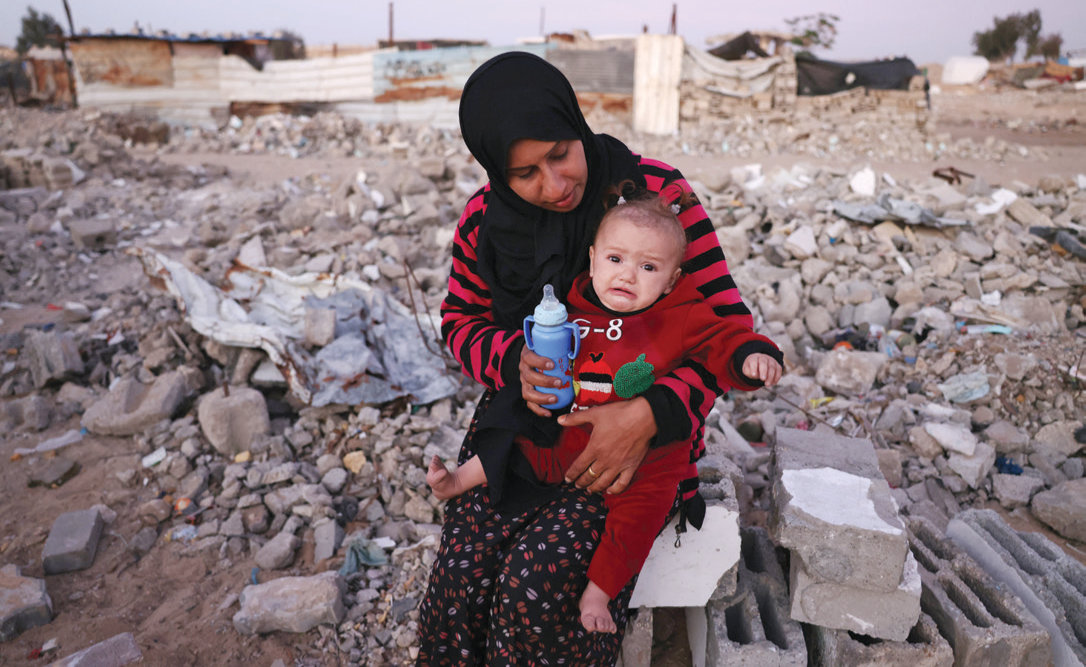

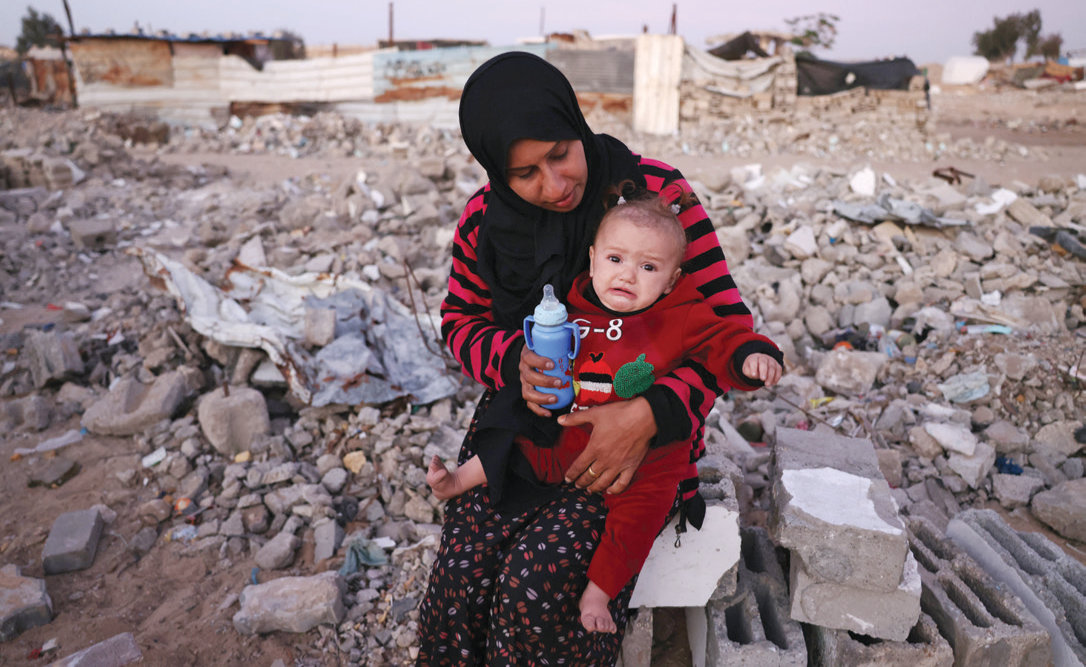
A woman feeds her child amid the rubble of destroyed buildings at a makeshift camp for displaced Palestinians in the Nahr al-Bared area in Khan Yunis, in the southern Gaza Strip on December 9, 2024. (AFP)
While the January ceasefire has improved conditions in the embattled enclave, Israel’s recent decision to again suspend the entry of assistance threatens to reverse progress, aid agencies warn.
The situation for girls is similarly dire in Yemen — a hotspot for child marriage, where there is no legal minimum marriage age. The ongoing civil war, which began in 2014, has stalled efforts to establish one.

Yemeni child brides, eight year-old Nojud Ali (L) and nine year-old Arwa (R), pose for a picture as they celebrate their divorces, granted them by a Yemeni court, with a party in the capital Saana on July 30, 2008. (AFP)/file)
ccording to UN figures, the war has displaced more than 4.5 million people, and 21.6 million are in urgent need of humanitarian assistance.
The economic strain of displacement and conflict, coupled with pre-existing cultural norms favoring early marriage, has significantly increased underage marriages.
“In the MENA region, it’s not just conflicts that impact child marriage — economic and natural disasters, as well as the rise in conservatism and the regression of women’s rights, also play a role,” Qazzaz said.
Owing to the rise in conservatism and geopolitical tensions, “the achievements women’s rights organizations have gained through years of activism are at risk of being reversed,” she added.
Sudan, for instance, already saw high rates of child marriage and female genital mutilation even before the civil war erupted in April 2023.
Despite efforts to curb these harmful practices, 21 percent of girls aged 15 to 19 were already married before the war began, according to UNICEF.
The ongoing hostilities, mass displacement, worsening economic conditions, and declining education threaten to deepen the crisis facing women and girls.

Eight-year old Sudanese girl Ashjan Yousef, who was wed at the age of five to a man in his 40s, was granted divorce by the national court in Khartoum on October 13, 2014. (AFP/file)
Since fighting erupted between rival factions of Sudan’s military government, more than 12.5 million people have been displaced, either within the country or to neighboring countries including Egypt and Ethiopia.
Similarly, in Syria, 13 percent of women aged 20 to 25 were married as minors before the 2011 conflict broke out, according to a report by the Norwegian Refugee Council.
However, more than a decade of war and displacement has significantly increased the rate of child marriage. Today, an estimated 41 percent of Syrian girls are married before the age of 18.
“Traditions, honor, economics, fear, and protection-related factors act as drivers of child marriage of refugees in Jordan and Lebanon,” said Qazzaz.
Around 6.2 million Syrian refugees live in neighboring countries, including Turkiye, Lebanon, Jordan, and Iraq, where most endure harsh living conditions, leading to a rise in child marriage as a coping mechanism.
In Jordan’s Zaatari camp, home to 80,000 Syrian refugees, girls as young as 13 are reportedly married to much older men. In Lebanon, 18 percent of adolescent Syrian refugee girls were married in 2014, according to UN figures.
National governments and international aid agencies are nonetheless working to improve the circumstances of women and girls and to protect them from early marriage. Oxfam, for instance, is a global partner of the Girls Not Brides campaign.

Child marriage in the Arab world denies girls the chance to pursue education or employment and strips them of power. (UNICEF/file photo)
“Most of our feminist and women rights partners work on child marriage as a major form of gender-based violence and seek to raise the age of marriage to 18,” Qazzaz said. “They document and challenge social and legal practices that allow for child marriage.”
Oxfam’s efforts in Yemen, in particular, have led to significant progress in raising awareness and influencing policy.
Through Oxfam’s work on sexual and reproductive health and rights, Qazzaz added: “We built youth networks in six countries to advocate for their rights and lead awareness campaigns, including the right to choose when and whom to marry.”






























